What is Terraform
Terraform IAC (Infrastructure as Code)
- Terraform is an infrastructure as code (IaC) tool that lets you define both cloud and on-prem resources in human-readable configuration files that you can version, reuse and share.
- It is an orchestration management tool, it is used to build cloud infrastructure.
- Terraform creates and manages resources on cloud platforms and other services through their application programming interfaces (APIs). Infrastrucutre can be created and managed on cloud manually but to perform automation used terraform.
- For example creating any resource (VM, Vnet etc) on azure cloud which can be perform using GUI and enter the values, the same resource can also be created using code through terraform.
- we create a configuration file in terraform, in which we define provider details and code for resources.
- It can be used with any cloud provider while cloudformation is used with AWS only.
- Mitchell Hashimoto design and developed Terraform, launched through hashicorop company in july 2014.
- Terraform is developed in GO language and its templates are written in custom DSL, terraform templates end with .tf
- In terraform folder is input, you create a folder and create .tf files in the folder. terraform run on this folder. you can create multiple .tf files for each resource and terraform will read all .tf files in the folder.
- Terraform is idempodent: if you have executed source and terraform created resoruces. When you execute the same source then it will not create another resource as it is already exist.
- Resources can be define anywhere in the file it does not have to be in sequence.
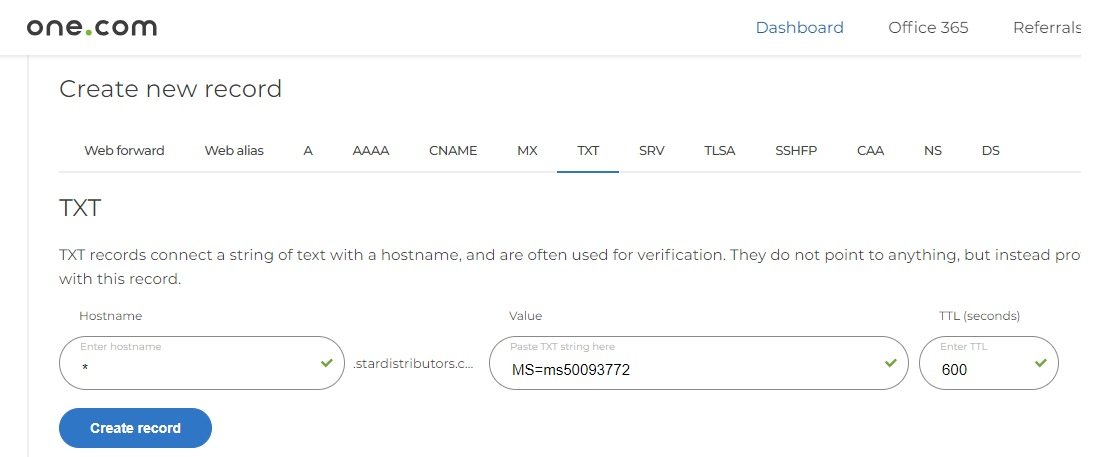
- terraform_IAC.jpg
- in the above we have 3 tier architecture (web for user, app for business processing and database tier), to create the infra it may take around 2 to 3 hours).
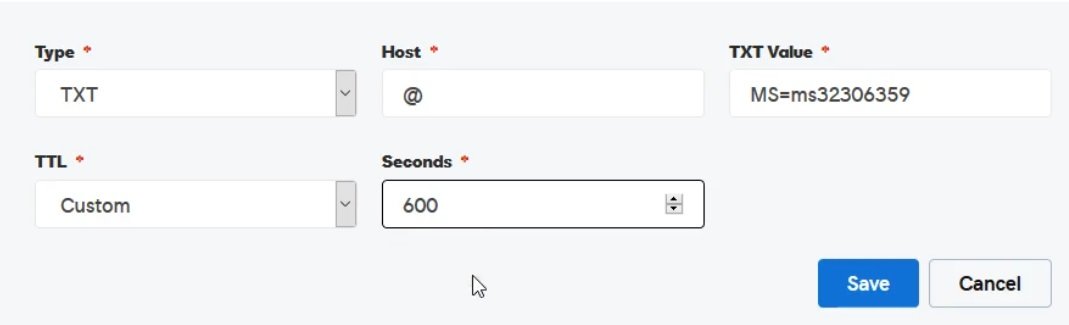
- terraform_IAC2.jpg
- To setup the infra for 3 tier architecture on above 6 environment, it may take lot of time, so if number of application are high than it may be hectic and time consuming so we prefer autoation provisioning using IAC.
How Terraform Works/commands?
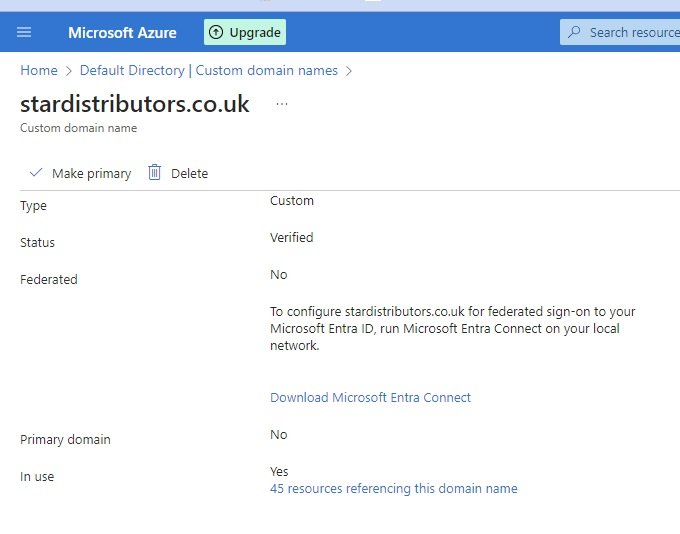
- terraform_IAC3.jpg
- Developers write the code using HCL (hashicorp language) and upload to repository (github).
- Terraform command can be executed manually or define in CI/CD pipeline and it call AWS API to create infrastructure on the defined provider. To check the list of providers go to www.terraform.io and click on registry and browse providers.
- Terraform workflow has following stages:
- Write code (file.tf)
- $terraform init - Initialize the working directory, it will download the provider plugin.
- $terraform validate - Validate the configuration files
- $terraform plan -out name.tfplan - run plan will compare the desired (code you written) state with actual (infra created) state, and provide the outcome, it will not create resource, it gives only plan of action
- $terraform apply -auto-approve or $terraform apply "name.tfplan" -auto-approve : Apply the changes to reach desired state
- $terraform destroy - Destroy the infrastructure when needed
Argument & Attributes
- Argument: input values are called argument. (ex, in creating vpc: cidr block, cidr name, tag are arguments)
- Attributes: output result are called attributes.(ex, VPC Id generated is attribute).
- code
- code
Code
- code
- code
code
- code
- code
- code
code
- code
- code
- code
code
- code
- code
- code
Installation of Terraform
Amazon Linux : Installing terrafom, AWS CLI, on Amazon Linux (AWS instance):
- Install and Launch Amazon Linux and connect with putty or any ssh tool
- Visit site https://developer.hashicorp.com/terraform/install
- Copy and paste the following command and execute.
- $sudo yum install -y yum-utils shadow-utils
sudo yum-config-manager --add-repo https://rpm.releases.hashicorp.com/AmazonLinux/hashicorp.repo
sudo yum install terraform - #ls (list the downloaded package, it will be in zip format, unzip it)
- #unzip terraform_xxxxxxxxx
- #cp terraform /bin (terraform executable is copied in /bin folder)
- Create a file with extension .tf and write code init
- #vim test.tf
- Enter Provider and version details:
- Go to terraform.io and select aws provider and click on provider and copy code.
-
terraform { required_providers { aws = { source = "hashicorp/aws" version = "5.74.0" } } } provider "aws" { # Configuration options }
- Click documentation and copy code for provider. Enter the below details by replacing #configuration options
-
provider "aws" { region = "us-west-2" access_key = "my-access-key" secret_key = "my-secret-key" } - how to get access_key: Get for root user or IAM user, Go to IAM and create a user and get access key. click on user top right corner and click my security credentials and generate access key.
- how to get secret_key:
-
Windows: Installing Terraform on Windows, VS Code, Extension of terraform in VS Code.
- Step 1: Download terraform.exe file from www.terraform.io download CLI/AMD64, Create a folder and paste terraforme.exe in the folder. copy location of file.
- Step 2: Set Environment variable: Go to system/advanced system settings/Environment variable/system variables/path, click edit/new and paste the file location.
- Step 3: Download visual studio code and install it from https://code.visualstudio.com/download and click on user installer x64 arm 64 . open visual studio code and click extensions and install two extensions, in search type terraform, hashicorp terraform & azure terraform.
- Step 4: In visual studio code click file and open folder and select terraform folder. click on explorer and you can see terraform.exe
- Step5: click on new fileand enter name (main.tf), write code in the file.
Windows using chocolatey install terraform, VS Code, Extension of Terrraform:
- Install chocolatey through powershell,
- Open cmd
- Run this command: C:\Set-ExecutionPolicy Bypass -Scope Process -Force; [System.Net.ServicePointManager]::SecurityProtocol = [System.Net.ServicePointManager]::SecurityProtocol -bor 3072; iex ((New-Object System.Net.WebClient).DownloadString('https://community.chocolatey.org/install.ps1'))
- C:\choco install terraform.
- Install visual studio code.
- In visual studio code install terraform extension
- Install AWS CLI:
-
# Using MSI installer (recommended)
# Download from: https://awscli.amazonaws.com/AWSCLIV2.msi# Using winget
winget install Amazon.AWSCLI# Using chocolatey
choco install awscli
-
- Code
- Install chocolatey through powershell,
Ubuntu: Terraform -->AWS CLI -->VS Code -->Terraform plugin for VS Code:
- Access Ubuntu:
- Visit site https://developer.hashicorp.com/terraform/install
- copy and paste the following link and execute.
- $wget -O - https://apt.releases.hashicorp.com/gpg | sudo gpg --dearmor -o /usr/share/keyrings/hashicorp-archive-keyring.gpg
echo "deb [arch=$(dpkg --print-architecture) signed-by=/usr/share/keyrings/hashicorp-archive-keyring.gpg] https://apt.releases.hashicorp.com $(grep -oP '(?<=UBUNTU_CODENAME=).*' /etc/os-release || lsb_release -cs) main" | sudo tee /etc/apt/sources.list.d/hashicorp.list
sudo apt update && sudo apt install terraform
- $wget -O - https://apt.releases.hashicorp.com/gpg | sudo gpg --dearmor -o /usr/share/keyrings/hashicorp-archive-keyring.gpg
- Verify the installation:
- $terraform -version
- $terraform -help (it will list the commands)
- Enable auto complete:
- If you use either Bash or Zsh as your command line shell, you can enable tab completion for Terraform commands. To enable autocomplete, first ensure that a configuration file exists for your chosen shell.
- $touch ~/.bashrc
- Then install the autocomplete package.
- $terraform -install-autocomplete
- Set alias for terraform
- $alias tf=terraform
- Install AWS CLI:
- visit https://docs.aws.amazon.com/cli/latest/userguide/getting-started-install.html
- To install the AWS CLI, run the following commands.
- $curl "https://awscli.amazonaws.com/awscli-exe-linux-x86_64.zip" -o "awscliv2.zip"
unzip awscliv2.zip
sudo ./aws/install - The -o option specifies the file name that the downloaded package is written to. The options on the above example command write the downloaded file (awscli-exe-linux-x86_64.zip) to the current directory with the local name awscliv2.zip
- unzip the doloaded file (unzip awscliv2.zip) , the acutal file awscli-exe-linux-x86_64.zip is stored in the name awscliv2.zip
- sudo ./aws/install (This will install AWS CLI)
- $aws --version: Confirm the installation
- Login to AWSL
- $aws configure
- enter access key, secret key of user, region.
- Install Visual Studio Code:
- Visit https://code.visualstudio.com/download
- Download .deb for Debian and ubuntu and .rpm for Red Hat, Fedora
- click on .deb and it will download the file.
- $cd Downloads
- $ls (code_1.107.1-1765982436_amd64.deb)
- Install the VS Code
- $sudo dpkg -i code_1.107.1-1765982436_amd64.deb (it will install VS code)
- $code (it will open visual studio code), you can search and open visual, once open right click on icon and click pin to dash
- Install terraform plugin in VS Code.
- open visual studio code/extensions and search terraform and select Hashicopr Terraform. Install
- open folder, on top right corner click folder and enter name (Terraform_lab_ and select open.
- now you can create files in this folder.
- Access Ubuntu:
Mac O/S: Installing terraform, aws lcli, vs code and terraform plugin for vs code.
- use homebrew, a free package manager and once it is installed in mac system than install terraform from command line terminal.
- Install howebrew:
- open terminal and run the script
- ~%/bin/bash -c "$(curl -fsSL https://raw.githubusercontent.com/Homebrew/install/HEAD/install.sh)"
- ~%brew
- First install hashicorp/tap
- ~%brew tap hashicorp/tap
- ~%brew install hashicorp/tap/terraform
- ~%terraform (it will display commands)
- code
- code
- use homebrew, a free package manager and once it is installed in mac system than install terraform from command line terminal.
Centos/RHEL:
- Access Centos/RHEL
- Visit site https://developer.hashicorp.com/terraform/install
- Copy and paste the following command and execute.
- $sudo yum install -y yum-utils
sudo yum-config-manager --add-repo https://rpm.releases.hashicorp.com/RHEL/hashicorp.repo
sudo yum -y install terraform - Verify the installation:
- $terraform -help (it will list the commands)
- Enable auto tab:
- If you use either Bash or Zsh as your command line shell, you can enable tab completion for Terraform commands. To enable autocomplete, first ensure that a configuration file exists for your chosen shell.
- $touch ~/.bashrc
- Then install the autocomplete package.
- $terraform -install-autocomplete
code
- code
- code
- code
Syntax in Azure:
Structure of terraform.tf file
- codes are define in different .tf files.
- File Structure:
- file_structure.jpg
- Environment-Specific Structure
- file_structure2.jpg
- Serviced-based Structure
- file_structure3.jpg
Provider:
- Provider is a plugin that transform your code into code that cloud provider understands.
- We careate the code (.tf) using HCL (Hashicorp Language) which needs to be translated to the code which cloud providers can understand, it can be done with prvider plugin.
- When you run $terraform init , it initialize the provider and download the provider's plugin.
- provider1.jpg
- AWS Provider Block
- Visit https://registry.terraform.io/providers/hashicorp/aws/latest
- for more details visit: https://registry.terraform.io/providers/hashicorp/aws/latest/docs
- Create a file with extension .tf and write code
- #vim test.tf
- Enter Provider and version details:
- Go to terraform.io and select aws provider and click on provider and copy code.
- If you want to define specific version than define with the below block or it will take lastest version.
- provider2.jpg
- There are different versions, AWS version (maintain by AWS), other providers and terraform version(maintian by Hashicorp). check version compatability, if you do not mention version number than it will take latst.
-
terraform { required_providers { aws = { source = "hashicorp/aws" version = "5.74.0" } } } provider "aws" {region = "eu-west-2"access_key = "AKIAX2XVEK27GJNREDX4"secret_key = "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"} - provider "AWS": The code enter in this file is written for AWS cloud.
- Region in which service should be created.
- Acces key and secret key is the authentication to get access into aws account. Create IAM user and use access key and secret key. It is not recommended to hardcode keys, use vault or AWS CLI.
- How to get access_key/secret_key: Get for root user or IAM user, Go to IAM and create a user and get access key. click on user top right corner and click my security credentials and create access key.
- $terraform init (Terraform has been initiated successfully. Plugin has been downloaded and installed. terraform.lock.hcl is created which contain provider details.
- $terraform plan -out provider.tfplan (it will check the resources on AWS and compare with the file and gives output what will be plan of action), it will not create resources.
- It shows plan which will be executed, check output.
- $terraform apply "provider.tfplan" (it will execute and create resource)
- Azure Provider Block
- Go to terraform.io and click providers and select azure, click on user provider and copy code and paste it.
- create a file provide.tf
-
terraform {required_providers {azurerm = {source = "hashicorp/azurerm"version = "4.8.0"}}}
provider "azurerm" {subscription_id = ""tenant_id = ""client_id = ""client_secret = ""features {}} - Subscription Id: login to portal.azure.com and click subscription and copy ID.
- Tenant Id: Go to entra ID and in overview coy tenant ID
- Client Id: Go to Entra ID/manage/App Registration/New Registration/Enter name (terraform) and click ok.
- Client_Secret: In terrafom blade/manage/Certificates & secrets/new client secret/enter name(star-ClientSecret), copy value and save it in notepad. If it is not copied than generate new one.
- Assign Required Permission to terraform application: To create resources required permission needed, Go to subscription/Access control (IAM)/add role assignment/select privileged administrator roles and select contributor role /search for member terraform and select terraform and review and assign.
- Now resrouces can be created. add code to create resource
Dependency: Azure
- Resources are dependant to other resources, for example VM, storage account, Vnet are depend on Resource Group, without RG these resources can be created.
- If all resources are created through one configuration file then we refer/call the dependency in the configuration file.
- Terraform used declarative method, it means it should not be in sequence.
- code
remove yellow boxes in VS code when copy and paste
- copy the yellow box and go to view/search or Ctrl+Shift+F and paste the box and in Replace = click space bar and click replace all
- Code
Map of Values:
-
terraform {required_providers {azurerm = {source = "hashicorp/azurerm"version = "4.8.0"}}}
provider "azurerm" {subscription_id = "bd2ade99-0834-4cfe-bb19-ddf0e89ed9f4"tenant_id = "4b9f3326-b87a-468f-89d4-4c34403eae39"client_id = "363c6475-89bc-4948-9396-6dc6849eeb14"client_secret = "YFU8Q~gf2nHQyuv50lQjGkCZ0-M8YdZbGVoklcvs"features {}}locals {resource_group_name = "star-RG"location = "UK South"virtual_network={name="star-Vnet1"address_space="10.0.0.0/16"
}}resource "azurerm_resource_group" "RG" {name = local.resource_group_namelocation = local.location}
resource "azurerm_virtual_network" "vnet1" {name = local.virtual_network.namelocation = local.locationresource_group_name = local.resource_group_nameaddress_space = [local.virtual_network.address_space]
subnet {name = "subnet1"address_prefixes = ["10.0.1.0/24"]}
subnet {name = "subnet2"address_prefixes = ["10.0.2.0/24"]}
tags = {environment = "vnet-production"}
depends_on = [ azurerm_resource_group.RG ]} - code
- code
-
Terraform command:
- You should run the execution commands from the folder in which terraform .tf template files exist.
- $terraform validate
- Validate the reorganized structure
- $terraform fmt -recursive
- Format all files consistently
- $terraform init: it will download providers plugin in.
- .terraform folder will be created which container providers details.
- $terraform validate:
- It will check the configuration.
- $terraform plan -out filename.tfplan :
- It will output the action will be performed.
- $terraform apply "filename.tfplan"
- It will create resources in the given provider's location. Before apply you will have xyz.tf and .terraform in the folder.
- terraform.tfstate: it stores the details what it has created. If you run #terraform apply again then it will check terraform.tfstate file and plan and perform task if there is any change.
- terraform.tfstate.backup: It contain last known good configuration.
- Code
Count Parameter/ Count Meta Argument:
- Creating multiple instances:
- we dont need to define resources multiple times in configuration file but use count parameter.
- It works like loop, if you define count =3 then it will create 3 resources, suppose if you want to create 3 instances/VM then in instance resource use parameter count =3.
- names for all three instances must be unique, tags name will be different for easy identification, we use count.index parameter where it adds number before name.
-
provider "aws" {
region = "eu-west-2"
access_key = "AKIAX2XVEK27GJNREDX4"
secret_key = "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"
}resource "aws_instance" "server"{
ami = "ami-0dbec48abfe298cab"
instance_type = "t2.micro"
count = 3tags = {
Name = "WebServer.${count.index}"
}
} - 3 servers will be created. but all three instance tag name will be webserver.
- You can use ${count.index} , index value start from 0, so tag name will be (webserver0, webserver1. webserver2). Index numbers can be use before or after the name. If you want to start index with 1 then user ${count.index+1}
- If you want to give particular names then should use variable list and call in tags.
-
provider "aws" {
region = "eu-west-2"
access_key = "AKIAX2XVEK27GJNREDX4"
secret_key = "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"
}
variable "instance_name" {
type = list
default = ["dev_server","test_server","prod_server"]
}resource "aws_instance" "server"{
ami = "ami-0dbec48abfe298cab"
instance_type = "t2.micro"
count = 3tags = {
Name = var.instance_name[count.index]
}
} - Instance tag names will be (dev_server, test_server, prod_server) but instane type for all is "t2.micro".
- To assign different instance type (t2.small,t2.medium, t2.large etc).
-
provider "aws" {
region = "eu-west-2"
access_key = "AKIAX2XVEK27GJNREDX4"
secret_key = "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"
}
variable "instance_name" {
type = list
default = ["dev_server","test_server","prod_server"]
}
variable "instance_type" {
type = list
default = ["t2.small","t2.medium","t2.large"]
}
resource "aws_instance" "server"{
ami = "ami-0dbec48abfe298cab"
instance_type = var.instance_type[count.index]
count = 3tags = {
Name = var.instance_name${count.index}
}
} - code
- Creating multiple storage accounts using count Meta Argument:
- Go to terraform.io, click documentation and search storage account, copy code.
-
resource "azurerm_resource_group" "RG" {name = "star-RG"location = "UK South"}
resource "azurerm_storage_account" "starstorage" {count = 3name = "starstorage${count.index}"resource_group_name = "star-RG"location = "UK South"account_tier = "Standard"account_replication_type = "GRS"
tags = {Dept = "testing"}depends_on = [ azurerm_resource_group.RG ]} - storage account is created in resource group so we can define depends_on.
- Go to portal and check in storage account.
- Creating multiple containers in the storage account using for_each Meta Argument:
- Go to terraform.io, click documentation and search container, copy code.
-
resource "azurerm_storage_container" "example" { name = "vhds" storage_account_id = azurerm_storage_account.example.id container_access_type = "private" }
- for_each Meta Argument with "tomap" function, upload blob in containers
- in C drive create 3 folders dir1, dir2, dir3 and 3 text files in each folder namely file1, file2, file3
- Go to terraform.io and click documentation and search blob, copy code
-
resource "azurerm_storage_blob" "example" { name = "my-awesome-content.zip" storage_account_name = azurerm_storage_account.example.name storage_container_name = azurerm_storage_container.example.name type = "Block" source = "some-local-file.zip" } - cc
- LAB: Creating multiple containers in the storage account using for_each Meta Argument:
-
resource "azurerm_resource_group" "RG" {name = "star-RG"location = "UK South"}
resource "azurerm_storage_account" "starstorage" {name = "starstorage1"resource_group_name = "star-RG"location = "UK South"account_tier = "Standard"account_replication_type = "GRS"
tags = {Dept = "testing"}depends_on = [ azurerm_resource_group.RG ]}
resource "azurerm_storage_container" "container" {for_each = toset(["container1","container2","container3"])name = each.keystorage_account_name = "starstorage1"container_access_type = "private"depends_on = [ azurerm_storage_account.starstorage ]}
- Creating multiple containers in the storage account without using for_each Meta Argument:
- code
-
- LAB: for_each Meta Argument with "tomap" function, upload blob in container using the above storage and containers:
- in C drive created 3 folders dir1, dir2, dir3 and 3 text files in each folder namely file1, file2, file3
- Go to terraform.io and click documentation and search blob, copy code
-
resource "azurerm_resource_group" "RG" {name = "star-RG"location = "UK South"}
resource "azurerm_storage_account" "starstorage" {name = "starstorage1"resource_group_name = "star-RG"location = "UK South"account_tier = "Standard"account_replication_type = "GRS"
tags = {Dept = "testing"}depends_on = [ azurerm_resource_group.RG ]}
resource "azurerm_storage_container" "container" {for_each = toset(["container1","container2","container3"])name = each.keystorage_account_name = "starstorage1"container_access_type = "private"depends_on = [ azurerm_storage_account.starstorage ]}
resource "azurerm_storage_blob" "blob" {for_each = tomap({file1 = "C:\\dir1\\file1.txt"file2 = "C:\\dir2\\file2.txt"file3 = "C:\\dir3\\file3.txt"})name = "${each.key}.txt"storage_account_name = "starstorage1"storage_container_name = "container1"type = "Block"source = each.valuedepends_on = [ azurerm_storage_container.container ]} - three files are uploaded in container1.
- Code
- Code
- Code
- Creating multiple instances:
Input Value:
- provider
- Code
Variables (Input, Output, Locals, precedence):

- Variables allows you to define piece of data in one location instead of repeating the hardcoded value of it in multiple different locations in the code. Then when you need to modify the variable's value, you do it in one location instead of changing each one of the hardcoded values in the entire code.
- When you need to use certain values repeatedly in a program or script than you define the variable & value and call anywhere to avoid repetative typing.
- Input Variable:
- visit https://developer.hashicorp.com/terraform/language/values/variables
- User will define variable and provide value.
- Types of constraints supported in terraform variables: String, number, bool, list, set, map, object, tuple, data source,
-
-
variable "variablename" {type = stringdefault = "value"}
- Interpolation: calling the values of variable is called interpolation. For Example var.variablename. or in previous version "${var.variablename}"
- Lab: Manually defining the values.
- Create two files:
- $vim variable.tf copy and paste the following:
-
variable "accesskey" {type = stringdefault = "AKIAYHJANJLZX2BBGS5K"}variable "secretkey" {type = stringdefault = "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"}variable "region" {type = stringdefault = "eu-west-2"}
-
- $provider.tf copy and paste the follwing code:
-
provider "aws" {access_key = var.accesskeysecret_key = var.secretkeyregion = var.region}
-
- You can hardcode variable values using default, if you do not hardcode then system will prompt to enter values.String: values could be in character, numbers etc..
- $terraform init
- $terraform validate (it will check the configuration is correct or not)
- $terraform plan -out provider.tfplan (system will ask to enter accesskey, secretkey and region as we have not defined in variable file.
- $terrraform apply "provider.tfplan"
- You can enter values during apply:
- $terraform apply "provider.tfplan" -var 'accesskey=AKIAX2XVEK27GJNREDX4' -var 'secretkey=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' -var 'region=eu-west-2' (variable values are defined in command)
- If you do not want to enter value each time, remove variable and enter value in configuration file. once you entered and variable file is still exist then system will ask to enter value then you only enter as value has been hardcoded.
- If you do not want system to ask the value, delete variable file or remove related variable block or comment the block.
- Lab: Variables defined for CIDR block and call it in creating vpc and subnet (string):
- Create a file vpcvariable.tf, define the variable, type and its value as default and call it in resource where it is creating.
-
variable "vpccidr" {type = stringdefault = "10.0.0.0/16"}
variable "publicsubnetcidr" {type = stringdefault = "10.0.1.0/24"}variable "privatesubnetcidr" {type = stringdefault = "10.0.2.0/24"} - Create a file vpc.tf and copy the following code in which it call values from vpcvariable.tf file.
-
resource "aws_vpc" "star_vpc" {cidr_block = var.vpccidrinstance_tenancy = "default"
tags = {Name = "star_vpc"}}
resource "aws_subnet" "public_subnet" {vpc_id = aws_vpc.star_vpc.idcidr_block = var.publicsubnetcidr
tags = {Name = "public_subnet"}}
resource "aws_subnet" "private_subnet" {vpc_id = aws_vpc.star_vpc.idcidr_block = var.privatesubnetcidr
tags = {Name = "private_subnet"}}
- #terraform validate (it will check the configuration is correct or not)
- #terraform plan -out vpc.tfplan (system will ask to enter accesskey, secretkey and region as we have not defined in variable file.
- #terrraform apply "vpc.tfplan"
-
- number: 123
- Create 10 AWS instances
-
resource "aws_instance" "star-web1" {ami = "ami-005e54dee72cc1d00" # us-west-2instance_type = "t2.micro"region = "us-west-2"count = 10subnet = "VPC1"tags = {Name = "star web server"}}
- Terraform initialization
- #terraform init
- Terraform Plan
- #terraform plan -out star_instance.tfplan
- Terraform apply
- #terrafrom apply "star_instance.tfplan"
- Delete resource
- #terraform destroy
- bool: true/false
- list: The syntax is var.list .For example, var.subnets would get the value of the list, as a list.
- map: The syntax is var.<map>["KEY"]. For example, var.az["eu-west-2"] would get the value of the eu-west-2 key within the az map variable.
- self: The syntax is
self.<ATTRIBUTE>. For example${self.private_ip}will interpolate that resource's private IP address. - data source:
- Data source used to get data from providers or in general from external resources to terraform, (ex. public clouds like AWS, Azure, GCP). It is read only.
- output from a module:
- path information:
- condition:
-
- Built-in-functions: Terraform ships with built-in functions. Functions are called with the syntax
name(arg, arg2, ...). For example, to read a file:${file("path.txt")}.
- Output Values:
- It gives value on screen which is assigned by providers after creating the resource. Every resource will have a unique ID which can be call or refer in other application/code.
- Create files: variable.tf, vpc.tf
- $vim variable.tf copy and paste the following:
-
variable "accesskey" {type = stringdefault = "AKIAYHJANJLZX2BBGS5K"}variable "secretkey" {type = stringdefault = "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"}variable "region" {type = stringdefault = "eu-west-2"}variable "vpccidr" {type = stringdefault = "10.0.0.0/16"}
variable "publicsubnetcidr" {type = stringdefault = "10.0.1.0/24"}variable "privatesubnetcidr" {type = stringdefault = "10.0.2.0/24"}
-
- $vim vpc.tf copy and paste the following code.
-
provider "aws" {access_key = var.accesskeysecret_key = var.secretkeyregion = var.region}resource "aws_vpc" "star_vpc" {cidr_block = var.vpccidrinstance_tenancy = "default"
tags = {Name = "star_vpc"}}
resource "aws_subnet" "public_subnet" {vpc_id = aws_vpc.star_vpc.idcidr_block = var.publicsubnetcidr
tags = {Name = "public_subnet"}}
resource "aws_subnet" "private_subnet" {vpc_id = aws_vpc.star_vpc.idcidr_block = var.privatesubnetcidr
tags = {Name = "private_subnet"}} - output "star_vpc_id" {
value = aws_vpc.star_vpc.id
}
- $vim variable.tf copy and paste the following:
- $terraform init
- $terraform plan -out vpc.tfplan
- $terraform apply "vpc.tfplan"
-
Outputs:
star_vpc_id = "vpc-0e450a7a8fab169ef"
- You can also run $terraform output
- $terraform destroy
- Locals:
- Some values are used repetatively in configuration file, it can be defined and use in code by giving reference.
- locals {
resource_group_name="star-RG"
location="UK South"
} - Call the locals in code.
- name = local.resource_group_name
location = local.location - System will search and assingn resource_group_name "star-RG" and location "UK South"
- Variable Precedence:
- The value which you define in variable precedence will take predence than value in code. There are 3 ways you can define variable precedence value.
-
Default Values (temporarily hide terraform.tfvars)
mv terraform.tfvars terraform.tfvars.backup
terraform plan
# Uses: environment = "staging" (from variables.tf default)
mv terraform.tfvars.backup terraform.tfvars # restore
2. Using terraform.tfvars (automatically loaded)
terraform plan
# Uses: environment = "demo" (from terraform.tfvars)
3. Command Line Override (highest precedence)
terraform plan -var="environment=production"
# Overrides tfvars: environment = "production"
4. Environment Variables
export TF_VAR_environment="staging-from-env"
terraform plan
# Uses environment variable (but command line still wins)
5. Using Different tfvars Files
terraform plan -var-file="dev.tfvars" # environment = "development"
terraform plan -var-file="production.tfvars" # environment = "production"## 📁 Simple File Structure
├── main.tf # S3 bucket resource ├── variables.tf # Input variables (2 simple variables) ├── locals.tf # Local variables (tags and computed name) ├── output.tf # Output variables (bucket details) ├── provider.tf # AWS provider ├── terraform.tfvars # Default variable values └── README.md # This file
## 🧪 Practical Examples### Example 1: Testing Different Input Values
```bash
# Test with defaults (temporarily hide terraform.tfvars)
mv terraform.tfvars terraform.tfvars.backup
terraform plan
# Shows: Environment = "staging", bucket will be "staging-my-terraform-bucket-xxxxx"# Test with terraform.tfvars
mv terraform.tfvars.backup terraform.tfvars
terraform plan
# Shows: Environment = "demo", bucket will be "demo-terraform-demo-bucket-xxxxx"# Test with command line override
terraform plan -var="environment=test" -var="bucket_name=my-test-bucket"
# Shows: Environment = "test", bucket will be "test-my-test-bucket-xxxxx"
Example 2: Viewing All Variable Types in Action
# Apply the configuration
terraform apply -auto-approve# See all outputs (shows output variables)
terraform output
# bucket_arn = "arn:aws:s3:::demo-terraform-demo-bucket-abc123"
# bucket_name = "demo-terraform-demo-bucket-abc123"
# environment = "demo" # (input variable)
# tags = { # (local variable)
# "Environment" = "demo"
# "Owner" = "DevOps-Team"
# "Project" = "Terraform-Demo"
# }# See how local variables computed the bucket name
echo "Input: environment = $(terraform output -raw environment)"
echo "Input: bucket_name = terraform-demo-bucket (from tfvars)"
echo "Local: full_bucket_name = $(terraform output -raw bucket_name)"
echo "Random suffix was added by local variable!"
Example 3: Variable Precedence in Action
# Start with terraform.tfvars (environment = "demo")
terraform plan | grep Environment
# Shows: "Environment" = "demo"# Override with environment variable
export TF_VAR_environment="from-env-var"
terraform plan | grep Environment
# Shows: "Environment" = "from-env-var"# Override with command line (highest precedence)
terraform plan -var="environment=from-command-line" | grep Environment
# Shows: "Environment" = "from-command-line"# Clean up
unset TF_VAR_environment
🔧 Try These Commands
# Initialize
terraform init# Plan with defaults
terraform plan# Plan with command line override
terraform plan -var="environment=test"# Plan with different tfvars file
terraform plan -var-file="dev.tfvars"# Apply and see outputs
terraform apply
terraform output# Clean up
terraform destroy
Split Configuration File:
- creating multiple resources result increasing the size of a file and will be difficult to manage. It can be split into files to manage easily.
- We have a complete code in a file vpc.tf, split into two, create a file provider.tf and copy provider portion in provider.tf and save both files. both files are in same folder.
- #terraform plan -out vpc.tfplan. Run terraform plan and both files will be considered and a plan will be generated.
- #terraform apply "vpc.tfplan" : it will create resources by reading provider.tf and vpc.tf
- Code
- Code
Loop:
- provider
- Code
Comments:
- comments are used in the configuration file to provider information about the code,
- Single line comment: use # or // and type
-
terraform {required_providers {azurerm = {source = "hashicorp/azurerm"version = "4.8.0"}}}
provider "azurerm" {subscription_id = ""tenant_id = ""client_id = ""client_secret = ""features {}} - # This block is used to provide azure provider details. or
- // This block is used to provide azure provider details.
-
- Multiple line comment:
-
terraform {required_providers {azurerm = {source = "hashicorp/azurerm"version = "4.8.0"}}}
provider "azurerm" {subscription_id = "bd2ade99-0834-4cfe-bb19-ddf0e89ed9f4"tenant_id = "4b9f3326-b87a-468f-89d4-4c34403eae39"client_id = "0df6190d-31bc-4d6a-ba38-3115d352e7ca"client_secret = "xkH8Q~OQ-Rg7XXu7Zz-I6IkVHijsxsZeOwGs5cKz"features {}} - /*
In this block azure providers details has been provided.
Values has been hard coded
*/
-
- Code
Condition statement:
- You can define condition in the code where if condition met then perform such action and if not perform different action.
- Creating X number of VMs if condition met.
- Define variables for instance type & image, and call variable where we enter condition.
- Creating x number of VMs in certain department if condition met.
- Code
syntax
- provider
- Code
syntax
- provider
- Code
syntax
- provider
- Code
syntax
- provider
- Code
syntax
- provider
- Code
syntax
- provider
- Code
syntax
- provider
- Code
syntax
- provider
- Code
syntax
- provider
- Code
Azure Resources
RG - Resource Group
- Resource Group code:
- Go to terraform.io and select provider Azure (azurerm) and click documentation, search resource group and select azurerm_resource_group
-
resource "azurerm_resource_group" "RG" { name = "star-RG" location = "UK South" } - "azure_resource_group" is refer to resource group and predefined. "RG" is defined as variable, it could be any name and can be refer in the code for resource group.
- name = "star-RG" is resource group name.
- Azure provider and Resource Group creation.
-
create a file rg.tf and use the following codeterraform {required_providers {azurerm = {source = "hashicorp/azurerm"version = "4.8.0"}}}
provider "azurerm" {subscription_id = "bd2ade99-0834-4cfe-bb19-ddf0e89ed9f4"tenant_id = "4b9f3326-b87a-468f-89d4-4c34403eae39"client_id = "0df6190d-31bc-4d6a-ba38-3115d352e7ca"client_secret = "xkH8Q~OQ-Rg7XXu7Zz-I6IkVHijsxsZeOwGs5cKz"features {}}
resource "azurerm_resource_group" "RG" {name = "star-RG"location = "UK South"}- save the file before initialize.
- Terraform Initialization: click Terminal and open new terminal:
- PS C:\terraform>terraform init
- Terraform has been initiated successfully. Plugin has been downloaded and installed. terraform.lock.hcl is created which contain provider details
- Terraform Plan:
- PS C:\terraform>terraform plan -out rg.tfplan
- It shows plan which will be executed, check output.
- Terraform apply:
- PS C:\terraform> terraform apply "rg.tfplan" (it will execute and create resource)
- Deleting resource:
- PS C:\terraform>terraform destroy
-
- Locals Block: provider and Resource Group creation with Locals block.
-
terraform {required_providers {azurerm = {source = "hashicorp/azurerm"version = "4.8.0"}}}
provider "azurerm" {subscription_id = "bd2ade99-0834-4cfe-bb19-ddf0e89ed9f4"tenant_id = "4b9f3326-b87a-468f-89d4-4c34403eae39"client_id = "363c6475-89bc-4948-9396-6dc6849eeb14"client_secret = "yUR8Q~2w~xi~~i6hUJkw4XCZRPCNVwIpIkTrcaPW"features {}}locals {resource_group_name="Star-RG"location="UK South"}resource "azurerm_resource_group" "RG" {name = local.resource_group_namelocation = local.location}
-
- Resource Group code:
Virtual Network (Vnet)
Creating virtual network with two subnets without calling values
- Vnet1 (10.0.0.0/16), subnet1 (10.0.1.024), subnet2(10.0.2.0/24).
- Go to terraform.io and click provider and select Azure and click documentation and search virtual network and select azurerm_virtual _network, copy code and make changes as follows.
-
terraform {required_providers {azurerm = {source = "hashicorp/azurerm"version = "4.8.0"}}}
provider "azurerm" {subscription_id = "bd2ade99-0834-4cfe-bb19-ddf0e89ed9f4"tenant_id = "4b9f3326-b87a-468f-89d4-4c34403eae39"client_id = "363c6475-89bc-4948-9396-6dc6849eeb14"client_secret = "YFU8Q~gf2nHQyuv50lQjGkCZ0-M8YdZbGVoklcvs"features {}}resource "azurerm_resource_group" "RG" {name = "star-RG"location = "UK South"}
resource "azurerm_virtual_network" "vnet1" {name = "star-Vnet1"location = "UK South"resource_group_name = "star-RG"address_space = ["10.0.0.0/16"]
subnet {name = "subnet1"address_prefixes = ["10.0.1.0/24"]}
subnet {name = "subnet2"address_prefixes = ["10.0.2.0/24"]}
tags = {environment = "vnet-production"}
depends_on = [ azurerm_resource_group.RG ]} -
- Save file (vnet) and open Terminal
- Terraform initialize
- #terraform init
- Terraform plan
- #terraform plan -out vnet.tfplan
- Terraform apply
- #terraform apply "vnet.tfplan"
- Destroy/Delete
- #terraform destroy
Creating virtual network, subnets by defining local variable block, separate variable file & Count Meta Argument:
-
locals {resource_group_name="Star-RG"location="UK South"security_group="SG"virtual_network ={name="star-Vnet1"address_space="10.0.0.0/16"}subnets=[{name = "subnet1"address_prefixes = ["10.0.1.0/24"]},
{name = "subnet2"address_prefixes = ["10.0.2.0/24"]}]}resource "azurerm_resource_group" "RG" {name = local.resource_group_namelocation = local.location}
resource "azurerm_virtual_network" "vnet" {name = local.virtual_network.namelocation = local.locationresource_group_name = local.resource_group_nameaddress_space = [local.virtual_network.address_space]
}
resource "azurerm_subnet" "subnet-A" {name = local.subnets[0].nameresource_group_name = local.resource_group_namevirtual_network_name = local.virtual_network.nameaddress_prefixes = local.subnets[0].address_prefixesdepends_on = [ azurerm_virtual_network.vnet ]}
resource "azurerm_subnet" "subnet-B" {name = local.subnets[1].nameresource_group_name = local.resource_group_namevirtual_network_name = local.virtual_network.nameaddress_prefixes = local.subnets[1].address_prefixesdepends_on = [ azurerm_virtual_network.vnet ]}resource "azurerm_network_interface" "NIC1" {name = "star-NIC1"location = local.locationresource_group_name = local.resource_group_name
ip_configuration {name = "internal"subnet_id = azurerm_subnet.subnet-A.idprivate_ip_address_allocation = "Dynamic"public_ip_address_id = azurerm_public_ip.publicIP.id}depends_on = [ azurerm_subnet.subnet-A ]}
resource "azurerm_public_ip" "publicIP" {name = "StarPublicIP1"resource_group_name = local.resource_group_namelocation = local.locationallocation_method = "Static"
tags = {Dept = "IT"}depends_on = [ azurerm_resource_group.RG ]}
resource "azurerm_network_security_group" "NSG" {name = "star-NSG1"location = local.locationresource_group_name = local.resource_group_name
security_rule {name = "NSG-Rule1"priority = 500direction = "Inbound"access = "Allow"protocol = "Tcp"source_port_range = "*"destination_port_range = "3389"source_address_prefix = "*"destination_address_prefix = "*"}
tags = {Name = "NSG"}}resource "azurerm_subnet_network_security_group_association" "NSG-Subnet" {subnet_id = azurerm_subnet.subnet-A.idnetwork_security_group_id = azurerm_network_security_group.NSG.id} - Creating virtual network, subnets by defining separate variable file & Count Meta Argument:
- Create a subnet_variable.tf
-
variable "no_of_subnet" {type = numberdefault = 2}
-
- Create a provider.tf
-
terraform {required_providers {azurerm = {source = "hashicorp/azurerm"version = "4.8.0"}}}
provider "azurerm" {subscription_id = "bd2ade99-0834-4cfe-bb19-ddf0e89ed9f4"tenant_id = "4b9f3326-b87a-468f-89d4-4c34403eae39"client_id = "363c6475-89bc-4948-9396-6dc6849eeb14"client_secret = "yUR8Q~2w~xi~~i6hUJkw4XCZRPCNVwIpIkTrcaPW"features {}}
-
- Create subnet_count.tf
-
locals {resource_group_name="star-RG"location="UK South"virtual_network={name="Vnet1"address_space="10.0.0.0/16"}subnets=[{name = "subnet1"address_prefix = "10.0.1.0/24"},
{name = "subnet2"address_prefix = "10.0.2.0/24"}]}
resource "azurerm_resource_group" "RG" {name = local.resource_group_namelocation = local.location}
resource "azurerm_virtual_network" "VNET" {name = local.virtual_network.namelocation = local.locationresource_group_name = local.resource_group_nameaddress_space = [local.virtual_network.address_space]depends_on = [ azurerm_resource_group.RG ]}
resource "azurerm_subnet" "subnets" {count = var.no_of_subnetname = local.subnets[count.index].nameresource_group_name = local.resource_group_namevirtual_network_name = local.virtual_network.nameaddress_prefixes = [local.subnets[count.index].address_prefix]depends_on = [ azurerm_virtual_network.VNET ]
-
- Create a subnet_variable.tf
- Create Number of Subnets based on Input:
- Create a subnet_variable.tf
-
variable "no_of_subnet" {type = numberdefault = 2}
-
- Create a provider.tf
-
terraform {required_providers {azurerm = {source = "hashicorp/azurerm"version = "4.8.0"}}}
provider "azurerm" {subscription_id = "bd2ade99-0834-4cfe-bb19-ddf0e89ed9f4"tenant_id = "4b9f3326-b87a-468f-89d4-4c34403eae39"client_id = "363c6475-89bc-4948-9396-6dc6849eeb14"client_secret = "yUR8Q~2w~xi~~i6hUJkw4XCZRPCNVwIpIkTrcaPW"features {}}
-
- Create subnet_count_input.tf
-
locals {resource_group_name="star-RG"location="UK South"virtual_network={name="Vnet1"address_space="10.0.0.0/16"}}
resource "azurerm_resource_group" "RG" {name = local.resource_group_namelocation = local.location}
resource "azurerm_virtual_network" "VNET" {name = local.virtual_network.namelocation = local.locationresource_group_name = local.resource_group_nameaddress_space = [local.virtual_network.address_space]
depends_on = [ azurerm_resource_group.RG ]}
resource "azurerm_subnet" "subnets" {count = var.no_of_subnetname = "Subnet${count.index}"resource_group_name = local.resource_group_namevirtual_network_name = local.virtual_network.nameaddress_prefixes = ["10.0.${count.index}.0/24"]depends_on = [ azurerm_virtual_network.VNET ]}
-
- #terraform plan -out subnet_count_input.tfplan -var="no_of_subnet=4"
- #terraform apply "subnet_count_input.tfplan"
- Create a subnet_variable.tf
- Create Number of Subnets based on Input & apply restriction:
- Create a subnet_variable.tf
-
variable "no_of_subnet" {type = numberdefault = 2validation {condition = var.no_of_subnet < 5error_message = "Value should be less than 5." (make sure V is capital and at the end of line there is full stop)}}
-
- Create a provider.tf
-
terraform {required_providers {azurerm = {source = "hashicorp/azurerm"version = "4.8.0"}}}
provider "azurerm" {subscription_id = "bd2ade99-0834-4cfe-bb19-ddf0e89ed9f4"tenant_id = "4b9f3326-b87a-468f-89d4-4c34403eae39"client_id = "363c6475-89bc-4948-9396-6dc6849eeb14"client_secret = "yUR8Q~2w~xi~~i6hUJkw4XCZRPCNVwIpIkTrcaPW"features {}}
-
- Create subnet_count_restrict.tf
-
locals {resource_group_name="star-RG"location="UK South"virtual_network={name="Vnet1"address_space="10.0.0.0/16"}}
resource "azurerm_resource_group" "RG" {name = local.resource_group_namelocation = local.location}
resource "azurerm_virtual_network" "VNET" {name = local.virtual_network.namelocation = local.locationresource_group_name = local.resource_group_nameaddress_space = [local.virtual_network.address_space]
depends_on = [ azurerm_resource_group.RG ]}
resource "azurerm_subnet" "subnets" {count = var.no_of_subnetname = "Subnet${count.index}"resource_group_name = local.resource_group_namevirtual_network_name = local.virtual_network.nameaddress_prefixes = ["10.0.${count.index}.0/24"]depends_on = [ azurerm_virtual_network.VNET ]} - #terraform plan -out subnet_count_input.tfplan -var="no_of_subnet=5"
- it will through error as no of subnets is 5, enter any value less than 5
- Remove default = 2 from variable.tf and you do not need to give -var="no_of_subnet=x" as system will ask to enter value.
- #terraform apply "subnet_count_input.tfplan"
-
- Create a subnet_variable.tf
- Create Multiple Subnets using for_each Meta Argument:
- Create a subnet_variable.tf
-
variable "no_of_subnet" {type = numberdefault = 2}
-
- Create a provider.tf
-
terraform {required_providers {azurerm = {source = "hashicorp/azurerm"version = "4.8.0"}}}
provider "azurerm" {subscription_id = "bd2ade99-0834-4cfe-bb19-ddf0e89ed9f4"tenant_id = "4b9f3326-b87a-468f-89d4-4c34403eae39"client_id = "363c6475-89bc-4948-9396-6dc6849eeb14"client_secret = "yUR8Q~2w~xi~~i6hUJkw4XCZRPCNVwIpIkTrcaPW"features {}}
-
- Create subnet_count.tf
-
locals {resource_group_name="star-RG"location="UK South"virtual_network={name="Vnet1"address_space="10.0.0.0/16"}subnets= {subnet1 = {name = "subnet1"address_prefix = "10.0.1.0/24"},subnet2 = {name = "subnet2"address_prefix = "10.0.2.0/24"}}}
resource "azurerm_resource_group" "RG" {name = local.resource_group_namelocation = local.location}
resource "azurerm_virtual_network" "VNET" {name = local.virtual_network.namelocation = local.locationresource_group_name = local.resource_group_nameaddress_space = [local.virtual_network.address_space]
depends_on = [ azurerm_resource_group.RG ]}
resource "azurerm_subnet" "subnets" {for_each = local.subnetsname = each.value.nameresource_group_name = local.resource_group_namevirtual_network_name = local.virtual_network.nameaddress_prefixes = [each.value.address_prefix]depends_on = [ azurerm_virtual_network.VNET ]} - #terraform plan -out subnet_for_each.tfplan
- #terraform apply "subnet_for_each.tfplan"
-
- Create a subnet_variable.tf
- Code
- Code
- Code
- Code
-
Using map of values for defining virtual network, name, location, security group, subnets
-
terraform {required_providers {azurerm = {source = "hashicorp/azurerm"version = "4.8.0"}}}
provider "azurerm" {subscription_id = "bd2ade99-0834-4cfe-bb19-ddf0e89ed9f4"tenant_id = "4b9f3326-b87a-468f-89d4-4c34403eae39"client_id = "363c6475-89bc-4948-9396-6dc6849eeb14"client_secret = "yUR8Q~2w~xi~~i6hUJkw4XCZRPCNVwIpIkTrcaPW"features {}}locals {resource_group_name="Star-RG"location="UK South"}resource "azurerm_resource_group" "RG" {name = local.resource_group_namelocation = local.location}
resource "azurerm_network_security_group" "SG" {name = "star-SG"location = local.locationresource_group_name = local.resource_group_name}
resource "azurerm_virtual_network" "vnet" {name = "star-vnet1"location = local.locationresource_group_name = local.resource_group_nameaddress_space = ["10.0.0.0/16"]
subnet {name = "subnet1"address_prefixes = ["10.0.1.0/24"]security_group = azurerm_network_security_group.SG.id}
subnet {name = "subnet2"address_prefixes = ["10.0.2.0/24"]security_group = azurerm_network_security_group.SG.id}
tags = {environment = "star-Vnet1"}}
-
Create a vnet, subnets defining in locals block/mapping values:
-
Subnets are creating withing a virtual network resource.terraform {required_providers {azurerm = {source = "hashicorp/azurerm"version = "4.8.0"}}}
provider "azurerm" {subscription_id = "bd2ade99-0834-4cfe-bb19-ddf0e89ed9f4"tenant_id = "4b9f3326-b87a-468f-89d4-4c34403eae39"client_id = "363c6475-89bc-4948-9396-6dc6849eeb14"client_secret = "yUR8Q~2w~xi~~i6hUJkw4XCZRPCNVwIpIkTrcaPW"features {}}locals {resource_group_name="Star-RG"location="UK South"security_group="SG"virtual_network ={name="star-Vnet1"address_space="10.0.0.0/16"}subnets=[{name = "subnet1"address_prefixes = ["10.0.1.0/24"]},
{name = "subnet2"address_prefixes = ["10.0.2.0/24"]}]}resource "azurerm_resource_group" "RG" {name = local.resource_group_namelocation = local.location}
resource "azurerm_network_security_group" "SG" {name = local.security_grouplocation = local.locationresource_group_name = local.resource_group_name}
resource "azurerm_virtual_network" "vnet" {name = local.virtual_network.namelocation = local.locationresource_group_name = local.resource_group_nameaddress_space = [local.virtual_network.address_space]
subnet {name = local.subnets[0].nameaddress_prefixes = local.subnets[0].address_prefixessecurity_group = azurerm_network_security_group.SG.id}
subnet {name = local.subnets[1].nameaddress_prefixes = local.subnets[1].address_prefixessecurity_group = azurerm_network_security_group.SG.id}
tags = {environment = "star-Vnet1"}}
-
Create Subnets as a separate resource using existing RG & Vnet:
- Go to terraform.io and click on documentation and search for subnets, copy resource subnet part only and leave RG & Vnet code and make necessary changes.
- Create a file subnet.tf and paste the following subnet code.
-
resource "azurerm_subnet" "example" { name = "example-subnet" resource_group_name = azurerm_resource_group.example.name virtual_network_name = azurerm_virtual_network.example.name address_prefixes = ["10.0.1.0/24"] delegation { name = "delegation" service_delegation { name = "Microsoft.ContainerInstance/containerGroups" actions = ["Microsoft.Network/virtualNetworks/subnets/join/action", "Microsoft.Network/virtualNetworks/subnets/prepareNetworkPolicies/action"] } } } -
terraform {required_providers {azurerm = {source = "hashicorp/azurerm"version = "4.8.0"}}}
provider "azurerm" {subscription_id = "bd2ade99-0834-4cfe-bb19-ddf0e89ed9f4"tenant_id = "4b9f3326-b87a-468f-89d4-4c34403eae39"client_id = "363c6475-89bc-4948-9396-6dc6849eeb14"client_secret = "yUR8Q~2w~xi~~i6hUJkw4XCZRPCNVwIpIkTrcaPW"features {}}locals {resource_group_name="Star-RG"location="UK South"security_group="SG"virtual_network ={name="star-Vnet1"address_space="10.0.0.0/16"}subnets=[{name = "subnet1"address_prefixes = ["10.0.1.0/24"]},
{name = "subnet2"address_prefixes = ["10.0.2.0/24"]}]}resource "azurerm_resource_group" "RG" {name = local.resource_group_namelocation = local.location}
resource "azurerm_virtual_network" "vnet" {name = local.virtual_network.namelocation = local.locationresource_group_name = local.resource_group_nameaddress_space = [local.virtual_network.address_space]
}resource "azurerm_network_security_group" "SG" {name = local.security_grouplocation = local.locationresource_group_name = local.resource_group_name}
resource "azurerm_subnet" "subnet-A" {name = local.subnets[0].nameresource_group_name = local.resource_group_namevirtual_network_name = local.virtual_network.nameaddress_prefixes = local.subnets[0].address_prefixesdepends_on = [ azurerm_virtual_network.vnet ]}
resource "azurerm_subnet" "subnet-B" {name = local.subnets[1].nameresource_group_name = local.resource_group_namevirtual_network_name = local.virtual_network.nameaddress_prefixes = local.subnets[1].address_prefixesdepends_on = [ azurerm_virtual_network.vnet ]} - In the above subnets are creating as a separate resource.
Create SG and associate with subnets.
- Creating Vnet, 2 Subnets, Security Group with default Rule, associate SG with subnets.
-
terraform {required_providers {azurerm = {source = "hashicorp/azurerm"version = "4.8.0"}}}
provider "azurerm" {subscription_id = "bd2ade99-0834-4cfe-bb19-ddf0e89ed9f4"tenant_id = "4b9f3326-b87a-468f-89d4-4c34403eae39"client_id = "363c6475-89bc-4948-9396-6dc6849eeb14"client_secret = "yUR8Q~2w~xi~~i6hUJkw4XCZRPCNVwIpIkTrcaPW"features {}}locals {resource_group_name="Star-RG"location="UK South"security_group="SG"virtual_network ={name="star-Vnet1"address_space="10.0.0.0/16"}subnets=[{name = "subnet1"address_prefixes = ["10.0.1.0/24"]},
{name = "subnet2"address_prefixes = ["10.0.2.0/24"]}]}resource "azurerm_resource_group" "RG" {name = local.resource_group_namelocation = local.location}
resource "azurerm_virtual_network" "vnet" {name = local.virtual_network.namelocation = local.locationresource_group_name = local.resource_group_nameaddress_space = [local.virtual_network.address_space]
}resource "azurerm_network_security_group" "SG" {name = local.security_grouplocation = local.locationresource_group_name = local.resource_group_namedepends_on = [ azurerm_resource_group.RG ]}
resource "azurerm_subnet" "subnet-A" {name = local.subnets[0].nameresource_group_name = local.resource_group_namevirtual_network_name = local.virtual_network.nameaddress_prefixes = local.subnets[0].address_prefixesdepends_on = [ azurerm_virtual_network.vnet ]}
resource "azurerm_subnet" "subnet-B" {name = local.subnets[1].nameresource_group_name = local.resource_group_namevirtual_network_name = local.virtual_network.nameaddress_prefixes = local.subnets[1].address_prefixesdepends_on = [ azurerm_virtual_network.vnet ]}resource "azurerm_subnet_network_security_group_association" "SG1" {subnet_id = azurerm_subnet.subnet-A.idnetwork_security_group_id = azurerm_network_security_group.SG.id}resource "azurerm_subnet_network_security_group_association" "SG2" {subnet_id = azurerm_subnet.subnet-B.idnetwork_security_group_id = azurerm_network_security_group.SG.id}
-
- Creating Vnet, 3 Subnets, Security Group with 3389 allowed Rule, associate SG with subnets using count parameter with Input Value.
- provider.tf:
-
terraform {required_providers {azurerm = {source = "hashicorp/azurerm"version = "4.8.0"}}}
provider "azurerm" {subscription_id = "bd2ade99-0834-4cfe-bb19-ddf0e89ed9f4"tenant_id = "4b9f3326-b87a-468f-89d4-4c34403eae39"client_id = "363c6475-89bc-4948-9396-6dc6849eeb14"client_secret = "yUR8Q~2w~xi~~i6hUJkw4XCZRPCNVwIpIkTrcaPW"features {}}
-
- Variable.tf:
-
variable "no_of_subnet" {type = number}
-
- subnet_count_input:
-
locals {resource_group_name="star-RG"location="UK South"virtual_network={name="Vnet1"address_space="10.0.0.0/16"}security_group = "star-SG"}
resource "azurerm_resource_group" "RG" {name = local.resource_group_namelocation = local.location}
resource "azurerm_virtual_network" "VNET" {name = local.virtual_network.namelocation = local.locationresource_group_name = local.resource_group_nameaddress_space = [local.virtual_network.address_space]depends_on = [ azurerm_resource_group.RG ]}
resource "azurerm_subnet" "subnets" {count = var.no_of_subnetname = "Subnet${count.index}"resource_group_name = local.resource_group_namevirtual_network_name = local.virtual_network.nameaddress_prefixes = ["10.0.${count.index}.0/24"]depends_on = [ azurerm_virtual_network.VNET ]}
resource "azurerm_network_security_group" "SG" {name = local.security_grouplocation = local.locationresource_group_name = local.resource_group_namedepends_on = [ azurerm_resource_group.RG ]
security_rule {name = "test123"priority = 100direction = "Inbound"access = "Allow"protocol = "Tcp"source_port_range = "*"destination_port_range = "3389"source_address_prefix = "*"destination_address_prefix = "*"}}
resource "azurerm_subnet_network_security_group_association" "assoc_subnet" {count = var.no_of_subnetsubnet_id = azurerm_subnet.subnets[count.index].idnetwork_security_group_id = azurerm_network_security_group.SG.id}
-
- #terraform init
- #terraform plan -out subnet_count_input.tfplan (system will ask to enter no of subnets)
- #terraform plan "subnet_count_input.tfplan"
- provider.tf:
- ss
- ss
- ss
- Creating Vnet, 2 Subnets, Security Group with default Rule, associate SG with subnets.
Create Network Interface (NIC), public IP:
- Go to terraform.io and click documentation and search network interface.
-
resource "azurerm_network_interface" "example" { name = "example-nic" location = azurerm_resource_group.example.location resource_group_name = azurerm_resource_group.example.name ip_configuration { name = "internal" subnet_id = azurerm_subnet.example.id private_ip_address_allocation = "Dynamic" } } - create a file and paste the following.
-
terraform {required_providers {azurerm = {source = "hashicorp/azurerm"version = "4.8.0"}}}
provider "azurerm" {subscription_id = "bd2ade99-0834-4cfe-bb19-ddf0e89ed9f4"tenant_id = "4b9f3326-b87a-468f-89d4-4c34403eae39"client_id = "363c6475-89bc-4948-9396-6dc6849eeb14"client_secret = "yUR8Q~2w~xi~~i6hUJkw4XCZRPCNVwIpIkTrcaPW"features {}}locals {resource_group_name="Star-RG"location="UK South"security_group="SG"virtual_network ={name="star-Vnet1"address_space="10.0.0.0/16"}subnets=[{name = "subnet1"address_prefixes = ["10.0.1.0/24"]},
{name = "subnet2"address_prefixes = ["10.0.2.0/24"]}]}resource "azurerm_resource_group" "RG" {name = local.resource_group_namelocation = local.location}
resource "azurerm_virtual_network" "vnet" {name = local.virtual_network.namelocation = local.locationresource_group_name = local.resource_group_nameaddress_space = [local.virtual_network.address_space]}resource "azurerm_network_security_group" "SG" {name = local.security_grouplocation = local.locationresource_group_name = local.resource_group_namedepends_on = [ azurerm_resource_group.RG ]}
resource "azurerm_subnet" "subnet-A" {name = local.subnets[0].nameresource_group_name = local.resource_group_namevirtual_network_name = local.virtual_network.nameaddress_prefixes = local.subnets[0].address_prefixesdepends_on = [ azurerm_virtual_network.vnet ]}
resource "azurerm_subnet" "subnet-B" {name = local.subnets[1].nameresource_group_name = local.resource_group_namevirtual_network_name = local.virtual_network.nameaddress_prefixes = local.subnets[1].address_prefixesdepends_on = [ azurerm_virtual_network.vnet ]}resource "azurerm_subnet_network_security_group_association" "SG1" {subnet_id = azurerm_subnet.subnet-A.idnetwork_security_group_id = azurerm_network_security_group.SG.id}resource "azurerm_subnet_network_security_group_association" "SG2" {subnet_id = azurerm_subnet.subnet-B.idnetwork_security_group_id = azurerm_network_security_group.SG.id}
resource "azurerm_network_interface" "NIC1" {name = "star-NIC1"location = local.locationresource_group_name = local.resource_group_name
ip_configuration {name = "internal"subnet_id = azurerm_subnet.subnet-A.idprivate_ip_address_allocation = "Dynamic"}} - To check NIC is created, go to vnet1 and in settings click connected devices. star-NIC1 is created with IP 10.0.1.4 in Subnet1.
-
- Create NIC, Public IP and assign public IP to subnet with Input Value.
- variable_nic.tf
-
variable "no_of_subnet" {type = numberdefault = 2}
variable "no_of_nic" {type = numberdefault = 2}
-
- provider.tf
-
terraform {required_providers {azurerm = {source = "hashicorp/azurerm"version = "4.8.0"}}}
provider "azurerm" {subscription_id = "bd2ade99-0834-4cfe-bb19-ddf0e89ed9f4"tenant_id = "4b9f3326-b87a-468f-89d4-4c34403eae39"client_id = "363c6475-89bc-4948-9396-6dc6849eeb14"client_secret = "yUR8Q~2w~xi~~i6hUJkw4XCZRPCNVwIpIkTrcaPW"features {}}
-
- nic.tf
-
locals {resource_group_name="star-RG"location="UK South"virtual_network={name="Vnet1"address_space="10.0.0.0/16"}security_group = "star-SG"}
resource "azurerm_resource_group" "RG" {name = local.resource_group_namelocation = local.location}
resource "azurerm_virtual_network" "VNET" {name = local.virtual_network.namelocation = local.locationresource_group_name = local.resource_group_nameaddress_space = [local.virtual_network.address_space]
depends_on = [ azurerm_resource_group.RG ]}
resource "azurerm_subnet" "subnets" {count = var.no_of_subnetname = "Subnet${count.index}"resource_group_name = local.resource_group_namevirtual_network_name = local.virtual_network.nameaddress_prefixes = ["10.0.${count.index}.0/24"]depends_on = [ azurerm_virtual_network.VNET ]}
resource "azurerm_network_security_group" "SG" {name = local.security_grouplocation = local.locationresource_group_name = local.resource_group_namedepends_on = [ azurerm_resource_group.RG ]
security_rule {name = "test123"priority = 100direction = "Inbound"access = "Allow"protocol = "Tcp"source_port_range = "*"destination_port_range = "3389"source_address_prefix = "*"destination_address_prefix = "*"}}
resource "azurerm_subnet_network_security_group_association" "assoc_subnet" {count = var.no_of_subnetsubnet_id = azurerm_subnet.subnets[count.index].idnetwork_security_group_id = azurerm_network_security_group.SG.id}
resource "azurerm_network_interface" "NIC" {count = var.no_of_nicname = "NIC${count.index}"location = local.locationresource_group_name = local.resource_group_name
ip_configuration {name = "Internal"subnet_id = azurerm_subnet.subnets[count.index].idprivate_ip_address_allocation = "Dynamic"public_ip_address_id = azurerm_public_ip.publicip[count.index].id}depends_on = [ azurerm_subnet.subnets,azurerm_public_ip.publicip ]}
resource "azurerm_public_ip" "publicip" {count = var.no_of_nicname = "publicip${count.index}"resource_group_name = local.resource_group_namelocation = local.locationallocation_method = "Static"
tags = {Dept = "IT"}depends_on = [ azurerm_resource_group.RG ]} - #terraform init
- #terraform plan -out nic.tfplan
- #terraform apply "nic.tfplan"
- cc
-
- variable_nic.tf
- Code
- Code
Create a Public IP and associate with NIC.
- Go to terraform.io and click documentation and search public IP.
-
resource "azurerm_resource_group" "example" { name = "example-resources" location = "West Europe" } resource "azurerm_public_ip" "example" { name = "acceptanceTestPublicIp1" resource_group_name = azurerm_resource_group.example.name location = azurerm_resource_group.example.location allocation_method = "Static" tags = { environment = "Production" } } -
LAB:terraform {required_providers {azurerm = {source = "hashicorp/azurerm"version = "4.8.0"}}}
provider "azurerm" {subscription_id = "bd2ade99-0834-4cfe-bb19-ddf0e89ed9f4"tenant_id = "4b9f3326-b87a-468f-89d4-4c34403eae39"client_id = "363c6475-89bc-4948-9396-6dc6849eeb14"client_secret = "yUR8Q~2w~xi~~i6hUJkw4XCZRPCNVwIpIkTrcaPW"features {}}locals {resource_group_name="Star-RG"location="UK South"security_group="SG"virtual_network ={name="star-Vnet1"address_space="10.0.0.0/16"}subnets=[{name = "subnet1"address_prefixes = ["10.0.1.0/24"]},
{name = "subnet2"address_prefixes = ["10.0.2.0/24"]}]}resource "azurerm_resource_group" "RG" {name = local.resource_group_namelocation = local.location}
resource "azurerm_virtual_network" "vnet" {name = local.virtual_network.namelocation = local.locationresource_group_name = local.resource_group_nameaddress_space = [local.virtual_network.address_space]
}resource "azurerm_network_security_group" "SG" {name = local.security_grouplocation = local.locationresource_group_name = local.resource_group_namedepends_on = [ azurerm_resource_group.RG ]}
resource "azurerm_subnet" "subnet-A" {name = local.subnets[0].nameresource_group_name = local.resource_group_namevirtual_network_name = local.virtual_network.nameaddress_prefixes = local.subnets[0].address_prefixesdepends_on = [ azurerm_virtual_network.vnet ]}
resource "azurerm_subnet" "subnet-B" {name = local.subnets[1].nameresource_group_name = local.resource_group_namevirtual_network_name = local.virtual_network.nameaddress_prefixes = local.subnets[1].address_prefixesdepends_on = [ azurerm_virtual_network.vnet ]}resource "azurerm_subnet_network_security_group_association" "SG1" {subnet_id = azurerm_subnet.subnet-A.idnetwork_security_group_id = azurerm_network_security_group.SG.id}resource "azurerm_subnet_network_security_group_association" "SG2" {subnet_id = azurerm_subnet.subnet-B.idnetwork_security_group_id = azurerm_network_security_group.SG.id}
resource "azurerm_network_interface" "NIC1" {name = "star-NIC1"location = local.locationresource_group_name = local.resource_group_name
ip_configuration {name = "internal"subnet_id = azurerm_subnet.subnet-A.idprivate_ip_address_allocation = "Dynamic"public_ip_address_id = azurerm_public_ip.publicIP.id}depends_on = [ azurerm_subnet.subnet-A ]}
resource "azurerm_public_ip" "publicIP" {name = "StarPublicIP1"resource_group_name = local.resource_group_namelocation = local.locationallocation_method = "Static"
tags = {Dept = "IT"}depends_on = [ azurerm_resource_group.RG ]} - ss
Create Network Security Group, Security Rule (allow RDP) and associate with subnet:
- Network Security Group: Go to terraform.io/documentation and search network security group.
-
resource "azurerm_network_security_group" "example" { name = "acceptanceTestSecurityGroup1" location = azurerm_resource_group.example.location resource_group_name = azurerm_resource_group.example.name security_rule { name = "test123" priority = 100 direction = "Inbound" access = "Allow" protocol = "Tcp" source_port_range = "*" destination_port_range = "*" source_address_prefix = "*" destination_address_prefix = "*" } tags = { environment = "Production" } }
-
- Associate NSG with Subnet:
-
resource "azurerm_subnet_network_security_group_association" "example" { subnet_id = azurerm_subnet.example.id network_security_group_id = azurerm_network_security_group.example.id }
-
- LAB:
-
terraform {required_providers {azurerm = {source = "hashicorp/azurerm"version = "4.8.0"}}}
provider "azurerm" {subscription_id = "bd2ade99-0834-4cfe-bb19-ddf0e89ed9f4"tenant_id = "4b9f3326-b87a-468f-89d4-4c34403eae39"client_id = "363c6475-89bc-4948-9396-6dc6849eeb14"client_secret = "yUR8Q~2w~xi~~i6hUJkw4XCZRPCNVwIpIkTrcaPW"features {}}locals {resource_group_name="Star-RG"location="UK South"security_group="SG"virtual_network ={name="star-Vnet1"address_space="10.0.0.0/16"}subnets=[{name = "subnet1"address_prefixes = ["10.0.1.0/24"]},
{name = "subnet2"address_prefixes = ["10.0.2.0/24"]}]}resource "azurerm_resource_group" "RG" {name = local.resource_group_namelocation = local.location}
resource "azurerm_virtual_network" "vnet" {name = local.virtual_network.namelocation = local.locationresource_group_name = local.resource_group_nameaddress_space = [local.virtual_network.address_space]
}
resource "azurerm_subnet" "subnet-A" {name = local.subnets[0].nameresource_group_name = local.resource_group_namevirtual_network_name = local.virtual_network.nameaddress_prefixes = local.subnets[0].address_prefixesdepends_on = [ azurerm_virtual_network.vnet ]}
resource "azurerm_subnet" "subnet-B" {name = local.subnets[1].nameresource_group_name = local.resource_group_namevirtual_network_name = local.virtual_network.nameaddress_prefixes = local.subnets[1].address_prefixesdepends_on = [ azurerm_virtual_network.vnet ]}
resource "azurerm_network_interface" "NIC1" {name = "star-NIC1"location = local.locationresource_group_name = local.resource_group_name
ip_configuration {name = "internal"subnet_id = azurerm_subnet.subnet-A.idprivate_ip_address_allocation = "Dynamic"public_ip_address_id = azurerm_public_ip.publicIP.id}depends_on = [ azurerm_subnet.subnet-A ]}
resource "azurerm_public_ip" "publicIP" {name = "StarPublicIP1"resource_group_name = local.resource_group_namelocation = local.locationallocation_method = "Static"
tags = {Dept = "IT"}depends_on = [ azurerm_resource_group.RG ]}
resource "azurerm_network_security_group" "NSG" {name = "star-NSG1"location = local.locationresource_group_name = local.resource_group_name
security_rule {name = "NSG-Rule1"priority = 500direction = "Inbound"access = "Allow"protocol = "Tcp"source_port_range = "*"destination_port_range = "3389"source_address_prefix = "*"destination_address_prefix = "*"}
tags = {Name = "NSG"}}resource "azurerm_subnet_network_security_group_association" "NSG-Subnet" {subnet_id = azurerm_subnet.subnet-A.idnetwork_security_group_id = azurerm_network_security_group.NSG.id}
-
- Network Security Group: Go to terraform.io/documentation and search network security group.
Standard Public Load Balancer:
Step1: Create Vnet, VMs, Install IIS:
- Create the environment which is required for load balancer.
- provider.tf
-
terraform {required_providers {azurerm = {source = "hashicorp/azurerm"version = "4.8.0"}}}
provider "azurerm" {subscription_id = "bd2ade99-0834-4cfe-bb19-ddf0e89ed9f4"tenant_id = "4b9f3326-b87a-468f-89d4-4c34403eae39"client_id = "289f6253-b6eb-4930-bc19-3557cad4b72d"client_secret = "LlM8Q~UauskuRH84yA1QDDxc3K0w8sGl1y4ZsbTi"features {}}
-
- variables.tf
-
variable "number_of_subnets" {type = numberdefault = 1validation {condition = var.number_of_subnets < 5error_message = "Value should be less than 5"}}
variable "number_of_machine" {type = number}
-
- vnet.tf
-
locals {resource_group_name="Star-RG"location="UK South"virtual_network ={name="Vnet1"address_space="10.0.0.0/16"}}resource "azurerm_resource_group" "RG" {name = local.resource_group_namelocation = local.location}resource "azurerm_virtual_network" "vnet" {name = local.virtual_network.namelocation = local.locationresource_group_name = local.resource_group_nameaddress_space = [local.virtual_network.address_space]
depends_on = [ azurerm_resource_group.RG ]
}resource "azurerm_subnet" "subnet1" {name = "subnet1"resource_group_name = local.resource_group_namevirtual_network_name = local.virtual_network.nameaddress_prefixes = ["10.0.1.0/24"]depends_on = [ azurerm_virtual_network.vnet ]}resource "azurerm_network_security_group" "NSG" {name = "NSG1"location = local.locationresource_group_name = local.resource_group_namesecurity_rule {name = "rule1"priority = 100direction = "Inbound"access = "Allow"protocol = "Tcp"source_port_range = "*"destination_port_range = "3389"source_address_prefix = "*"destination_address_prefix = "*"}
security_rule {name = "rule2"priority = 101direction = "Inbound"access = "Allow"protocol = "Tcp"source_port_range = "*"destination_port_range = "80"source_address_prefix = "*"destination_address_prefix = "*"}depends_on = [ azurerm_resource_group.RG ]}
resource "azurerm_subnet_network_security_group_association" "NSGAssociation" {subnet_id = azurerm_subnet.subnet1.idnetwork_security_group_id=azurerm_network_security_group.NSG.id}
resource "azurerm_network_interface" "NIC" {count = var.number_of_machinename = "NIC${count.index}"location = local.locationresource_group_name = local.resource_group_name
ip_configuration {name = "internal"subnet_id = azurerm_subnet.subnet1.idprivate_ip_address_allocation = "Dynamic"}depends_on = [ azurerm_subnet.subnet1 ]}
-
- availabilityset.tf
-
resource "azurerm_availability_set" "star-AS" {name = "star-AS"location = local.locationresource_group_name = local.resource_group_nameplatform_fault_domain_count = 2platform_update_domain_count = 3
tags = {name = "availability_set"}depends_on = [ azurerm_resource_group.RG ]}
-
- iis.tf (install_iis.ps1 file is located in the same folder as all these .tf files) open a text file named install_iis.ps1 and paste this script
Install-WindowsFeature -name Web-Server -IncludeManagementTools
-
resource "azurerm_storage_account" "starstorage1" {name = "starstorage1"resource_group_name = local.resource_group_namelocation = local.locationaccount_tier = "Standard"account_replication_type = "LRS"account_kind = "StorageV2"
depends_on = [ azurerm_resource_group.RG ]}
resource "azurerm_storage_container" "container" {name = "starcontainer1"storage_account_name = "starstorage1"container_access_type = "blob"depends_on = [ azurerm_storage_account.starstorage1 ]}
resource "azurerm_storage_blob" "iisconfig" {name = "install_iis.ps1"storage_account_name = "starstorage1"storage_container_name = "starcontainer1"type = "Block"source = "install_iis.ps1"depends_on = [ azurerm_storage_container.container ]}
resource "azurerm_virtual_machine_extension" "starextension" {count = var.number_of_machinename = "extension${count.index}"virtual_machine_id = azurerm_windows_virtual_machine.VM[count.index].idpublisher = "Microsoft.Compute"type = "CustomScriptExtension"type_handler_version = "1.10"
settings = <<SETTINGS{"fileUris": ["https://${azurerm_storage_account.starstorage1.name}.blob.core.windows.net/starcontainer1/install_iis.ps1"],"commandToExecute": "powershell -ExecutionPolicy Unrestricted -file install_iis.ps1"}SETTINGS
tags = {environment = "Production"}}
-
- vm.tf
-
resource "azurerm_windows_virtual_machine" "VM" {count = var.number_of_machinename = "VM${count.index}"resource_group_name = local.resource_group_namelocation = local.locationsize = "Standard_DS1_v2"admin_username = "abdul"admin_password = "India123456789"availability_set_id = azurerm_availability_set.star-AS.idnetwork_interface_ids = [azurerm_network_interface.NIC[count.index].id,]
os_disk {caching = "ReadWrite"storage_account_type = "Standard_LRS"}
source_image_reference {publisher = "MicrosoftWindowsServer"offer = "WindowsServer"sku = "2016-Datacenter"version = "latest"}depends_on = [ azurerm_network_interface.NIC, azurerm_resource_group.RG,azurerm_availability_set.star-AS ]}
-
- #terraform init
- #terraform plan -out vm.tfplan
- #terraform apply "vm.tfplan"
Step2: Create Public IP, Create Standard Load Balancer, create FrontendIP, Associate with public IP
- lb.tf
#creating public IP for load balancer#creating public IP for load balancerresource "azurerm_public_ip" "loadbalancerIP" {name = "loadbalancerIP"resource_group_name = local.resource_group_namelocation = local.locationallocation_method = "Static"sku = "Standard"
tags = {environment = "webserver"}}
#creating Basic Load Balancer & frontendIP association with public IPresource "azurerm_lb" "lb" {name = "StarLoadBalancer"location = local.locationresource_group_name = local.resource_group_namesku = "Standard"sku_tier = "Regional"
frontend_ip_configuration {name = "FrontendIP"public_ip_address_id = azurerm_public_ip.loadbalancerIP.id}depends_on = [ azurerm_public_ip.loadbalancerIP ]}
#creating backend poolresource "azurerm_lb_backend_address_pool" "backendpool" {loadbalancer_id = azurerm_lb.lb.idname = "Basicbackendpool"depends_on = [ azurerm_lb.lb ]}
#Adding VMs in backend poolresource "azurerm_lb_backend_address_pool_address" "addvm" {count = var.number_of_machinename = "VM${count.index}"backend_address_pool_id = azurerm_lb_backend_address_pool.backendpool.idvirtual_network_id = azurerm_virtual_network.vnet.idip_address = azurerm_network_interface.NIC[count.index].private_ip_addressdepends_on = [ azurerm_lb_backend_address_pool.backendpool,azurerm_network_interface.NIC ]}#Creating health probe which will check the health of VMs attached in backendpoolresource "azurerm_lb_probe" "starHP" {loadbalancer_id = azurerm_lb.lb.idname = "healthprobe"port = 80protocol = "Tcp"depends_on = [ azurerm_lb.lb ]}
#Creating LB ruleresource "azurerm_lb_rule" "LBRule" {loadbalancer_id = azurerm_lb.lb.idname = "LBRule"protocol = "Tcp"frontend_port = 80backend_port = 80frontend_ip_configuration_name = "FrontendIP"backend_address_pool_ids = [azurerm_lb_backend_address_pool.backendpool.id]probe_id = azurerm_lb_probe.starHP.iddepends_on = [ azurerm_lb.lb ]} - #terraform plan -out lb.tfplan
- #terraform apply "lb.tfplan"
Step3: Add Targets in Backend pool & Create LB Rule, Create Health Probe, Create Inbound & Outbound rule
- To add targets in backend pool, go to terraform.io/azure/documentation/search load balancer, click azurerm_lb_backend_address_pool_address, search azurerm_lb_probe, LB Rule,
- Add the below code in lb.tf in step 1
-
#Adding VMs in backend poolresource "azurerm_lb_backend_address_pool_address" "addvm" {count = var.number_of_machinename = "VM${count.index}"backend_address_pool_id = azurerm_lb_backend_address_pool.backendpool.idvirtual_network_id = azurerm_virtual_network.vnet.idip_address = azurerm_network_interface.NIC[count.index].private_ip_addressdepends_on = [ azurerm_lb_backend_address_pool.backendpool,azurerm_network_interface.NIC ]}#Creating health probe which will check the health of VMs attached in backendpoolresource "azurerm_lb_probe" "starHP" {loadbalancer_id = azurerm_lb.lb.idname = "healthprobe"port = 80protocol = "Tcp"depends_on = [ azurerm_lb.lb ]}
#Creating LB ruleresource "azurerm_lb_rule" "LBRule" {loadbalancer_id = azurerm_lb.lb.idname = "LBRule"protocol = "Tcp"frontend_port = 80backend_port = 80frontend_ip_configuration_name = "FrontendIP"backend_address_pool_ids = [azurerm_lb_backend_address_pool.backendpool.id]probe_id = azurerm_lb_probe.starHP.iddepends_on = [ azurerm_lb.lb ]} - #terraform plan -out lb.tfplan
- #terraform apply "lb.tfplan"
Complete Code for Standard Public Load Balancer for the above Step 1, 2, 3
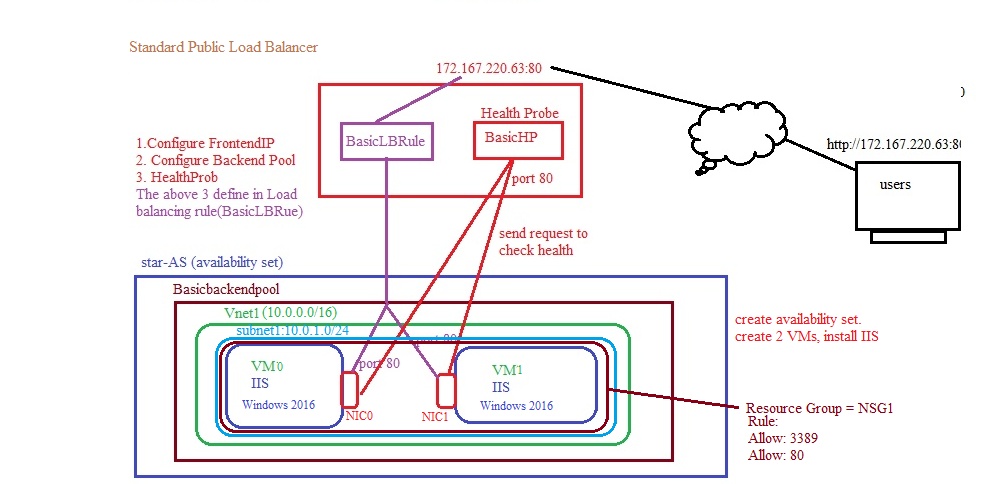
- provider.tf
-
terraform {required_providers {azurerm = {source = "hashicorp/azurerm"version = "4.8.0"}}}
provider "azurerm" {subscription_id = "bd2ade99-0834-4cfe-bb19-ddf0e89ed9f4"tenant_id = "4b9f3326-b87a-468f-89d4-4c34403eae39"client_id = "289f6253-b6eb-4930-bc19-3557cad4b72d"client_secret = "LlM8Q~UauskuRH84yA1QDDxc3K0w8sGl1y4ZsbTi"features {}}
-
- variables.tf
-
variable "number_of_subnets" {type = numberdefault = 1validation {condition = var.number_of_subnets < 5error_message = "Value should be less than 5"}}
variable "number_of_machine" {type = number}
-
- vnet.tf
-
locals {resource_group_name="Star-RG"location="UK South"virtual_network ={name="Vnet1"address_space="10.0.0.0/16"}}resource "azurerm_resource_group" "RG" {name = local.resource_group_namelocation = local.location}resource "azurerm_virtual_network" "vnet" {name = local.virtual_network.namelocation = local.locationresource_group_name = local.resource_group_nameaddress_space = [local.virtual_network.address_space]
depends_on = [ azurerm_resource_group.RG ]
}resource "azurerm_subnet" "subnet1" {name = "subnet1"resource_group_name = local.resource_group_namevirtual_network_name = local.virtual_network.nameaddress_prefixes = ["10.0.1.0/24"]depends_on = [ azurerm_virtual_network.vnet ]}resource "azurerm_network_security_group" "NSG" {name = "NSG1"location = local.locationresource_group_name = local.resource_group_namesecurity_rule {name = "rule1"priority = 100direction = "Inbound"access = "Allow"protocol = "Tcp"source_port_range = "*"destination_port_range = "3389"source_address_prefix = "*"destination_address_prefix = "*"}
security_rule {name = "rule2"priority = 101direction = "Inbound"access = "Allow"protocol = "Tcp"source_port_range = "*"destination_port_range = "80"source_address_prefix = "*"destination_address_prefix = "*"}depends_on = [ azurerm_resource_group.RG ]}
resource "azurerm_subnet_network_security_group_association" "NSGAssociation" {subnet_id = azurerm_subnet.subnet1.idnetwork_security_group_id=azurerm_network_security_group.NSG.id}
resource "azurerm_network_interface" "NIC" {count = var.number_of_machinename = "NIC${count.index}"location = local.locationresource_group_name = local.resource_group_name
ip_configuration {name = "internal"subnet_id = azurerm_subnet.subnet1.idprivate_ip_address_allocation = "Dynamic"}depends_on = [ azurerm_subnet.subnet1 ]}
-
- availabilityset.tf
-
resource "azurerm_availability_set" "star-AS" {name = "star-AS"location = local.locationresource_group_name = local.resource_group_nameplatform_fault_domain_count = 2platform_update_domain_count = 3
tags = {name = "availability_set"}depends_on = [ azurerm_resource_group.RG ]}
-
- iis.tf
-
resource "azurerm_storage_account" "starstorage1" {name = "starstorage1"resource_group_name = local.resource_group_namelocation = local.locationaccount_tier = "Standard"account_replication_type = "LRS"account_kind = "StorageV2"
depends_on = [ azurerm_resource_group.RG ]}
resource "azurerm_storage_container" "container" {name = "starcontainer1"storage_account_name = "starstorage1"container_access_type = "blob"depends_on = [ azurerm_storage_account.starstorage1 ]}
resource "azurerm_storage_blob" "iisconfig" {name = "install_iis.ps1"storage_account_name = "starstorage1"storage_container_name = "starcontainer1"type = "Block"source = "install_iis.ps1"depends_on = [ azurerm_storage_container.container ]}
resource "azurerm_virtual_machine_extension" "starextension" {count = var.number_of_machinename = "extension${count.index}"virtual_machine_id = azurerm_windows_virtual_machine.VM[count.index].idpublisher = "Microsoft.Compute"type = "CustomScriptExtension"type_handler_version = "1.10"
settings = <<SETTINGS{"fileUris": ["https://${azurerm_storage_account.starstorage1.name}.blob.core.windows.net/starcontainer1/install_iis.ps1"],"commandToExecute": "powershell -ExecutionPolicy Unrestricted -file install_iis.ps1"}SETTINGS
tags = {environment = "Production"}}
-
- vm.tf
-
resource "azurerm_windows_virtual_machine" "VM" {count = var.number_of_machinename = "VM${count.index}"resource_group_name = local.resource_group_namelocation = local.locationsize = "Standard_DS1_v2"admin_username = "abdul"admin_password = "India123456789"availability_set_id = azurerm_availability_set.star-AS.idnetwork_interface_ids = [azurerm_network_interface.NIC[count.index].id,]
os_disk {caching = "ReadWrite"storage_account_type = "Standard_LRS"}
source_image_reference {publisher = "MicrosoftWindowsServer"offer = "WindowsServer"sku = "2016-Datacenter"version = "latest"}depends_on = [ azurerm_network_interface.NIC, azurerm_resource_group.RG,azurerm_availability_set.star-AS ]}
-
- lb.tf
#creating public IP for load balancer#creating public IP for load balancerresource "azurerm_public_ip" "loadbalancerIP" {name = "loadbalancerIP"resource_group_name = local.resource_group_namelocation = local.locationallocation_method = "Static"sku = "Standard"
tags = {environment = "webserver"}}
#creating Basic Load Balancer & frontendIP association with public IPresource "azurerm_lb" "lb" {name = "StarLoadBalancer"location = local.locationresource_group_name = local.resource_group_namesku = "Standard"sku_tier = "Regional"
frontend_ip_configuration {name = "FrontendIP"public_ip_address_id = azurerm_public_ip.loadbalancerIP.id}depends_on = [ azurerm_public_ip.loadbalancerIP ]}
#creating backend poolresource "azurerm_lb_backend_address_pool" "backendpool" {loadbalancer_id = azurerm_lb.lb.idname = "Basicbackendpool"depends_on = [ azurerm_lb.lb ]}
#Adding VMs in backend poolresource "azurerm_lb_backend_address_pool_address" "addvm" {count = var.number_of_machinename = "VM${count.index}"backend_address_pool_id = azurerm_lb_backend_address_pool.backendpool.idvirtual_network_id = azurerm_virtual_network.vnet.idip_address = azurerm_network_interface.NIC[count.index].private_ip_addressdepends_on = [ azurerm_lb_backend_address_pool.backendpool,azurerm_network_interface.NIC ]}#Creating health probe which will check the health of VMs attached in backendpoolresource "azurerm_lb_probe" "starHP" {loadbalancer_id = azurerm_lb.lb.idname = "healthprobe"port = 80protocol = "Tcp"depends_on = [ azurerm_lb.lb ]}
#Creating LB ruleresource "azurerm_lb_rule" "LBRule" {loadbalancer_id = azurerm_lb.lb.idname = "LBRule"protocol = "Tcp"frontend_port = 80backend_port = 80frontend_ip_configuration_name = "FrontendIP"backend_address_pool_ids = [azurerm_lb_backend_address_pool.backendpool.id]probe_id = azurerm_lb_probe.starHP.iddepends_on = [ azurerm_lb.lb ]}resource "azurerm_lb_backend_address_pool_address" "addvm" {count = var.number_of_machinename = "VM${count.index}"backend_address_pool_id = azurerm_lb_backend_address_pool.backendpool.idvirtual_network_id = azurerm_virtual_network.vnet.idip_address = azurerm_network_interface.NIC[count.index].private_ip_addressdepends_on = [ azurerm_lb_backend_address_pool.backendpool,azurerm_network_interface.NIC ]}#Creating health probe which will check the health of VMs attached in backendpoolresource "azurerm_lb_probe" "starHP" {loadbalancer_id = azurerm_lb.lb.idname = "healthprobe"port = 80protocol = "Tcp"depends_on = [ azurerm_lb.lb ]}
#Creating LB ruleresource "azurerm_lb_rule" "LBRule" {loadbalancer_id = azurerm_lb.lb.idname = "LBRule"protocol = "Tcp"frontend_port = 80backend_port = 80frontend_ip_configuration_name = "FrontendIP"backend_address_pool_ids = [azurerm_lb_backend_address_pool.backendpool.id]probe_id = azurerm_lb_probe.starHP.iddepends_on = [ azurerm_lb.lb ]} - #terraform init
- #terraform plan -out lb.tfplan
- #terraform apply "lb.tfplan"
Traffic Manager:
Distributing traffic based on Priority routing method with portal:
- Create Traffic Manager profile using Prority routing method
- Go to All Services/Networking/Load Balancer/Traffic Manager create
- Name: startrafficmgr
- Routing Method: Priority
- Subscription & Resource Group:
- Resource Group Location: Grayed out as Traffic Manager is not location specific.
- Endpoints: Create 2 Web App in two different regions as primary and failover, if primary is down then traffic goes to failover (secondary application).
- Deployment: Go to web app blade/development tools/App Service Editor/open editor/WWWROOT/
- Traffic Manager Profile Configuration:
- Go to Traffic Manager Blade/Settings/Configuration
- Routing Method: Priority
- Endpoint moitor settings: HTTPS
- Port: 443
- Path: /
- Custom Header Settings:
- Endpoints: +Add
- Type: Azure endpoint
- Name: primary
- Target resource type: App Service
- Target resource: starapp1
- priority : 1
- Customer Header Settings: host: copy and paste url from app1
- +Add (add second app)
- Type: Azure endpoint
- Name: secondary
- Target resource type: App Service
- Target resource: starapp2
- priority : 1
- Customer Header Settings: host: copy and paste url from app2
- Test: copy url from traffic manger overview and paste it in browser: Traffic goes to priority 1 site (starapp1), disable starapp1 and now traffic goes to secondary.
Distributing traffic based on Priority routing method with terraform:

- provider.tf
-
terraform {required_providers {azurerm = {source = "hashicorp/azurerm"version = "4.8.0"}}}
provider "azurerm" {subscription_id = "bd2ade99-0834-4cfe-bb19-ddf0e89ed9f4"tenant_id = "4b9f3326-b87a-468f-89d4-4c34403eae39"client_id = "289f6253-b6eb-4930-bc19-3557cad4b72d"client_secret = "LlM8Q~UauskuRH84yA1QDDxc3K0w8sGl1y4ZsbTi"features {}}
-
- Create 2 Web Apps (starapp1, starapp2), two app plans (star-plan1, star-plan2) in two different regions (uk south, central canada)
- Go to terraform.io/azure/documentation/search service plan, app service,
-
app.tf#creating resource groupresource "azurerm_resource_group" "RG" {name = "star-RG"location = "UK South"}
#creating app plan1resource "azurerm_service_plan" "plan1" {name = "star-plan1"resource_group_name = "star-RG"location = "uk South"os_type = "Windows"sku_name = "S1"depends_on = [ azurerm_resource_group.RG ]}
#creating app1 in plan1resource "azurerm_windows_web_app" "app1" {name = "starapp1"resource_group_name = "star-RG"location = "UK South"service_plan_id = azurerm_service_plan.plan1.id
site_config {application_stack {current_stack = "dotnet"dotnet_version = "v8.0"}}depends_on = [ azurerm_service_plan.plan1 ]}
#creating app plan2resource "azurerm_service_plan" "plan2" {name = "star-plan2"resource_group_name = "star-RG"location = "Canada Central"os_type = "Windows"sku_name = "S1"depends_on = [ azurerm_resource_group.RG ]}
#creating app2 in plan2resource "azurerm_windows_web_app" "app2" {name = "starapp2"resource_group_name = "star-RG"location = "Canada Central"service_plan_id = azurerm_service_plan.plan2.id
site_config {application_stack {current_stack = "dotnet"dotnet_version = "v8.0"}}depends_on = [ azurerm_service_plan.plan2 ]}Create 4 resources.#terraform init#terraform plan -out app.tfplan#terrafor apply "app.tfplan"
- Deploy code or manually create html pages in both webapps
- Go to starapp1/development tools/app service editor/open editor/WWWROOT/write code <h1> Primary Site - UK South </h1>
- Go to starapp2/development tools/app service editor/open editor/WWWROOT/write code <h1> Failover Site - Canada Central </h1>
- Click on overview, copy url and paste it in browser
- Create Traffic Manager Profile and Add endpoints primary & secondary with priorty 1 & 2
- Go to terraform.io/azure/documentation/search traffic manager, traffic manager azure endpoint,
- tm.tf
-
resource "azurerm_traffic_manager_profile" "tm" {name = "startrafficmgr"resource_group_name = "star-RG"traffic_routing_method = "Priority"
dns_config {relative_name = "startrafficmgr"ttl = 100}
monitor_config {protocol = "HTTPS"port = 443path = "/"interval_in_seconds = 30timeout_in_seconds = 9tolerated_number_of_failures = 3}depends_on = [ azurerm_resource_group.RG ]}resource "azurerm_traffic_manager_azure_endpoint" "primary" {name = "primary"profile_id = azurerm_traffic_manager_profile.tm.idalways_serve_enabled = true#enter routing method prioritypriority = 1#Enter target reource starapp1 so traffic goes to primary apptarget_resource_id = azurerm_windows_web_app.app1.idcustom_header {name = "host"#this value can be get after apps deployed from overview, or can be retrievevalue = "${azurerm_windows_web_app.app1.name}.azurewebsites.net"}depends_on = [ azurerm_traffic_manager_profile.tm,azurerm_windows_web_app.app1 ]}
resource "azurerm_traffic_manager_azure_endpoint" "failover" {name = "faiover"profile_id = azurerm_traffic_manager_profile.tm.idalways_serve_enabled = true#enter routing method prioritypriority = 2#Enter target reource starapp2 so traffic goes to failover apptarget_resource_id = azurerm_windows_web_app.app2.idcustom_header {name = "host"#this value can be get after apps deployed from overview, or can be retrievevalue = "${azurerm_windows_web_app.app2.name}.azurewebsites.net"}depends_on = [ azurerm_traffic_manager_profile.tm,azurerm_windows_web_app.app2 ]}
- Testing: copy traffic manager DNS name: http://startrafficmgr.trafficmanager.net and paste it in browser, primary site will appear,
- stop starapp1 and check, now it goes to failover site after few minutes.
- Distributing traffic based on Performance routing method with terraform:
- Distributing traffic based on Geographic routing method with terraform:
- Distributing traffic based on Weighted routing method with terraform:
- Distributing traffic based on Multivalue routing method with terraform:
- Distributing traffic based on Subnet routing method with terraform:
Azure Public DNS:
- In the above Standard Public Load Balancer where we have two web servers intalled IIS and they are attached to backend pool,
- Frontend IP, health probe, public IP, inbound/outbound rules are created and attached with load balancer. Users will hit public IP of load balancer and their request will be distributed to webservers accordingly.
- With the help of public DNS users will use URL instead of public IP. Public DNS Domain will resolve name to IP address. Usually domain registrar provides DNS service.
- Domain Purchase: Custom Domains can also be purchase in Azure, search App Service Domain or Go to All services/Web & Mobile/Application infrastructure/App Service Domains.
- If domain is already purchased and want to create DNS Zone in Azure which will be use for name resolution. copy name servers from Azure DNS and paste it in domain registrar panel.
Create Azure Public DNS Zone with portal:
- search DNS zones and + create
- Basics:
- select subscription, RG,
- Name= stardistributors.co.uk
- Resource Group Location: UK South
- DNS Zone Editor:;A DNS zone file is a text file that contains details of every Domain Name System (DNS) record in the zone. It follows a standard format, making it suitable for transferring DNS records between DNS systems. Using a zone file is a quick, reliable and convenient way to transfer a DNS zone into or out of Azure DNS. It's important to note that files should not exceed 10,000 lines, and the DNS zone import feature currently supports a maximum of 799 record sets
- In DNS zone editor you can enter zone records, either bowse file or paste the records.
- Tags: Enter tag
- Review and create.
DNS Zone Blade:
- Overview:
- Activity Log:
- Access Control (IAM):
- Tags:
- Diagnose and solve problems:
- Settings:
- Properties:
- Locks:
- DNS Management:
- Recordsets: By default there are 2 recor sets, NS (nameserver), SOA (Email), copy NS record sets and paste it in authoritative name server portal.
- ns1-06.azure-dns.com.
- ns2-06.azure-dns.net.
- ns3-06.azure-dns.org.
- ns4-06.azure-dns.info.
- Monitoring:
- Alerts:
- Metrics:
- Automation:
- CLI/PS
- Tasks:
- Export Teplate
- Help:
Authoritative DNS Server: (one.com, go daddy)
Login to authoritative DNS server and go to DNS Nameservers and click change to custom nameservers- add the above copied nameservers of Azure. (remove . at the end)
- ns1-06.azure-dns.com
- ns2-06.azure-dns.net
- Now click DNS Records and select txt record for verification and ownership confirmation.
-
After adding txt record go back to azure and click verify and once it is verified custom domain is configured.
- You can make this custom domain as primary.
Create Azure Public DNS Zone & Record set using Terraform:
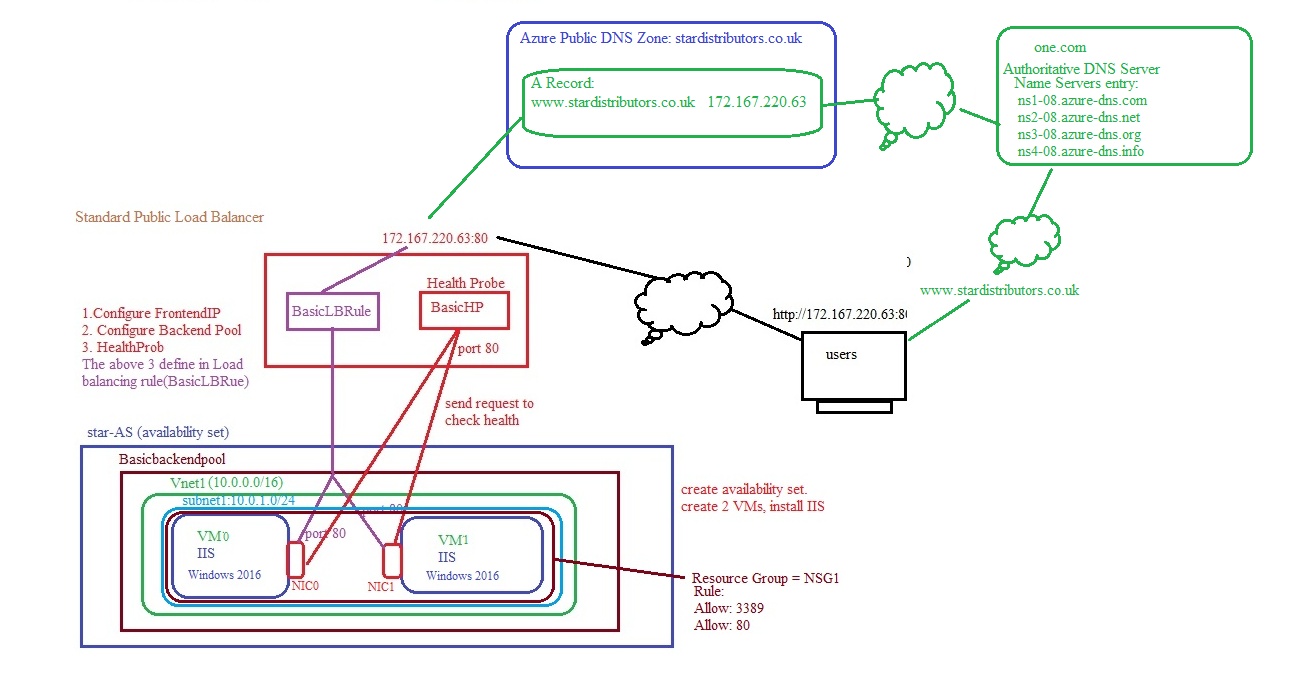
- Go to terraform.io/azure/documentation/ search dns zone, dns a record.
- dns.tf
-
resource "azurerm_dns_zone" "publicdns" {name = "stardistributors.co.uk"resource_group_name = local.resource_group_namedepends_on = [ azurerm_resource_group.RG ]}output "Name-Servers" {value = azurerm_dns_zone.publicdns.name_servers}
resource "azurerm_dns_a_record" "dns_a_record" {name = "www"zone_name = azurerm_dns_zone.publicdns.nameresource_group_name = local.resource_group_namettl = 300records = ["azurerm_public_ip, loadbalancerIP.ip_address"]}
-
- provider.tf
-
terraform {required_providers {azurerm = {source = "hashicorp/azurerm"version = "4.8.0"}}}
provider "azurerm" {subscription_id = "bd2ade99-0834-4cfe-bb19-ddf0e89ed9f4"tenant_id = "4b9f3326-b87a-468f-89d4-4c34403eae39"client_id = "289f6253-b6eb-4930-bc19-3557cad4b72d"client_secret = "LlM8Q~UauskuRH84yA1QDDxc3K0w8sGl1y4ZsbTi"features {}}
-
- variables.tf
-
variable "number_of_subnets" {type = numberdefault = 1validation {condition = var.number_of_subnets < 5error_message = "Value should be less than 5"}}
variable "number_of_machine" {type = number}
-
- vnet.tf
-
locals {resource_group_name="Star-RG"location="UK South"virtual_network ={name="Vnet1"address_space="10.0.0.0/16"}}resource "azurerm_resource_group" "RG" {name = local.resource_group_namelocation = local.location}resource "azurerm_virtual_network" "vnet" {name = local.virtual_network.namelocation = local.locationresource_group_name = local.resource_group_nameaddress_space = [local.virtual_network.address_space]
depends_on = [ azurerm_resource_group.RG ]
}resource "azurerm_subnet" "subnet1" {name = "subnet1"resource_group_name = local.resource_group_namevirtual_network_name = local.virtual_network.nameaddress_prefixes = ["10.0.1.0/24"]depends_on = [ azurerm_virtual_network.vnet ]}resource "azurerm_network_security_group" "NSG" {name = "NSG1"location = local.locationresource_group_name = local.resource_group_namesecurity_rule {name = "rule1"priority = 100direction = "Inbound"access = "Allow"protocol = "Tcp"source_port_range = "*"destination_port_range = "3389"source_address_prefix = "*"destination_address_prefix = "*"}
security_rule {name = "rule2"priority = 101direction = "Inbound"access = "Allow"protocol = "Tcp"source_port_range = "*"destination_port_range = "80"source_address_prefix = "*"destination_address_prefix = "*"}depends_on = [ azurerm_resource_group.RG ]}
resource "azurerm_subnet_network_security_group_association" "NSGAssociation" {subnet_id = azurerm_subnet.subnet1.idnetwork_security_group_id=azurerm_network_security_group.NSG.id}
resource "azurerm_network_interface" "NIC" {count = var.number_of_machinename = "NIC${count.index}"location = local.locationresource_group_name = local.resource_group_name
ip_configuration {name = "internal"subnet_id = azurerm_subnet.subnet1.idprivate_ip_address_allocation = "Dynamic"}depends_on = [ azurerm_subnet.subnet1 ]}
-
- availabilityset.tf
-
resource "azurerm_availability_set" "star-AS" {name = "star-AS"location = local.locationresource_group_name = local.resource_group_nameplatform_fault_domain_count = 2platform_update_domain_count = 3
tags = {name = "availability_set"}depends_on = [ azurerm_resource_group.RG ]}
-
- iis.tf
-
resource "azurerm_storage_account" "starstorage1" {name = "starstorage1"resource_group_name = local.resource_group_namelocation = local.locationaccount_tier = "Standard"account_replication_type = "LRS"account_kind = "StorageV2"
depends_on = [ azurerm_resource_group.RG ]}
resource "azurerm_storage_container" "container" {name = "starcontainer1"storage_account_name = "starstorage1"container_access_type = "blob"depends_on = [ azurerm_storage_account.starstorage1 ]}
resource "azurerm_storage_blob" "iisconfig" {name = "install_iis.ps1"storage_account_name = "starstorage1"storage_container_name = "starcontainer1"type = "Block"source = "install_iis.ps1"depends_on = [ azurerm_storage_container.container ]}
resource "azurerm_virtual_machine_extension" "starextension" {count = var.number_of_machinename = "extension${count.index}"virtual_machine_id = azurerm_windows_virtual_machine.VM[count.index].idpublisher = "Microsoft.Compute"type = "CustomScriptExtension"type_handler_version = "1.10"
settings = <<SETTINGS{"fileUris": ["https://${azurerm_storage_account.starstorage1.name}.blob.core.windows.net/starcontainer1/install_iis.ps1"],"commandToExecute": "powershell -ExecutionPolicy Unrestricted -file install_iis.ps1"}SETTINGS
tags = {environment = "Production"}}
-
- vm.tf
-
resource "azurerm_windows_virtual_machine" "VM" {count = var.number_of_machinename = "VM${count.index}"resource_group_name = local.resource_group_namelocation = local.locationsize = "Standard_DS1_v2"admin_username = "abdul"admin_password = "India123456789"availability_set_id = azurerm_availability_set.star-AS.idnetwork_interface_ids = [azurerm_network_interface.NIC[count.index].id,]
os_disk {caching = "ReadWrite"storage_account_type = "Standard_LRS"}
source_image_reference {publisher = "MicrosoftWindowsServer"offer = "WindowsServer"sku = "2016-Datacenter"version = "latest"}depends_on = [ azurerm_network_interface.NIC, azurerm_resource_group.RG,azurerm_availability_set.star-AS ]}
-
- lb.tf
#creating public IP for load balancer#creating public IP for load balancerresource "azurerm_public_ip" "loadbalancerIP" {name = "loadbalancerIP"resource_group_name = local.resource_group_namelocation = local.locationallocation_method = "Static"sku = "Standard"
tags = {environment = "webserver"}}
#creating Basic Load Balancer & frontendIP association with public IPresource "azurerm_lb" "lb" {name = "StarLoadBalancer"location = local.locationresource_group_name = local.resource_group_namesku = "Standard"sku_tier = "Regional"
frontend_ip_configuration {name = "FrontendIP"public_ip_address_id = azurerm_public_ip.loadbalancerIP.id}depends_on = [ azurerm_public_ip.loadbalancerIP ]}
#creating backend poolresource "azurerm_lb_backend_address_pool" "backendpool" {loadbalancer_id = azurerm_lb.lb.idname = "Basicbackendpool"depends_on = [ azurerm_lb.lb ]}
#Adding VMs in backend poolresource "azurerm_lb_backend_address_pool_address" "addvm" {count = var.number_of_machinename = "VM${count.index}"backend_address_pool_id = azurerm_lb_backend_address_pool.backendpool.idvirtual_network_id = azurerm_virtual_network.vnet.idip_address = azurerm_network_interface.NIC[count.index].private_ip_addressdepends_on = [ azurerm_lb_backend_address_pool.backendpool,azurerm_network_interface.NIC ]}#Creating health probe which will check the health of VMs attached in backendpoolresource "azurerm_lb_probe" "starHP" {loadbalancer_id = azurerm_lb.lb.idname = "healthprobe"port = 80protocol = "Tcp"depends_on = [ azurerm_lb.lb ]}
#Creating LB ruleresource "azurerm_lb_rule" "LBRule" {loadbalancer_id = azurerm_lb.lb.idname = "LBRule"protocol = "Tcp"frontend_port = 80backend_port = 80frontend_ip_configuration_name = "FrontendIP"backend_address_pool_ids = [azurerm_lb_backend_address_pool.backendpool.id]probe_id = azurerm_lb_probe.starHP.iddepends_on = [ azurerm_lb.lb ]}resource "azurerm_lb_backend_address_pool_address" "addvm" {count = var.number_of_machinename = "VM${count.index}"backend_address_pool_id = azurerm_lb_backend_address_pool.backendpool.idvirtual_network_id = azurerm_virtual_network.vnet.idip_address = azurerm_network_interface.NIC[count.index].private_ip_addressdepends_on = [ azurerm_lb_backend_address_pool.backendpool,azurerm_network_interface.NIC ]}#Creating health probe which will check the health of VMs attached in backendpoolresource "azurerm_lb_probe" "starHP" {loadbalancer_id = azurerm_lb.lb.idname = "healthprobe"port = 80protocol = "Tcp"depends_on = [ azurerm_lb.lb ]}
#Creating LB ruleresource "azurerm_lb_rule" "LBRule" {loadbalancer_id = azurerm_lb.lb.idname = "LBRule"protocol = "Tcp"frontend_port = 80backend_port = 80frontend_ip_configuration_name = "FrontendIP"backend_address_pool_ids = [azurerm_lb_backend_address_pool.backendpool.id]probe_id = azurerm_lb_probe.starHP.iddepends_on = [ azurerm_lb.lb ]} - #terraform init
- #terraform plan -out dns.tfplan
- #terraform apply "dns.tfplan"
- Name Servers has been displayed, copy and paste it in authoritative dns server portal.
- The following recources has been created.
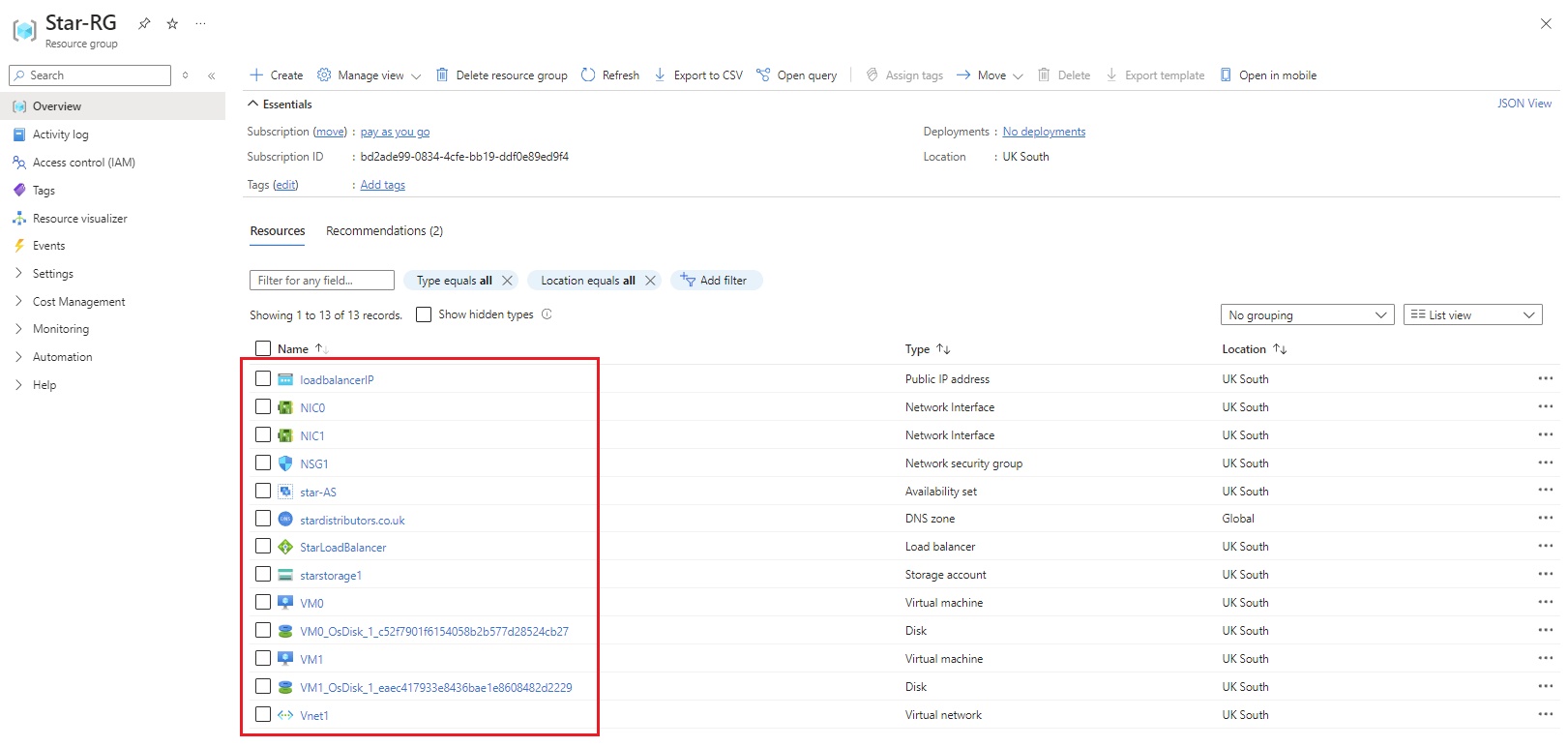
- check in browser www.stardistributors.co.uk
Application Gateway:
Overview:
- It works as Load Balancer, Application Gateway distributes traffic on content based/path based traffic like in URL www.abc.com/videos and www.abc.com/Audios, it distributes the traffic accordingly.
- It provides load balancing & Web Application Firewall (LB + WAF): It has four version, Basic, Standard v2, WAF v2
- It provides the following features:
- Content based routing: It distribute the traffic to endpoint based on URL path www.abc.com/videos and www.abc.com/Audios
- SSL off loading /SSL Termination: It encrypt and decrypt the data
- End to End SSL Termination:
- HTTP to HTTPS: It uses these two protocols.
- Multisite hosting: it supports multisite hosting.
- Cookies bases session affinity:
- Connection Draining:
- WAF : Web Application Firewall:
- It can be use for load balancing and firewall as well.
Creating Application Gateway with portal:
- s
- Create a RG (star-RG), Virtual Network (Vnet1 (10.0.0.0/16), subnet-VM (10.0.1.0/24), subnet-AG (10.0.10.0/24), security group (star-SG) allow 3389,80,443 ports.
- Two Virtual Machines in subnet-VM namely image1 & video1, install IIS and make two html pages.
- Create application gateway/Go to Networking/Load Balancer / Application Gteway/ Create
- Basics:
- Subscription & Resource Group : star-RG
- Name: star-AG
- Region: UK South
- Tier:
- Basic:
- Standard V2
- WAF2:
- Enable Autoscaling: yes/No
- Instance count: 1, Enter based on requirement
- Availability Zone: 1,2,3 (select check boxes), AG will be deployed on selected zones.
- IP Address type: IPv4 or both IPv4 & IPv6
- HTTP2: HTTP/2 protocol support is available to clients that connect to application gateway listeners only. The communication to backend server pools is over HTTP/1.1. Disabled
- WAF Policy: Choose a WAF Policy from the selected subscription and location.You can also create a new WAF policy. (wafpolicy1)
- Configure Virtual Network: Vnet1, subnet-AG
- Frontend:
- Frontend IP Address type:
- Public (Add new: AGPublicIP), SKU=Standard, Assignent = Static
- Private
- Both
- Frontend IP Address type:
- Backends:
- Add a backendpool:
- name:ImageServerPool
- Targets: you will have 4 options [IP addres or FQDN, virtual machine, VMSS, App Services] Virtual Machine, image2 (In LB there is only two options, VM & VMSS)
- Add a backendpool
- name:VideoServerPool
- Targets:you will have 4 options [IP addres or FQDN, virtual machine, VMSS, App Services] Virtual Machine, video2 (In LB there is only two options, VM & VMSS)
- Configuration:
- Routing Rules:
- Add a Routing Rule:
- Rule Name = AGRule1
- Priority = 1, Rule priority defines the order in which the rules are processed.
- Listener: A listener “listens” on a specified port and IP address for traffic that uses a specified protocol. If the listener criteria are met, the application gateway will apply this routing rule. We are instructing listener if public ip with http protocol on port 80 then send traffic to backend target.
- Listener Name: AGListener1
- Frontend IP: Public IPv4,
- Protocol: HTTP, HTTPS
- Port: 80, 443
- Listener Type: Basic, Multi site
- Custom Error Pages: Bad Gateway - 502 Enter HTML file URL, Forbidden - 403, Enter HTML file URL, click for more status codes.
- Backend targets:
- Add backend pool:
- Name: AGbackednpool
- Target type: virtual machine:
- Add both vms
- Rule:
- Rule name: AGRule1
- Priority: 1
- Listener: AGListener1
- Backend Targets:
- AGbackendpool, HTTP1
- Tags:
- Review+Create (takes 15 to 20 Minutes)
- Testing: Go to application gateway, copy public ip, paste it in browser, traffic will be send to both vms one by one.
Application Gateway with terraform:
- Step 1: Create Vnet, subnet1, subnet2, NSG1, 2 VMs, starstorage1, starcontainer1, upload install_iis.ps1, Install IIS with extension:
- provider.tf
-
terraform {required_providers {azurerm = {source = "hashicorp/azurerm"version = "4.8.0"}}}
provider "azurerm" {subscription_id = "bd2ade99-0834-4cfe-bb19-ddf0e89ed9f4"tenant_id = "4b9f3326-b87a-468f-89d4-4c34403eae39"client_id = "289f6253-b6eb-4930-bc19-3557cad4b72d"client_secret = "LlM8Q~UauskuRH84yA1QDDxc3K0w8sGl1y4ZsbTi"features {}}
-
- variables.tf
-
variable "number_of_subnets" {type = numberdefault = 1validation {condition = var.number_of_subnets < 5error_message = "Value should be less than 5"}}
variable "number_of_machine" {type = number}
-
- vnet.tf
-
locals {resource_group_name="Star-RG"location="UK South"virtual_network ={name="Vnet1"address_space="10.0.0.0/16"}}resource "azurerm_resource_group" "RG" {name = local.resource_group_namelocation = local.location}resource "azurerm_virtual_network" "vnet" {name = local.virtual_network.namelocation = local.locationresource_group_name = local.resource_group_nameaddress_space = [local.virtual_network.address_space]
depends_on = [ azurerm_resource_group.RG ]
}resource "azurerm_subnet" "subnet1" {name = "subnet1"resource_group_name = local.resource_group_namevirtual_network_name = local.virtual_network.nameaddress_prefixes = ["10.0.1.0/24"]depends_on = [ azurerm_virtual_network.vnet ]}resource "azurerm_subnet" "subnet2" {name = "subnet2"resource_group_name = local.resource_group_namevirtual_network_name = local.virtual_network.nameaddress_prefixes = ["10.0.10.0/24"]depends_on = [ azurerm_virtual_network.vnet ]}resource "azurerm_network_security_group" "NSG" {name = "NSG1"location = local.locationresource_group_name = local.resource_group_namesecurity_rule {name = "rule1"priority = 100direction = "Inbound"access = "Allow"protocol = "Tcp"source_port_range = "*"destination_port_range = "3389"source_address_prefix = "*"destination_address_prefix = "*"}
security_rule {name = "rule2"priority = 101direction = "Inbound"access = "Allow"protocol = "Tcp"source_port_range = "*"destination_port_range = "80"source_address_prefix = "*"destination_address_prefix = "*"}depends_on = [ azurerm_resource_group.RG ]}
resource "azurerm_subnet_network_security_group_association" "NSGAssociation" {subnet_id = azurerm_subnet.subnet1.idnetwork_security_group_id=azurerm_network_security_group.NSG.id}
resource "azurerm_network_interface" "NIC" {count = var.number_of_machinename = "NIC${count.index}"location = local.locationresource_group_name = local.resource_group_name
ip_configuration {name = "internal"subnet_id = azurerm_subnet.subnet1.idprivate_ip_address_allocation = "Dynamic"}depends_on = [ azurerm_subnet.subnet1 ]}
-
- iis.tf (install_iis.ps1 file is located in the same folder as all these .tf files) open a text file named install_iis.ps1 and paste this script
Install-WindowsFeature -name Web-Server -IncludeManagementTools
-
resource "azurerm_storage_account" "starstorage1" {name = "starstorage1"resource_group_name = local.resource_group_namelocation = local.locationaccount_tier = "Standard"account_replication_type = "LRS"account_kind = "StorageV2"
depends_on = [ azurerm_resource_group.RG ]}
resource "azurerm_storage_container" "container" {name = "starcontainer1"storage_account_name = "starstorage1"container_access_type = "blob"depends_on = [ azurerm_storage_account.starstorage1 ]}
resource "azurerm_storage_blob" "iisconfig" {name = "install_iis.ps1"storage_account_name = "starstorage1"storage_container_name = "starcontainer1"type = "Block"source = "install_iis.ps1"depends_on = [ azurerm_storage_container.container ]}
resource "azurerm_virtual_machine_extension" "starextension" {count = var.number_of_machinename = "extension${count.index}"virtual_machine_id = azurerm_windows_virtual_machine.VM[count.index].idpublisher = "Microsoft.Compute"type = "CustomScriptExtension"type_handler_version = "1.10"
settings = <<SETTINGS{"fileUris": ["https://${azurerm_storage_account.starstorage1.name}.blob.core.windows.net/starcontainer1/install_iis.ps1"],"commandToExecute": "powershell -ExecutionPolicy Unrestricted -file install_iis.ps1"}SETTINGS
tags = {environment = "Production"}}
-
- vm.tf
-
resource "azurerm_windows_virtual_machine" "VM" {count = var.number_of_machinename = "VM${count.index}"resource_group_name = local.resource_group_namelocation = local.locationsize = "Standard_DS1_v2"admin_username = "abdul"admin_password = "India123456789"network_interface_ids = [azurerm_network_interface.NIC[count.index].id,]
os_disk {caching = "ReadWrite"storage_account_type = "Standard_LRS"}
source_image_reference {publisher = "MicrosoftWindowsServer"offer = "WindowsServer"sku = "2016-Datacenter"version = "latest"}depends_on = [ azurerm_network_interface.NIC, azurerm_resource_group.RG ]}
-
- #terraform init
- #terraform plan -out iis.tfplan
- #terraform apply "iis.tfplan"
- provider.tf
- Step2: Create public IP for AG, create AG, Associate public IP with AG,
- Go to terraform.io/azure/documentation/search public IP, application gateway,
- ag.tf
-
resource "azurerm_public_ip" "AGPublicIP" {name = "AGPublicIP"resource_group_name = local.resource_group_namelocation = local.locationallocation_method = "Static"sku = "Standard"
}#creating application gatewayresource "azurerm_application_gateway" "star-AG" {name = "star-AG"resource_group_name = local.resource_group_namelocation = local.location#When sku of AG is standard than public IP sku must also be standardsku {name = "Standard_v2"tier = "Standard_v2"capacity = 1}#Associating application gateway with Subnet2gateway_ip_configuration {name = "my-gateway-ip-configuration"subnet_id = azurerm_subnet.subnet2.id}#Creating Frontend portfrontend_port {name = "AGFrontendPort"port = 80}#Associating frontendip with public IPfrontend_ip_configuration {name = "FrontendIP"public_ip_address_id = azurerm_public_ip.AGPublicIP.id}#Creating backend poolbackend_address_pool {name = "AGBackendpool"}#Creating Backend HTTP settingsbackend_http_settings {name = "http-setting"cookie_based_affinity = "Disabled"path = "/path1/"port = 80protocol = "Http"request_timeout = 60}#Creating Listenerhttp_listener {name = "AGListener1"frontend_ip_configuration_name = "FrontendIP"frontend_port_name = "AGFrontendPort"protocol = "Http"}#Creating Routing Rulerequest_routing_rule {name = "AGRule1"priority = 1rule_type = "Basic"http_listener_name = "AGListener1"backend_address_pool_name = "AGBackendpool"backend_http_settings_name = "http-setting"}depends_on = [ azurerm_public_ip.AGPublicIP,azurerm_subnet.app-gateway ]}#terraform plan -out iis.tfplan#terraform apply "iis.tfplan"
-
- Add vms to backend pool. search for application gateway
- addvm.tf
-
resource "azurerm_network_interface_application_gateway_backend_address_pool_association" "addvm" {count = var.number_of_machinenetwork_interface_id = azurerm_network_interface.NIC[count.index].idip_configuration_name = "internal"backend_address_pool_id = tolist(azurerm_application_gateway.star-AG.backend_address_pool).0.iddepends_on = [ azurerm_application_gateway.star-AG,azurerm_network_interface.NIC ]}
- #terraform plan -out iis.tfplan
- #terraform apply "iis.tfplan"
- Step 3: Test:
- Step 1: Create Vnet, subnet1, subnet2, NSG1, 2 VMs, starstorage1, starcontainer1, upload install_iis.ps1, Install IIS with extension:
- Code:
- Code:
- Code:
- Code
- Code
VM
Create Windows VM with RG, Vnet, Subnet, SG with Rule 3389 allow, NIC, Pubic/Private IP
- Go to terraform.io / documentation/ search for azurerm windows virtual machine.
-
resource "azurerm_windows_virtual_machine" "example" { name = "example-machine" resource_group_name = azurerm_resource_group.example.name location = azurerm_resource_group.example.location size = "Standard_F2" admin_username = "adminuser" admin_password = "P@$$w0rd1234!" network_interface_ids = [ azurerm_network_interface.example.id, ] os_disk { caching = "ReadWrite" storage_account_type = "Standard_LRS" } source_image_reference { publisher = "MicrosoftWindowsServer" offer = "WindowsServer" sku = "2016-Datacenter" version = "latest" } } - ss
- sss
-
- LAB:
-
terraform {required_providers {azurerm = {source = "hashicorp/azurerm"version = "4.8.0"}}}
provider "azurerm" {subscription_id = "bd2ade99-0834-4cfe-bb19-ddf0e89ed9f4"tenant_id = "4b9f3326-b87a-468f-89d4-4c34403eae39"client_id = "363c6475-89bc-4948-9396-6dc6849eeb14"client_secret = "yUR8Q~2w~xi~~i6hUJkw4XCZRPCNVwIpIkTrcaPW"features {}}
locals {resource_group_name="Star-RG"location="UK South"security_group="SG"virtual_network ={name="star-Vnet1"address_space="10.0.0.0/16"}subnets=[{name = "subnet1"address_prefixes = ["10.0.1.0/24"]},
{name = "subnet2"address_prefixes = ["10.0.2.0/24"]}]}
resource "azurerm_resource_group" "RG" {name = local.resource_group_namelocation = local.location}
resource "azurerm_virtual_network" "vnet" {name = local.virtual_network.namelocation = local.locationresource_group_name = local.resource_group_nameaddress_space = [local.virtual_network.address_space]
}
resource "azurerm_subnet" "subnet-A" {name = local.subnets[0].nameresource_group_name = local.resource_group_namevirtual_network_name = local.virtual_network.nameaddress_prefixes = local.subnets[0].address_prefixesdepends_on = [ azurerm_virtual_network.vnet ]}
resource "azurerm_subnet" "subnet-B" {name = local.subnets[1].nameresource_group_name = local.resource_group_namevirtual_network_name = local.virtual_network.nameaddress_prefixes = local.subnets[1].address_prefixesdepends_on = [ azurerm_virtual_network.vnet ]}resource "azurerm_network_interface" "NIC1" {name = "star-NIC1"location = local.locationresource_group_name = local.resource_group_name
ip_configuration {name = "internal"subnet_id = azurerm_subnet.subnet-A.idprivate_ip_address_allocation = "Dynamic"public_ip_address_id = azurerm_public_ip.publicIP.id}depends_on = [ azurerm_subnet.subnet-A ]}
resource "azurerm_public_ip" "publicIP" {name = "StarPublicIP1"resource_group_name = local.resource_group_namelocation = local.locationallocation_method = "Static"
tags = {Dept = "IT"}depends_on = [ azurerm_resource_group.RG ]}
resource "azurerm_network_security_group" "NSG" {name = "star-NSG1"location = local.locationresource_group_name = local.resource_group_name
security_rule {name = "NSG-Rule1"priority = 500direction = "Inbound"access = "Allow"protocol = "Tcp"source_port_range = "*"destination_port_range = "3389"source_address_prefix = "*"destination_address_prefix = "*"}
tags = {Name = "NSG"}depends_on = [ azurerm_resource_group.RG ]}resource "azurerm_subnet_network_security_group_association" "NSG-Subnet" {subnet_id = azurerm_subnet.subnet-A.idnetwork_security_group_id = azurerm_network_security_group.NSG.id}
resource "azurerm_windows_virtual_machine" "VM" {name = "VM1"resource_group_name = local.resource_group_namelocation = local.locationsize = "Standard_DS1_v2"admin_username = "abdul"admin_password = "India123456789"network_interface_ids = [azurerm_network_interface.NIC1.id,]
os_disk {caching = "ReadWrite"storage_account_type = "Standard_LRS"}
source_image_reference {publisher = "MicrosoftWindowsServer"offer = "WindowsServer"sku = "2016-Datacenter"version = "latest"}depends_on = [ azurerm_network_interface.NIC1, azurerm_resource_group.RG ]} - code
- Code
- Code
- Code
-
- Go to terraform.io / documentation/ search for azurerm windows virtual machine.
Create and attach Data Disk
- A O/S disk is created while creating a VM, additional data disks can created and attached with an existing VM.
- Create a data disk:
-
resource "azurerm_managed_disk" "example" { name = "${local.vm_name}-disk1" location = azurerm_resource_group.example.location resource_group_name = azurerm_resource_group.example.name storage_account_type = "Standard_LRS" create_option = "Empty" disk_size_gb = 10 } - enter required fields:
-
resource "azurerm_managed_disk" "datadisk1" {name = "datadisk1"location = local.locationresource_group_name = local.resource_group_namestorage_account_type = "Standard_LRS"create_option = "Empty"disk_size_gb = 10}
-
- Attach data disk with VM:
-
resource "azurerm_virtual_machine_data_disk_attachment" "example" { managed_disk_id = azurerm_managed_disk.example.id virtual_machine_id = azurerm_virtual_machine.example.id lun = "10" caching = "ReadWrite" } -
resource "azurerm_virtual_machine_data_disk_attachment" "datadisk1attach" {managed_disk_id = azurerm_managed_disk.datadisk1.idvirtual_machine_id = azurerm_windows_virtual_machine.vm.idlun = "1"caching = "ReadWrite"}
- cc
-
- LAB:
- input.tf
-
variable "client_secret" {type = stringsensitive = true}
-
- provider.tf
-
terraform {required_providers {azurerm = {source = "hashicorp/azurerm"version = "4.8.0"}}}
provider "azurerm" {subscription_id = "bd2ade99-0834-4cfe-bb19-ddf0e89ed9f4"tenant_id = "4b9f3326-b87a-468f-89d4-4c34403eae39"client_id = "363c6475-89bc-4948-9396-6dc6849eeb14"client_secret = "yUR8Q~2w~xi~~i6hUJkw4XCZRPCNVwIpIkTrcaPW"features {}}
-
- vm.tf
-
locals {resource_group_name="Star-RG"location="UK South"security_group="SG"virtual_network ={name="star-Vnet1"address_space="10.0.0.0/16"}subnets=[{name = "subnet1"address_prefixes = ["10.0.1.0/24"]},
{name = "subnet2"address_prefixes = ["10.0.2.0/24"]}]}
resource "azurerm_resource_group" "RG" {name = local.resource_group_namelocation = local.location}
resource "azurerm_virtual_network" "vnet" {name = local.virtual_network.namelocation = local.locationresource_group_name = local.resource_group_nameaddress_space = [local.virtual_network.address_space]
depends_on = [ azurerm_resource_group.RG ]
}
resource "azurerm_subnet" "subnet-A" {name = local.subnets[0].nameresource_group_name = local.resource_group_namevirtual_network_name = local.virtual_network.nameaddress_prefixes = local.subnets[0].address_prefixesdepends_on = [ azurerm_virtual_network.vnet ]}
resource "azurerm_subnet" "subnet-B" {name = local.subnets[1].nameresource_group_name = local.resource_group_namevirtual_network_name = local.virtual_network.nameaddress_prefixes = local.subnets[1].address_prefixesdepends_on = [ azurerm_virtual_network.vnet ]}resource "azurerm_network_interface" "NIC1" {name = "star-NIC1"location = local.locationresource_group_name = local.resource_group_name
ip_configuration {name = "internal"subnet_id = azurerm_subnet.subnet-A.idprivate_ip_address_allocation = "Dynamic"public_ip_address_id = azurerm_public_ip.publicIP.id}depends_on = [ azurerm_subnet.subnet-A ]}
resource "azurerm_public_ip" "publicIP" {name = "StarPublicIP1"resource_group_name = local.resource_group_namelocation = local.locationallocation_method = "Static"
tags = {Dept = "IT"}depends_on = [ azurerm_resource_group.RG ]}
resource "azurerm_network_security_group" "NSG" {name = "star-NSG1"location = local.locationresource_group_name = local.resource_group_name
security_rule {name = "NSG-Rule1"priority = 500direction = "Inbound"access = "Allow"protocol = "Tcp"source_port_range = "*"destination_port_range = "3389"source_address_prefix = "*"destination_address_prefix = "*"}
tags = {Name = "NSG"}depends_on = [ azurerm_resource_group.RG ]}resource "azurerm_subnet_network_security_group_association" "NSG-Subnet" {subnet_id = azurerm_subnet.subnet-A.idnetwork_security_group_id = azurerm_network_security_group.NSG.id}
resource "azurerm_windows_virtual_machine" "VM" {name = "VM1"resource_group_name = local.resource_group_namelocation = local.locationsize = "Standard_DS1_v2"admin_username = "abdul"admin_password = "India123456789"network_interface_ids = [azurerm_network_interface.NIC1.id,]
os_disk {caching = "ReadWrite"storage_account_type = "Standard_LRS"}
source_image_reference {publisher = "MicrosoftWindowsServer"offer = "WindowsServer"sku = "2016-Datacenter"version = "latest"}depends_on = [ azurerm_network_interface.NIC1, azurerm_resource_group.RG ]}
resource "azurerm_managed_disk" "datadisk1" {name = "datadisk1"location = local.locationresource_group_name = local.resource_group_namestorage_account_type = "Standard_LRS"create_option = "Empty"disk_size_gb = 10}
resource "azurerm_virtual_machine_data_disk_attachment" "datadisk1attach" {managed_disk_id = azurerm_managed_disk.datadisk1.idvirtual_machine_id = azurerm_windows_virtual_machine.VM.idlun = "1"caching = "ReadWrite"}
-
- input.tf
- code
Resize VM
- The current size of VM is "Standard_DS1_v2" , It will be resize to "Standard_DS2_v4"
- Go to the code and change size to "Standard_DS2_v4" manually,
- When you make changes in configuration file manually, it is best execute terraform plan and this will update terrafor.tfstate file and this will avoid conflict.
Create Linux (ubuntu) VM with RG, Vnet, Subnet, SG with Rule (port 22 allow), NIC, Pubic/Private IP, configure SSH key, connect to vm using ssh
- Go to terraform.io and click documentation and search virtual machine and click azurerm_linux_virtu_machine.
- copy linux virtual machine resouce code.
-
resource "azurerm_linux_virtual_machine" "example" { name = "example-machine" resource_group_name = azurerm_resource_group.example.name location = azurerm_resource_group.example.location size = "Standard_F2" admin_username = "adminuser" network_interface_ids = [ azurerm_network_interface.example.id, ] admin_ssh_key { username = "adminuser" public_key = file("~/.ssh/id_rsa.pub") } os_disk { caching = "ReadWrite" storage_account_type = "Standard_LRS" } source_image_reference { publisher = "Canonical" offer = "0001-com-ubuntu-server-jammy" sku = "22_04-lts" version = "latest" } } - Create/Generate a Private Key: search in tls provider
- Search tls private key: The TLS provider provides utilities for working with Transport Layer Security keys and certificates. It provides resources that allow private keys, certificates and certificate requests to be created as part of a Terraform deployment.
- A private key is generating in this block and its reference name is linuxprivatekey
-
resource "tls_private_key" "linuxprivatekey" { algorithm = "RSA" rsa_bits = 4096 }
- Convert private key into pem format:
- resource "local_file" "pemkey" {
filename = "keypair1.pem"
content = tls_private_key.linuxprivatekey.private_key_pem
depends_on = [tls_private_key.linuxprivatekey]
}
- resource "local_file" "pemkey" {
- Define public key in configuration file:
- admin_ssh_key {
username = "abdul"
public_key = tls_private_key.linuxprivatekey.public_key_openssh
}
- admin_ssh_key {
- Generate new Private key & Public Key
-
- LAB: Creating Linux (ubuntu) VM with RG, Vnet, Subnet, SG with Rule (port 22 allow), NIC, Pubic/Private IP, configure public /private key,
- input.tf
-
variable "client_secret" {type = stringsensitive = true}
-
- provider.tf
-
terraform {required_providers {azurerm = {source = "hashicorp/azurerm"version = "4.8.0"}}}
provider "azurerm" {subscription_id = "bd2ade99-0834-4cfe-bb19-ddf0e89ed9f4"tenant_id = "4b9f3326-b87a-468f-89d4-4c34403eae39"client_id = "363c6475-89bc-4948-9396-6dc6849eeb14"client_secret = "yUR8Q~2w~xi~~i6hUJkw4XCZRPCNVwIpIkTrcaPW"features {}}
-
- vm1.tf
-
locals {resource_group_name="Star-RG"location="UK South"virtual_network ={name="star-Vnet1"address_space="10.0.0.0/16"}subnets=[{name = "subnet1"address_prefixes = ["10.0.1.0/24"]},
{name = "subnet2"address_prefixes = ["10.0.2.0/24"]}]}
resource "azurerm_resource_group" "RG" {name = local.resource_group_namelocation = local.location}
resource "azurerm_virtual_network" "vnet" {name = local.virtual_network.namelocation = local.locationresource_group_name = local.resource_group_nameaddress_space = [local.virtual_network.address_space]
depends_on = [ azurerm_resource_group.RG ]
}
resource "azurerm_subnet" "subnet-A" {name = local.subnets[0].nameresource_group_name = local.resource_group_namevirtual_network_name = local.virtual_network.nameaddress_prefixes = local.subnets[0].address_prefixesdepends_on = [ azurerm_virtual_network.vnet ]}
resource "azurerm_subnet" "subnet-B" {name = local.subnets[1].nameresource_group_name = local.resource_group_namevirtual_network_name = local.virtual_network.nameaddress_prefixes = local.subnets[1].address_prefixesdepends_on = [ azurerm_virtual_network.vnet ]}resource "azurerm_network_interface" "NIC1" {name = "star-NIC1"location = local.locationresource_group_name = local.resource_group_name
ip_configuration {name = "internal"subnet_id = azurerm_subnet.subnet-A.idprivate_ip_address_allocation = "Dynamic"public_ip_address_id = azurerm_public_ip.publicIP.id}depends_on = [ azurerm_subnet.subnet-A ]}
resource "azurerm_public_ip" "publicIP" {name = "StarPublicIP1"resource_group_name = local.resource_group_namelocation = local.locationallocation_method = "Static"
tags = {Dept = "IT"}depends_on = [ azurerm_resource_group.RG ]}
resource "azurerm_network_security_group" "NSG" {name = "star-NSG1"location = local.locationresource_group_name = local.resource_group_name
security_rule {name = "NSG-Rule1"priority = 500direction = "Inbound"access = "Allow"protocol = "Tcp"source_port_range = "*"destination_port_range = "22"source_address_prefix = "*"destination_address_prefix = "*"}
tags = {Name = "NSG"}depends_on = [ azurerm_resource_group.RG ]}resource "azurerm_subnet_network_security_group_association" "NSG-Subnet" {subnet_id = azurerm_subnet.subnet-A.idnetwork_security_group_id = azurerm_network_security_group.NSG.id}
/*resource "azurerm_windows_virtual_machine" "VM1" {name = "VM1"resource_group_name = local.resource_group_namelocation = local.locationsize = "Standard_DS1_v2"admin_username = "abdul"admin_password = "India123456789"network_interface_ids = [azurerm_network_interface.NIC1.id,]
os_disk {caching = "ReadWrite"storage_account_type = "Standard_LRS"}
source_image_reference {publisher = "MicrosoftWindowsServer"offer = "WindowsServer"sku = "2016-Datacenter"version = "latest"}depends_on = [ azurerm_network_interface.NIC1, azurerm_resource_group.RG ]}
resource "azurerm_managed_disk" "datadisk1" {name = "datadisk1"location = local.locationresource_group_name = local.resource_group_namestorage_account_type = "Standard_LRS"create_option = "Empty"disk_size_gb = 10}
resource "azurerm_virtual_machine_data_disk_attachment" "datadisk1attach" {managed_disk_id = azurerm_managed_disk.datadisk1.idvirtual_machine_id = azurerm_windows_virtual_machine.VM.idlun = "1"caching = "ReadWrite"}
*/
#private key is generatingresource "tls_private_key" "linuxprivatekey" {algorithm = "RSA"rsa_bits = 4096}
#converting privte key into pem formatresource "local_file" "pemkey" {filename = "keypair1.pem"content = tls_private_key.linuxprivatekey.private_key_pemdepends_on = [tls_private_key.linuxprivatekey]}
#defining virtual machine details and public keyresource "azurerm_linux_virtual_machine" "vm2" {name = "star-ubuntu"resource_group_name = local.resource_group_namelocation = local.locationsize = "Standard_DS1_v2"admin_username = "abdul"network_interface_ids = [azurerm_network_interface.NIC1.id,]
admin_ssh_key {username = "abdul"public_key = tls_private_key.linuxprivatekey.public_key_openssh}
os_disk {caching = "ReadWrite"storage_account_type = "Standard_LRS"}
source_image_reference {publisher = "Canonical"offer = "0001-com-ubuntu-server-jammy"sku = "22_04-lts"version = "latest"}}
-
- #terraform init
- #terraform plan -out vm1.tfplan
- #terraform apply "vm1.tfplan"
- keypair1.pem key created in the folder where all configuration files are stored.
- SSH connection to vm1:
- from visual studio code terminal run the following command
- PS C:\Terraform> ssh -i keypair1.pem abdul@172.167.46.106
- Warning: permission denied: give user permission
- Go to C:\user and check logged in user name
- Go to configuration file folder and right click/properties/security/advanced/Disable inheritance/Remove all inherited permissions from this object. Apply,
- Click Edit/Add/search user account (admin), check names, give full control apply and ok
- Run the command: PS C:\Terraform> ssh -i keypair1.pem abdul@172.167.46.106
- input.tf
- code
Create Linux (ubuntu) VM with username & password:
-
resource "azurerm_linux_virtual_machine" "VM3" {
name = "star-VM3"
resource_group_name = local.resource_group_name
location = local.location
size = "Standard_D2s_v3"
admin_username = "abdul"
admin_password = "India123456789"
disable_password_authentication = false
network_interface_ids = [
azurerm_network_interface.NIC1.id,
]source_image_reference {
publisher = "Canonical"
offer = "0001-com-ubuntu-server-jammy"
sku = "22_04-lts"
version = "latest"
}os_disk {
storage_account_type = "Standard_LRS"
caching = "ReadWrite"
}
} - code
- LAB: Creating Linux (ubuntu) VM with RG, Vnet, Subnet, SG with Rule (port 22 allow), NIC, Pubic/Private IP, configure username & password,
- input.tf
-
variable "client_secret" {type = stringsensitive = true}
-
- provider.tf
-
terraform {required_providers {azurerm = {source = "hashicorp/azurerm"version = "4.8.0"}}}
provider "azurerm" {subscription_id = "bd2ade99-0834-4cfe-bb19-ddf0e89ed9f4"tenant_id = "4b9f3326-b87a-468f-89d4-4c34403eae39"client_id = "363c6475-89bc-4948-9396-6dc6849eeb14"client_secret = "yUR8Q~2w~xi~~i6hUJkw4XCZRPCNVwIpIkTrcaPW"features {}}
-
- vm3.tf
-
locals {resource_group_name="Star-RG"location="UK South"virtual_network ={name="star-Vnet1"address_space="10.0.0.0/16"}subnets=[{name = "subnet1"address_prefixes = ["10.0.1.0/24"]},
{name = "subnet2"address_prefixes = ["10.0.2.0/24"]}]}
resource "azurerm_resource_group" "RG" {name = local.resource_group_namelocation = local.location}
resource "azurerm_virtual_network" "vnet" {name = local.virtual_network.namelocation = local.locationresource_group_name = local.resource_group_nameaddress_space = [local.virtual_network.address_space]
depends_on = [ azurerm_resource_group.RG ]
}
resource "azurerm_subnet" "subnet-A" {name = local.subnets[0].nameresource_group_name = local.resource_group_namevirtual_network_name = local.virtual_network.nameaddress_prefixes = local.subnets[0].address_prefixesdepends_on = [ azurerm_virtual_network.vnet ]}
resource "azurerm_subnet" "subnet-B" {name = local.subnets[1].nameresource_group_name = local.resource_group_namevirtual_network_name = local.virtual_network.nameaddress_prefixes = local.subnets[1].address_prefixesdepends_on = [ azurerm_virtual_network.vnet ]}resource "azurerm_network_interface" "NIC1" {name = "star-NIC1"location = local.locationresource_group_name = local.resource_group_name
ip_configuration {name = "internal"subnet_id = azurerm_subnet.subnet-A.idprivate_ip_address_allocation = "Dynamic"public_ip_address_id = azurerm_public_ip.publicIP.id}depends_on = [ azurerm_subnet.subnet-A ]}
resource "azurerm_public_ip" "publicIP" {name = "StarPublicIP1"resource_group_name = local.resource_group_namelocation = local.locationallocation_method = "Static"
tags = {Dept = "IT"}depends_on = [ azurerm_resource_group.RG ]}
resource "azurerm_network_security_group" "NSG" {name = "star-NSG1"location = local.locationresource_group_name = local.resource_group_name
security_rule {name = "NSG-Rule1"priority = 500direction = "Inbound"access = "Allow"protocol = "Tcp"source_port_range = "*"destination_port_range = "22"source_address_prefix = "*"destination_address_prefix = "*"}
tags = {Name = "NSG"}depends_on = [ azurerm_resource_group.RG ]}resource "azurerm_subnet_network_security_group_association" "NSG-Subnet" {subnet_id = azurerm_subnet.subnet-A.idnetwork_security_group_id = azurerm_network_security_group.NSG.id}
resource "azurerm_linux_virtual_machine" "VM3" {name = "star-VM3"resource_group_name = local.resource_group_namelocation = local.locationsize = "Standard_D2s_v3"admin_username = "abdul"admin_password = "India123456789"disable_password_authentication = falsenetwork_interface_ids = [azurerm_network_interface.NIC1.id,]
source_image_reference {publisher = "Canonical"offer = "0001-com-ubuntu-server-jammy"sku = "22_04-lts"version = "latest"}
os_disk {storage_account_type = "Standard_LRS"caching = "ReadWrite"}}
-
- cc
- input.tf
- Code
- Code
- Code
-
Create VM based on Input Value for number of subnets, NIC, VM:
- It will create a RG in which 2 Subnets, 2 NIC, 2 publicIP, one SG, 2 VM
- provider.tf
-
terraform {required_providers {azurerm = {source = "hashicorp/azurerm"version = "4.8.0"}}}
provider "azurerm" {subscription_id = "bd2ade99-0834-4cfe-bb19-ddf0e89ed9f4"tenant_id = "4b9f3326-b87a-468f-89d4-4c34403eae39"client_id = "363c6475-89bc-4948-9396-6dc6849eeb14"client_secret = "yUR8Q~2w~xi~~i6hUJkw4XCZRPCNVwIpIkTrcaPW"features {}}
-
- input.tf
-
variable "client_secret" {type = stringsensitive = true}
variable "no_of_subnet" {type = number}
variable "no_of_nic" {type = number}variable "no_of_vm" {type = number}
-
- subnet_count.tf
-
locals {resource_group_name="star-RG"location="UK South"virtual_network={name="Vnet1"address_space="10.0.0.0/16"}security_group = "star-SG"}
resource "azurerm_resource_group" "RG" {name = local.resource_group_namelocation = local.location}
resource "azurerm_network_interface" "NIC" {count = var.no_of_nicname = "NIC${count.index}"location = local.locationresource_group_name = local.resource_group_name
ip_configuration {name = "Internal"subnet_id = azurerm_subnet.subnets[count.index].idprivate_ip_address_allocation = "Dynamic"public_ip_address_id = azurerm_public_ip.publicip[count.index].id}depends_on = [ azurerm_subnet.subnets,azurerm_public_ip.publicip ]}
resource "azurerm_public_ip" "publicip" {count = var.no_of_nicname = "publicip${count.index}"resource_group_name = local.resource_group_namelocation = local.locationallocation_method = "Static"
tags = {Dept = "IT"}depends_on = [ azurerm_resource_group.RG ]}
resource "azurerm_virtual_network" "VNET" {name = local.virtual_network.namelocation = local.locationresource_group_name = local.resource_group_nameaddress_space = [local.virtual_network.address_space]
depends_on = [ azurerm_resource_group.RG ]}
resource "azurerm_subnet" "subnets" {count = var.no_of_subnetname = "Subnet${count.index}"resource_group_name = local.resource_group_namevirtual_network_name = local.virtual_network.nameaddress_prefixes = ["10.0.${count.index}.0/24"]depends_on = [ azurerm_virtual_network.VNET ]}
resource "azurerm_network_security_group" "SG" {name = local.security_grouplocation = local.locationresource_group_name = local.resource_group_namedepends_on = [ azurerm_resource_group.RG ]
security_rule {name = "test123"priority = 100direction = "Inbound"access = "Allow"protocol = "Tcp"source_port_range = "*"destination_port_range = "3389"source_address_prefix = "*"destination_address_prefix = "*"}}
resource "azurerm_subnet_network_security_group_association" "assoc_subnet" {count = var.no_of_subnetsubnet_id = azurerm_subnet.subnets[count.index].idnetwork_security_group_id = azurerm_network_security_group.SG.id}
-
- vm_count.tf
-
resource "azurerm_windows_virtual_machine" "VM1" {count = var.no_of_vmname = "VM${count.index}"resource_group_name = local.resource_group_namelocation = local.locationsize = "Standard_DS1_v2"admin_username = "abdul"admin_password = "India123456789"network_interface_ids = [azurerm_network_interface.NIC[count.index].id]
os_disk {caching = "ReadWrite"storage_account_type = "Standard_LRS"}
source_image_reference {publisher = "MicrosoftWindowsServer"offer = "WindowsServer"sku = "2016-Datacenter"version = "latest"}depends_on = [ azurerm_network_interface.NIC, azurerm_resource_group.RG ]}
-
- #terraform init
- #terraform plan -out vm_count.tfplan
- #terraform apply "vim_count.tfplan"
- #terraform destroy
VM Extension
- Azure VM extensions are small applications that provide post-deployment configuration and automation tasks on Azure VMS. For example, if a virtual machine requires software installation, antivirtus protection, or the ability to run a script inside, we can use VM extensions.
- Installing IIS on a VM, either login to VM and install IIS manually or using the script install IIS while VM creation.
- Installing IIS with VM extension using script.
- provider.tf
-
terraform {required_providers {azurerm = {source = "hashicorp/azurerm"version = "4.8.0"}}}
provider "azurerm" {subscription_id = "bd2ade99-0834-4cfe-bb19-ddf0e89ed9f4"tenant_id = "4b9f3326-b87a-468f-89d4-4c34403eae39"client_id = "289f6253-b6eb-4930-bc19-3557cad4b72d"client_secret = "LlM8Q~UauskuRH84yA1QDDxc3K0w8sGl1y4ZsbTi"features {}}
-
- vnet.tf
-
locals {resource_group_name="star-RG"location="UK South"virtual_network={name="Vnet1"address_space="10.0.0.0/16"}security_group = "star-SG"}
resource "azurerm_resource_group" "RG" {name = local.resource_group_namelocation = local.location}
resource "azurerm_virtual_network" "VNET" {name = local.virtual_network.namelocation = local.locationresource_group_name = local.resource_group_nameaddress_space = [local.virtual_network.address_space]
depends_on = [ azurerm_resource_group.RG ]}
resource "azurerm_subnet" "subnets" {
name = "vmsubnet"resource_group_name = local.resource_group_namevirtual_network_name = local.virtual_network.nameaddress_prefixes = ["10.0.1.0/24"]depends_on = [ azurerm_virtual_network.VNET ]}
resource "azurerm_network_security_group" "SG" {name = local.security_grouplocation = local.locationresource_group_name = local.resource_group_namedepends_on = [ azurerm_resource_group.RG ]
security_rule {name = "test123"priority = 100direction = "Inbound"access = "Allow"protocol = "Tcp"source_port_range = "*"destination_port_range = "3389"source_address_prefix = "*"destination_address_prefix = "*"}security_rule {name = "test124"priority = 101direction = "Inbound"access = "Allow"protocol = "Tcp"source_port_range = "*"destination_port_range = "80"source_address_prefix = "*"destination_address_prefix = "*"}}
resource "azurerm_subnet_network_security_group_association" "assoc_subnet" {subnet_id = azurerm_subnet.subnets.idnetwork_security_group_id = azurerm_network_security_group.SG.id}
resource "azurerm_network_interface" "NIC" {name = "NIC1"location = local.locationresource_group_name = local.resource_group_name
ip_configuration {name = "Internal"subnet_id = azurerm_subnet.subnets.idprivate_ip_address_allocation = "Dynamic"public_ip_address_id = azurerm_public_ip.publicip.id}depends_on = [ azurerm_subnet.subnets,azurerm_public_ip.publicip]}
resource "azurerm_public_ip" "publicip" {name = "StarPublicIP1"resource_group_name = local.resource_group_namelocation = local.locationallocation_method = "Static"sku = "Standard"
tags = {Dept = "IT"}depends_on = [ azurerm_resource_group.RG ]}
-
- vm_count.tf
-
resource "azurerm_windows_virtual_machine" "VM1" {name = "VM1"resource_group_name = local.resource_group_namelocation = local.locationsize = "Standard_DS1_v2"admin_username = "abdul"admin_password = "India123456789"network_interface_ids = [azurerm_network_interface.NIC.id]
os_disk {caching = "ReadWrite"storage_account_type = "Standard_LRS"}
source_image_reference {publisher = "MicrosoftWindowsServer"offer = "WindowsServer"sku = "2016-Datacenter"version = "latest"}depends_on = [ azurerm_network_interface.NIC, azurerm_resource_group.RG]}
-
- customscript.tf
-
resource "azurerm_storage_account" "starstorage1" {name = "starstorage1"resource_group_name = local.resource_group_namelocation = local.locationaccount_tier = "Standard"account_replication_type = "LRS"account_kind = "StorageV2"depends_on = [ azurerm_resource_group.RG ]
tags = {name = "storage"}}
resource "azurerm_storage_container" "starcontainer1" {name = "starcontainer1"storage_account_name = "starstorage1"container_access_type = "blob"depends_on = [ azurerm_storage_account.starstorage1 ]}
resource "azurerm_storage_blob" "starblob" {name = "install_iis.ps1"storage_account_name = azurerm_storage_account.starstorage1.namestorage_container_name = azurerm_storage_container.starcontainer1.nametype = "Block"source = "install_iis.ps1"depends_on = [ azurerm_storage_container.starcontainer1 ]}
resource "azurerm_virtual_machine_extension" "starextension" {name = "starextension"virtual_machine_id = azurerm_windows_virtual_machine.VM1.idpublisher = "Microsoft.Compute"type = "CustomScriptExtension"type_handler_version = "1.10"
settings = <<SETTINGS{"fileUris": ["https://${azurerm_storage_account.starstorage1.name}.blob.core.windows.net/starcontainer1/install_iis.ps1"],"commandToExecute": "powershell.exe -executionpolicy Unrestricted -file install_iis.ps1"}SETTINGS
tags = {environment = "Production"}}
-
- #terraform init
- #terraform plan -out customscript.tfplan
- #terraform apply "customscript.tfplan"
- provider.tf
- code
Availability Zone / Avalability Set:
Availability Zone:
- Azure Redundancy/ Clustering: These services are part of compute resource. It is use to make sure services are available on any hypothetical situation like, natural disaster, human interference or hardware failure. To make resources available at all times, Azure provides Availability zone and Availability sets and Regional pair.
- High Availability through Availability zone (Datacenter level failure protection): High availability can be achieved at data center level. Configure the service on more than one data center so that if any data center crashed than service is still available from other data center. For load distribution you can create multiple identical resources VM and installed web application. Keep these VM's in different zones and instead of keeping them in same zone.
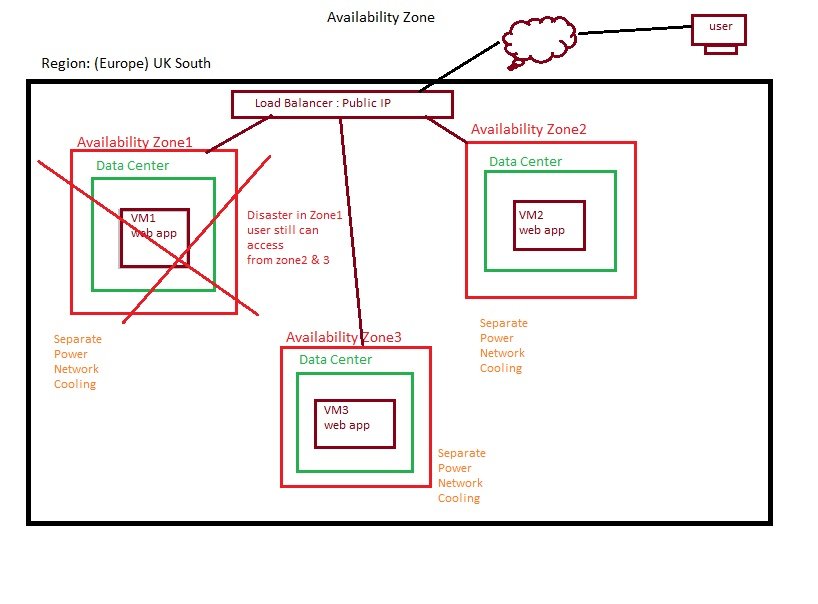
- Redundancy at data centre level, There will be separate physical availability zones within a Azure Region. There will be 3 availability zones in a region. It gives 99.99% SLA. Every zone have its own power supply, cooling, ups etc.
- If a resource in one zone is not avilable due to power failure, network failure or cooling failure or other disaster then application still accessible from another zone.
- Every region will have min 3 zones so you can create resources in these zones to make resilient.
- It works same in case of storage acccount and selected zone redundancy then data will be stored in selected availability zones.
- Services that support Availability zones:
- VM (Linux, Windows), VM Scale set, Managed Disks, Load Balancer, Piblic IP, Zone-redundant storage, SQL Database, Events Hubs, Service Bus, VPN Gateway, Express Route, Application Gateway
- LAB: Create Availability zone for public IP
- It will create a RG in which 2 Subnets, 2 NIC, 2 publicIP in Zones, one SG, 2 VM (Selection of zones depend on the sku type in public IP)
- provider.tf
-
terraform {required_providers {azurerm = {source = "hashicorp/azurerm"version = "4.8.0"}}}
provider "azurerm" {subscription_id = "bd2ade99-0834-4cfe-bb19-ddf0e89ed9f4"tenant_id = "4b9f3326-b87a-468f-89d4-4c34403eae39"client_id = "363c6475-89bc-4948-9396-6dc6849eeb14"client_secret = "yUR8Q~2w~xi~~i6hUJkw4XCZRPCNVwIpIkTrcaPW"features {}}
-
- input.tf
-
variable "client_secret" {type = stringsensitive = true}
variable "no_of_subnet" {type = number}
variable "no_of_nic" {type = number}variable "no_of_vm" {type = number}
-
- subnet_count.tf
-
locals {resource_group_name="star-RG"location="UK South"virtual_network={name="Vnet1"address_space="10.0.0.0/16"}security_group = "star-SG"}
resource "azurerm_resource_group" "RG" {name = local.resource_group_namelocation = local.location}
resource "azurerm_network_interface" "NIC" {count = var.no_of_nicname = "NIC${count.index}"location = local.locationresource_group_name = local.resource_group_name
ip_configuration {name = "Internal"subnet_id = azurerm_subnet.subnets[count.index].idprivate_ip_address_allocation = "Dynamic"public_ip_address_id = azurerm_public_ip.publicip[count.index].id}depends_on = [ azurerm_subnet.subnets,azurerm_public_ip.publicip ]}
resource "azurerm_public_ip" "publicip" {count = var.no_of_nicname = "publicip${count.index}"resource_group_name = local.resource_group_namelocation = local.locationallocation_method = "Static"sku = "Standard"zones = ["${count.index}"]#it is zones
tags = {Dept = "IT"}depends_on = [ azurerm_resource_group.RG ]}
resource "azurerm_virtual_network" "VNET" {name = local.virtual_network.namelocation = local.locationresource_group_name = local.resource_group_nameaddress_space = [local.virtual_network.address_space]
depends_on = [ azurerm_resource_group.RG ]}
resource "azurerm_subnet" "subnets" {count = var.no_of_subnetname = "Subnet${count.index}"resource_group_name = local.resource_group_namevirtual_network_name = local.virtual_network.nameaddress_prefixes = ["10.0.${count.index}.0/24"]depends_on = [ azurerm_virtual_network.VNET ]}
resource "azurerm_network_security_group" "SG" {name = local.security_grouplocation = local.locationresource_group_name = local.resource_group_namedepends_on = [ azurerm_resource_group.RG ]
security_rule {name = "test123"priority = 100direction = "Inbound"access = "Allow"protocol = "Tcp"source_port_range = "*"destination_port_range = "3389"source_address_prefix = "*"destination_address_prefix = "*"}}
resource "azurerm_subnet_network_security_group_association" "assoc_subnet" {count = var.no_of_subnetsubnet_id = azurerm_subnet.subnets[count.index].idnetwork_security_group_id = azurerm_network_security_group.SG.id}
-
- vm_count.tf
-
resource "azurerm_windows_virtual_machine" "VM1" {count = var.no_of_vmname = "VM${count.index}"resource_group_name = local.resource_group_namelocation = local.locationsize = "Standard_DS1_v2"admin_username = "abdul"admin_password = "India123456789"zone = (count.index+1)#it is zone not zones as it is defined in publicIPnetwork_interface_ids = [azurerm_network_interface.NIC[count.index].id]
os_disk {caching = "ReadWrite"storage_account_type = "Standard_LRS"}
source_image_reference {publisher = "MicrosoftWindowsServer"offer = "WindowsServer"sku = "2016-Datacenter"version = "latest"}depends_on = [ azurerm_network_interface.NIC, azurerm_resource_group.RG ]}
-
- #terraform init
- #terraform plan vm_count.tfplan
- #terraform apply "vm_count.tfplan"
Availability Set:
- High Availability through Availability Set (Within a datacenter): High availability of recource can be achieved within a data center where any hardware, power or cooling failure or any planned/unplanned maintenance.
- It is a logical grouping, it is the feature of compute section.it is use to grouping the server to get 99.95% SLA otherwise Microsoft offers 99.9% SLA. It provides redundancy / clustering within a single data center, if that data center got crashed than there will be no service, to overcome this azure also provide availability zone where it keeps copy of VM in different zones. It is available at server lever where configuration of servers could be similar or different. When one server is not available than another server should provide service. You cannot define availability set once VM is created. Need to recreate VM .
- In a datacenter there are lots of Racks and each rack has multiple servers in which we create resource.
- To get high availability within a datacenter we create availability set in which each rack is called fault domain.
- each fault domain has its own power and network connection but cooling is provided on data center level.
- If you select 3 fault domain means you will be assgin 3 racks.
- downtime can occur in case of power failure, network failure or maintenance (planned / unplanned). some time in maintenance they required to reboot servers and during that period a downtime will occur.
- Fault Domain:
- Microsoft combined group of servers at their data center which shares common power supply, cooling, ups and other hardware related resources. It make sure the service is available in the event of hardware failure, power supply or rack failure, Azure will keep copies of your server in different fault domain and update domain in the datacenter. By default you can have 2 fault domain and can extend to 3. FD0, FD1 or FD2. Suppose if you have 6 VM where fault domain be like FD0, FD1, FD0, FD1, FD0, FD1.
- update domain: it is a logical collection of servers from different fault domain.
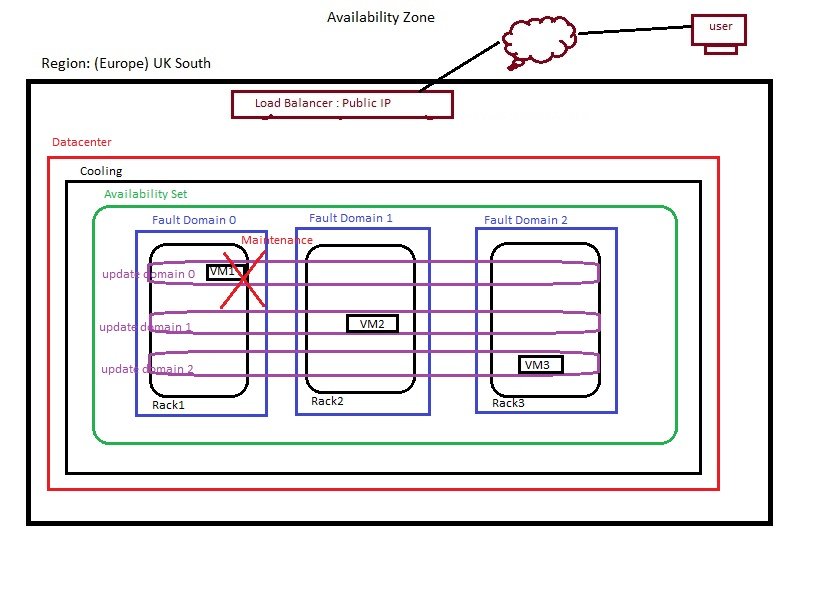
- You can create max 3 fault domain and 20 update domains,
- Microsoft will perform maintenance on one update domain at a time and after 30 minutes it will start on second update domain.
- Virtual machines deployed on Microsoft's physcial server using hypervisor and which may need updating and patching. During update or patching by Microsoft it is required to restart server, there will be downtime until server is up, to make sure service is available at all times server copies will be available in different rack. For example hypervisor which runs on these hardware and required patching and update. You can have 5 Update Domain by default and can stretch to 20, UD0 to UD4. Thosse servers lies in that fault domain or update domain may get impacted only.
- Create availability set, deplot VM in that AS.
- variables.tf
-
variable "client_secret" {type = stringsensitive = true}
variable "no_of_subnet" {type = number}
variable "no_of_nic" {type = number}variable "no_of_vm" {type = number}
-
- provider.tf
-
terraform {required_providers {azurerm = {source = "hashicorp/azurerm"version = "4.8.0"}}}
provider "azurerm" {subscription_id = "bd2ade99-0834-4cfe-bb19-ddf0e89ed9f4"tenant_id = "4b9f3326-b87a-468f-89d4-4c34403eae39"client_id = "363c6475-89bc-4948-9396-6dc6849eeb14"client_secret = "yUR8Q~2w~xi~~i6hUJkw4XCZRPCNVwIpIkTrcaPW"features {}}
-
- avail_set.tf
- Go to terraformio and click aure provider and documentation and in search type availabity set. copy code, define fault domain and update domain.
-
resource "azurerm_availability_set" "as" {name = "star-as1"location = local.locationresource_group_name = local.resource_group_nameplatform_fault_domain_count = 3platform_update_domain_count = 3
tags = {environment = "testing-as"}depends_on = [ azurerm_resource_group.RG ]} -
- vm_count.tf
-
resource "azurerm_windows_virtual_machine" "VM1" {count = var.no_of_vmname = "VM${count.index}"resource_group_name = local.resource_group_namelocation = local.locationsize = "Standard_DS1_v2"admin_username = "abdul"admin_password = "India123456789"availability_set_id = azurerm_availability_set.as.idnetwork_interface_ids = [azurerm_network_interface.NIC[count.index].id]
os_disk {caching = "ReadWrite"storage_account_type = "Standard_LRS"}
source_image_reference {publisher = "MicrosoftWindowsServer"offer = "WindowsServer"sku = "2016-Datacenter"version = "latest"}depends_on = [ azurerm_network_interface.NIC, azurerm_resource_group.RG,azurerm_availability_set.as ]}
-
- vnet.tf
-
locals {resource_group_name="star-RG"location="UK South"virtual_network={name="Vnet1"address_space="10.0.0.0/16"}security_group = "star-SG"}
resource "azurerm_resource_group" "RG" {name = local.resource_group_namelocation = local.location}
resource "azurerm_network_interface" "NIC" {count = var.no_of_nicname = "NIC${count.index}"location = local.locationresource_group_name = local.resource_group_name
ip_configuration {name = "Internal"subnet_id = azurerm_subnet.subnets[count.index].idprivate_ip_address_allocation = "Dynamic"public_ip_address_id = azurerm_public_ip.publicip[count.index].id}depends_on = [ azurerm_subnet.subnets,azurerm_public_ip.publicip ]}
resource "azurerm_public_ip" "publicip" {count = var.no_of_nicname = "publicip${count.index}"resource_group_name = local.resource_group_namelocation = local.locationallocation_method = "Static"sku = "Standard"zones = ["${count.index+1}"]
tags = {Dept = "IT"}depends_on = [ azurerm_resource_group.RG ]}
resource "azurerm_virtual_network" "VNET" {name = local.virtual_network.namelocation = local.locationresource_group_name = local.resource_group_nameaddress_space = [local.virtual_network.address_space]
depends_on = [ azurerm_resource_group.RG ]}
resource "azurerm_subnet" "subnets" {count = var.no_of_subnetname = "Subnet${count.index}"resource_group_name = local.resource_group_namevirtual_network_name = local.virtual_network.nameaddress_prefixes = ["10.0.${count.index}.0/24"]depends_on = [ azurerm_virtual_network.VNET ]}
resource "azurerm_network_security_group" "SG" {name = local.security_grouplocation = local.locationresource_group_name = local.resource_group_namedepends_on = [ azurerm_resource_group.RG ]
security_rule {name = "test123"priority = 100direction = "Inbound"access = "Allow"protocol = "Tcp"source_port_range = "*"destination_port_range = "3389"source_address_prefix = "*"destination_address_prefix = "*"}}
resource "azurerm_subnet_network_security_group_association" "assoc_subnet" {count = var.no_of_subnetsubnet_id = azurerm_subnet.subnets[count.index].idnetwork_security_group_id = azurerm_network_security_group.SG.id}
-
- #terraform init
- #terraform plan -out avail_set.tfplan
- #terraform apply "vm_count.tfplan"
- High Availability through Availability Set (Within a datacenter): High availability of recource can be achieved within a data center where any hardware, power or cooling failure or any planned/unplanned maintenance.
- Code
- Code
Scale Sets:
VM Scale Sets Overview:
- Azure will create identical VMs with option to scale in and scale out.
- There are two types of scaling:
- Horizontal Scaling (VMs added/removed): Scale in (reduce) and scale out (increase), you define threshold values in scaling options to execute scaling. When CPU utilization increases / decreases then VMs will be added or removed. When you have more than one identical servers than you need a load balancer to access application. Load balancer distributed the traffic among servers.
- Vertical Scaling (Hardware Resources increase/decrease): Hardware resources scale up and scale down.
- Configuration of Scaling:
- Manual Scale: When threshold values reaches to define values then you will perform scaling manually.
- Custom Autoscale: When threshold values reaches to define values than azure will perform scaling automatically.
- In one scale set you can create upto 1000 VMs.
- In scale set all VMs are identical with same configuration and application, first create a vm with all required configuration and application/softwares deployed and create an image. Now deploy VM and scale set using this image so that every time when scale set need to add a new VM in the scale set it will use this image to make all VMs identical.
- When you have more than one VM and their application can be accessed with load balancer which distributes the traffic among them.
- You can create a VM standalone or part of scale set.
- Mostly used in web servers where you have ecommerce running.
- You should have load balancer to access these VMs.
- Code
Creating VM Scale Sets through Portal using image:
- Step 1: Create a Vnet, Subnet1, SG with Allow port 3389,80 and attach with Subnet1, VM & Install all required applications(IIS):
- Through Portal: check in VM section
- Through Script:
- Create a windows virtual machine using powershell.
- Launch Azure Cloud Shell / windows power shell and login to azure:
- To open the Cloud Shell, just select Open Cloudshell from the upper right corner of a code block. You can also launch Cloud Shell in a separate browser tab by going to https://shell.azure.com/powershell Select Copy to copy the code blocks, paste them into the Cloud Shell, and press enter to run the them.
- Create a resource group.
- New-AzResourceGroup -Name 'ScaleSet-RG' -Location 'UK South'
- Create virtual machine
- New-Vm `
-ResourceGroupName 'ScaleSet-RG' `
-Name 'star-webserver' `
-Location 'East US' `
-Image 'MicrosoftWindowsServer:WindowsServer:2019-datacenter-azure-edition:latest' `
-VirtualNetworkName 'Star-Vnet' `
-SubnetName 'Star-Subnet' `
-SecurityGroupName 'Star-SecurityGroup' `
-PublicIpAddressName 'Star-IpAddress' `
-OpenPorts 80,3389 - When prompted, provide a username and password to be used as the sign-in credentials for the VM:
- New-Vm `
- Install web server (IIS).
- Logon to the server created above.
- open power shell and run the following.
-
#Install IIS server role.
Install-WindowsFeature -name Star-WebServer -IncludeManagementTools#Remove default html file
Remove-Item c:\inetpub\wwwroot\iisstart.htm#Add a new html file that display server name
Add-Content -Path "C:\inetpub\wwwroot\iisstart.htm" -Value $("Welcome from " + $env:computername)
- Step 2: Create Golden/Master Image of the above VM so it can be use for scaling.
- Generalise this server by running sysprep tool.
- Go to command prompt with administrative permission of IIS server.
- Go to c:\users\user cd %windir%\system32\sysprep
- Run sysprep and select Generalise check box and select shutdown.
- It will generalise and remove any configuration which is related with this VM only, so system can make multiple copies using the image.
- VM will be in stopped state.
- Capture Image of this VM.
- Through GUI:
- Go to virtual machine to which you want to take image or capture.
- click capture image.
- Give Name for this image along with Resource group(use existing or give new RG name), uncheck delete this virtual machine after creating the image. Click create.
- Now it will stop the virtual machine from running state and take capture.
- After creating an image if you want to start VM, then go to VM and start the VM, if you have unchecked delete after creating the image.
- To check the created image: Go to market place, shared images.
- Through script:
- Through GUI:
- Generalise this server by running sysprep tool.
- Step 3: Create a standard Public Load Balancer, Backend pool, Health Probe, Load Balancer Rule, attach VMs to Backend pool
- check in networking section
- Step 4: Create storage account, container and upload install_iis.ps1
- check in networking load balancer section.
- Step 5: Create VM Scale Set using Master Image.
- Manual scaling:
- Go to market place, shared images and select the custom image and during VM creation create scale set.
- Go to compute \ virtual machine scale set and click new.
-
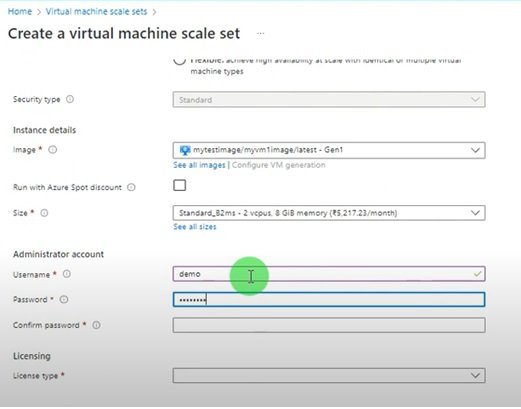
-
Enter required fields.
- Disk: enter details
- Networking: allow public IP
-
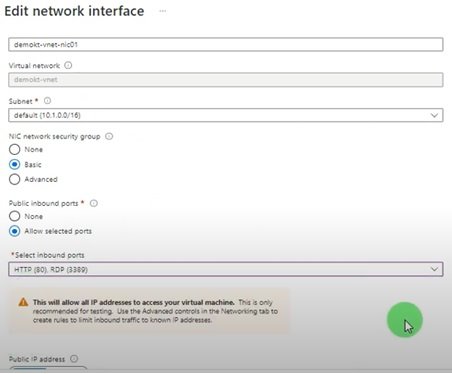
- Scaling:
- Enter instance count.
- Scaling policy:
- Manual
- Custom
- Management:
- Health:
- Advanced:
- Tags:
- Create
- Scaling Configuration: go to scale set and edit scaling section.
-
-
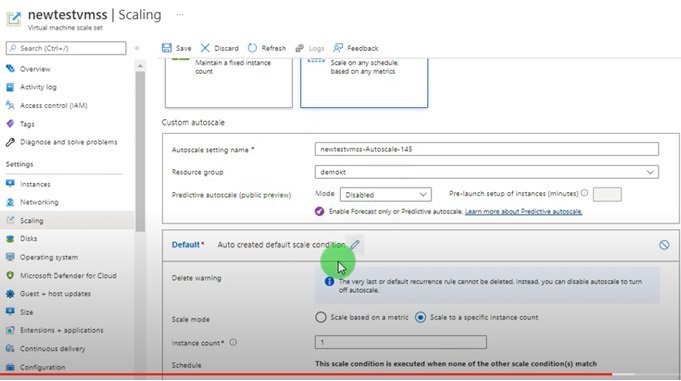
- Enter required details:
- select scale based on a metrics:
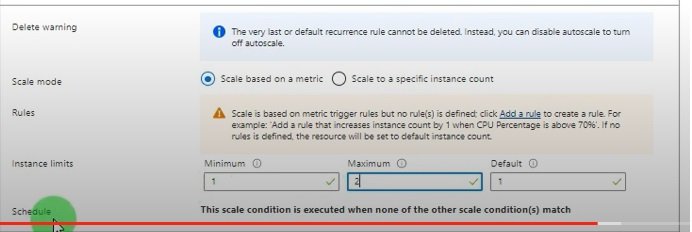
- Enter min, max and default numbers.
- Click on add a rule.
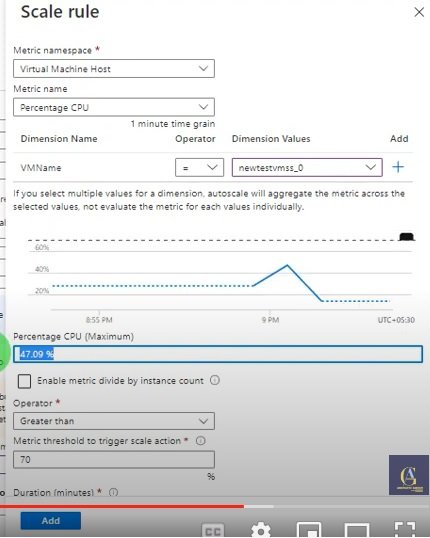
- Create profile:
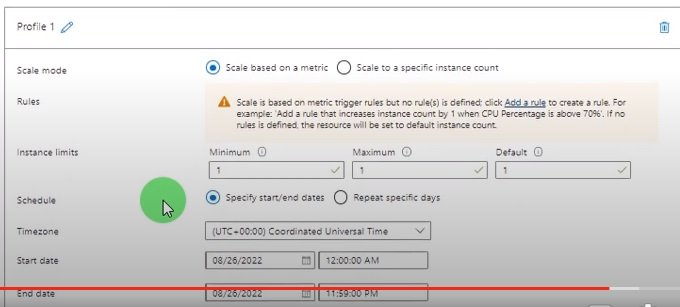
- Increase CPU utilization to check horizontol scaling:
- Run the following script in the VM created.
-
paste the following text into a vbs file:
Dim goal Dim before Dim x Dim y Dim i goal = 2181818 Do While True before = Timer For i = 0 to goal x = 0.000001 y = sin(x) y = y + 0.00001 Next y = y + 0.01 Loop
-
- Open a txt file and save as name.vbs and run in the command prompt
- right click file and click more options and choose to run on command prompt.
- now check the CPU utilization, goes high.
- Custom Autoscaling.
- Manual scaling:
- Step 1: Create a Vnet, Subnet1, SG with Allow port 3389,80 and attach with Subnet1, VM & Install all required applications(IIS):
Creating VM Scale Sets through portal using scale sets to deploy 2 VMs Manually:
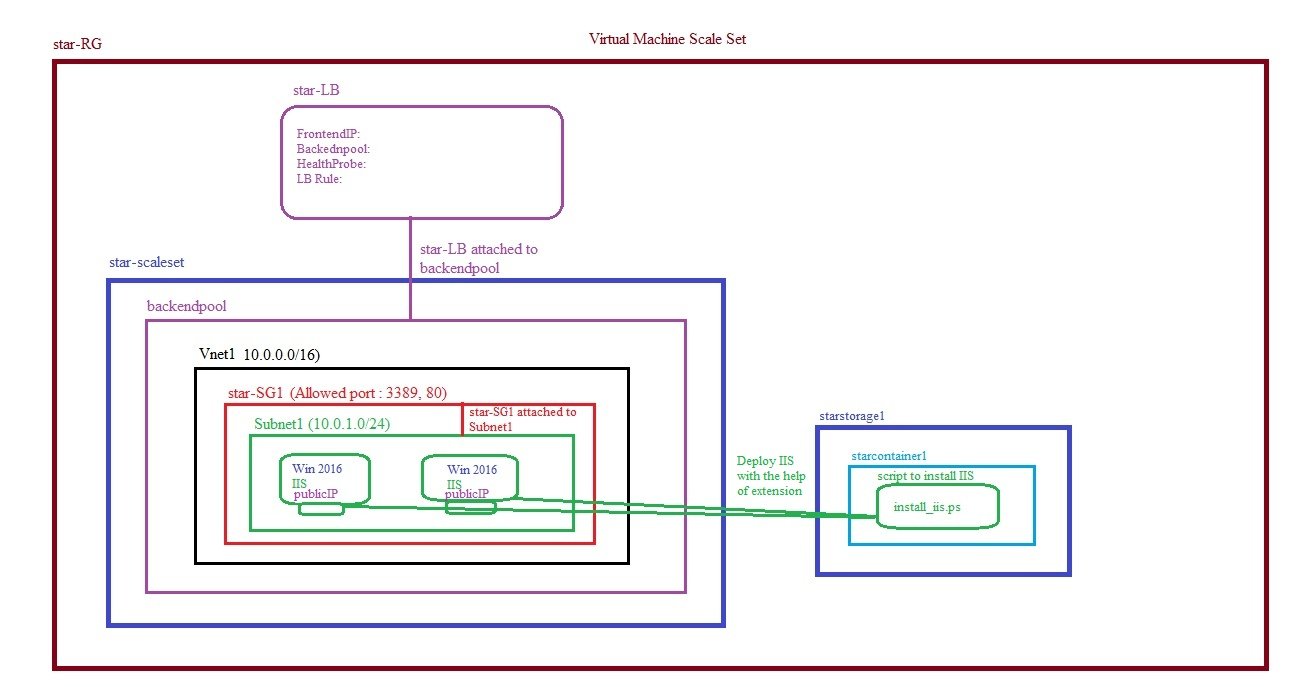
- Step1: Create a vnet, Subnet
- Vnet1 (10.0.0.0/16)
- Subnet1 (10.0.1.0/24)
- Step 2: Create Load Balancer, FrontendIP, Backendpool, Inbound Rule, Healthprobe
- star-LB (sku=standard, type = public, Tier = Regional)
- FrontendIP (IPv4, LBPublicIP (standard, Regional))
- backendpool(Vnet1), No Vms are attaching in the target as it will be done through scaleset.
- LBRule1 (attach FrontendIP & backendpool)
- starHP (port 80, backend port 80)
- Step 3: Create Network Security Group (star-SG1), Inbound security rule allowed 3389, 80. Associate star-SG1 to Subnet1.
- star-SG1
- Inbound Security Rule Allowed 3389, Priority 100, Allowed 80, Priority 200
- Associate star-SG1 with Subnet1
- Step 4: Create Storage Account, Container, upload script
- starstorage1 (Standard, LRS)
- starcontainer1
- upload blob install_iis.ps1
- Step 5: Create Scale Set
- star-scaleset
- Orchestration Mode: Uniform (Automatic upgrade: it applies to all instances if we make any changes in scale set)
- security type: Standard
- Scaling: Manually update the capacity
- Instance count: 2 (two vms will be created and attached with backednpool)
- Image: Windows server 2016
- Size: Standard_B1s
- Administrator account:
- Networking:
- virtual network: Vnet1
- Network Interface: NIC for the instances created in virtual machine scale set, to assign public IP to VMs click edit and Enabled public IP address.
- Load balancing, Azure load balancer: select star-LB, backend pool.
- Management:
- Upgrade policy: Automatic (if any changes made in instance which will update automatically in all other instances, it only supports with uniform option which was selected in orchestration mode)
- Advanced: Extension +Add and search custom scription extension and select, browse script file (script has been uploaded in step4, which will be use to install IIS in instances)
- Review & Create
- Step 6: Testing
- Go to virtual machine scale set and check instances, click any instance and copy pubic IP, paste it in browser to display IIS default page.
- Upgrade policy: Automatic
- Go to load balancer: Backednpool: check both instances appear, FrontendIP, copy and paste IP in browser.
Creating VM Scale Sets through Terraform:

- Step1: Create a vnet, Subnet, Network Security Group (star-SG1), Inbound security rule allowed 3389, 80. Associate star-SG1 to Subnet1.
- Vnet1 (10.0.0.0/16)
- Subnet1 (10.0.1.0/24)
- star-SG1
- Inbound Security Rule Allowed 3389, Priority 100, Allowed 80, Priority 200
- Associate star-SG1 with Subnet1
- NIC is not creating as VM arr installing with scale set.
- vnet.tf
-
locals {resource_group_name="Star-RG"location="UK South"virtual_network ={name="Vnet1"address_space="10.0.0.0/16"}}resource "azurerm_resource_group" "RG" {name = local.resource_group_namelocation = local.location}resource "azurerm_virtual_network" "vnet" {name = local.virtual_network.namelocation = local.locationresource_group_name = local.resource_group_nameaddress_space = [local.virtual_network.address_space]
depends_on = [ azurerm_resource_group.RG ]
}resource "azurerm_subnet" "subnet1" {name = "subnet1"resource_group_name = local.resource_group_namevirtual_network_name = local.virtual_network.nameaddress_prefixes = ["10.0.1.0/24"]depends_on = [ azurerm_virtual_network.vnet ]}resource "azurerm_network_security_group" "NSG" {name = "NSG1"location = local.locationresource_group_name = local.resource_group_namesecurity_rule {name = "rule1"priority = 100direction = "Inbound"access = "Allow"protocol = "Tcp"source_port_range = "*"destination_port_range = "3389"source_address_prefix = "*"destination_address_prefix = "*"}
security_rule {name = "rule2"priority = 101direction = "Inbound"access = "Allow"protocol = "Tcp"source_port_range = "*"destination_port_range = "80"source_address_prefix = "*"destination_address_prefix = "*"}depends_on = [ azurerm_resource_group.RG ]}
resource "azurerm_subnet_network_security_group_association" "NSGAssociation" {subnet_id = azurerm_subnet.subnet1.idnetwork_security_group_id=azurerm_network_security_group.NSG.id}
- Step 2: Create Load Balancer, FrontendIP, Backendpool, Inbound Rule, Healthprobe
- star-LB (sku=standard, type = public, Tier = Regional)
- FrontendIP (IPv4, LBPublicIP (standard, Regional))
- backendpool(Vnet1), No Vms are attaching in the target as it will be done through scaleset.
- LBRule1 (attach FrontendIP & backendpool)
- starHP (port 80, backend port 80)
- lb.tf
-
#creating public IP for load balancerresource "azurerm_public_ip" "loadbalancerIP" {name = "loadbalancerIP"resource_group_name = local.resource_group_namelocation = local.locationallocation_method = "Static"sku = "Standard"
tags = {environment = "webserver"}depends_on = [ azurerm_resource_group.RG ]}
#creating Basic Load Balancer & frontendIP association with public IPresource "azurerm_lb" "lb" {name = "StarLoadBalancer"location = local.locationresource_group_name = local.resource_group_namesku = "Standard"sku_tier = "Regional"
frontend_ip_configuration {name = "FrontendIP"public_ip_address_id = azurerm_public_ip.loadbalancerIP.id}depends_on = [ azurerm_public_ip.loadbalancerIP ]}
#creating backend poolresource "azurerm_lb_backend_address_pool" "backendpool" {loadbalancer_id = azurerm_lb.lb.idname = "Basicbackendpool"depends_on = [ azurerm_lb.lb ]}
#Creating health probe which will check the health of VMs attached in backendpoolresource "azurerm_lb_probe" "starHP" {loadbalancer_id = azurerm_lb.lb.idname = "healthprobe"port = 80protocol = "Tcp"depends_on = [ azurerm_lb.lb ]}
#Creating LB ruleresource "azurerm_lb_rule" "LBRule" {loadbalancer_id = azurerm_lb.lb.idname = "LBRule"protocol = "Tcp"frontend_port = 80backend_port = 80frontend_ip_configuration_name = "FrontendIP"backend_address_pool_ids = [azurerm_lb_backend_address_pool.backendpool.id]probe_id = azurerm_lb_probe.starHP.iddepends_on = [ azurerm_lb.lb ]}
-
- Step 3: Create Storage Account, Container, upload script
- starstorage1 (Standard, LRS)
- starcontainer1
- upload blob install_iis.ps1
- iis.tf
- Go to terraform.io/azure/documentation and search virtual machine scale set extension
-
resource "azurerm_storage_account" "starstorage1" {name = "starstorage1"resource_group_name = local.resource_group_namelocation = local.locationaccount_tier = "Standard"account_replication_type = "LRS"account_kind = "StorageV2"
depends_on = [ azurerm_resource_group.RG ]}
resource "azurerm_storage_container" "container" {name = "starcontainer1"storage_account_name = "starstorage1"container_access_type = "blob"depends_on = [ azurerm_storage_account.starstorage1 ]}
resource "azurerm_storage_blob" "iisconfig" {name = "install_iis.ps1"storage_account_name = "starstorage1"storage_container_name = "starcontainer1"type = "Block"source = "install_iis.ps1"depends_on = [ azurerm_storage_container.container ]}
resource "azurerm_virtual_machine_extension" "starextension" {count = var.number_of_machinename = "extension${count.index}"virtual_machine_id = azurerm_windows_virtual_machine.VM[count.index].idpublisher = "Microsoft.Compute"type = "CustomScriptExtension"type_handler_version = "1.10"
settings = <<SETTINGS{"fileUris": ["https://${azurerm_storage_account.starstorage1.name}.blob.core.windows.net/starcontainer1/install_iis.ps1"],"commandToExecute": "powershell -ExecutionPolicy Unrestricted -file install_iis.ps1"}SETTINGS
tags = {environment = "Production"}}
resource "azurerm_virtual_machine_scale_set_extension" "extension" {name = "scalesetextension"virtual_machine_scale_set_id = azurerm_windows_virtual_machine_scale_set.scaleset.idpublisher = "Microsoft.Compute"type = "CustomScriptExtension"type_handler_version = "1.10"settings = <<SETTINGS{"fileUris": ["https://${azurerm_storage_account.starstorage1.name}.blob.core.windows.net/starcontainer1/install_iis.ps1"],"commandToExecute": "powershell -ExecutionPolicy Unrestricted -file install_iis.ps1"}SETTINGSdepends_on = [ azurerm_storage_blob.iisconfig ]}
- Step 5: Create Scale Set
- star-scaleset
- Orchestration Mode: Uniform (Automatic upgrade: it applies to all instances if we make any changes in scale set)
- security type: Standard
- Scaling: Manually update the capacity
- Instance count: 2 (two vms will be created and attached with backednpool)
- Image: Windows server 2016
- Size: Standard_B1s
- Administrator account:
- Networking:
- virtual network: Vnet1
- Network Interface: NIC for the instances created in virtual machine scale set, to assign public IP to VMs click edit and Enabled public IP address.
- Load balancing, Azure load balancer: select star-LB, backend pool.
- Management:
- Upgrade policy: Automatic (if any changes made in instance which will update automatically in all other instances, it only supports with uniform option which was selected in orchestration mode)
- Advanced: Extension +Add and search custom scription extension and select, browse script file (script has been uploaded in step4, which will be use to install IIS in instances)
- Review & Create
- scaleset.tf
- Go to terraform.io/azure/documentation/search virtual machine scale set
-
resource "azurerm_windows_virtual_machine_scale_set" "scaleset" {name = "star-scaleset"resource_group_name = local.resource_group_namelocation = local.location#While creating vm we define size and in scale set it is define as skusku = "Standard_B1s"instances = var.number_of_machineadmin_password = "India123456789"admin_username = "abdul"computer_name_prefix = "VM-"upgrade_mode = "Automatic"
source_image_reference {publisher = "MicrosoftWindowsServer"offer = "WindowsServer"sku = "2016-Datacenter"version = "latest"}
os_disk {storage_account_type = "Standard_LRS"caching = "ReadWrite"}
network_interface {name = "NIC"primary = true
ip_configuration {name = "internal"primary = truesubnet_id = azurerm_subnet.subnet1.idload_balancer_backend_address_pool_ids = [azurerm_lb_backend_address_pool.backendpool.id]}}depends_on = [ azurerm_subnet.subnet1,azurerm_lb_backend_address_pool.backendpool,azurerm_resource_group.RG ]}
- Step 6: Testing
- Go to virtual machine scale set and check instances, click any instance and copy pubic IP, paste it in browser to display IIS default page.
- Upgrade policy: Automatic
- Go to load balancer: Backednpool: check both instances appear, FrontendIP, copy and paste IP in browser.
- Code
- code
Code
- code
- code
- code
Code
- code
- code
- code
Code
- code
- code
- code
Code
- code
- code
- code
Code
- code
- code
- code
Code
- code
- code
- code
Code
- code
- code
- code
Code
- code
- code
- code
Code
- code
- code
- code
Code
- code
- code
- code
- code
- code
- code
Code
- Code
- Code
- Code
- Code
Data Block
- Creating a resource in an existing resource with terraform.
- In the existing Vnet1, creating a subnet
- Go to terraform.io select azure provider, click documentation and search virtual network and in data sources, copy and paste code.
- provider.tf
-
terraform {required_providers {azurerm = {source = "hashicorp/azurerm"version = "4.8.0"}}}
provider "azurerm" {subscription_id = "bd2ade99-0834-4cfe-bb19-ddf0e89ed9f4"tenant_id = "4b9f3326-b87a-468f-89d4-4c34403eae39"client_id = "363c6475-89bc-4948-9396-6dc6849eeb14"client_secret = "yUR8Q~2w~xi~~i6hUJkw4XCZRPCNVwIpIkTrcaPW"features {}}
-
- data_block.tf
-
data "azurerm_virtual_network" "Vnet1" { name = "Vnet1" resource_group_name = "star-RG" } output "virtual_network_id" { value = data.azurerm_virtual_network.example.id } -
Values has been taken from existing Vnet1.resource "azurerm_subnet" "subnet1" {name = "subnet1"resource_group_name = "star-RG"virtual_network_name = data.azurerm_virtual_network.Vnet1.nameaddress_prefixes = ["10.0.1.0/24"]}
- Creating a new subnet and providing reference of data block for vnet.
-
- #terraform init
- #terraform plan data_block.tfplan
- #terraform apply "data_block.tfplan"
- Code
- Code
Key Vault
- Creating a key vault:
- Go to terrform.io/ azure/ documentation/ search for key vault, copy the code.
- azurerm_key_vault.tf
-
resource "azurerm_key_vault" "example" { name = "examplekeyvault" location = azurerm_resource_group.example.location resource_group_name = azurerm_resource_group.example.name enabled_for_disk_encryption = true tenant_id = data.azurerm_client_config.current.tenant_id soft_delete_retention_days = 7 purge_protection_enabled = false sku_name = "standard" access_policy { tenant_id = data.azurerm_client_config.current.tenant_id object_id = data.azurerm_client_config.current.object_id key_permissions = [ "Get", ] secret_permissions = [ "Get", ] storage_permissions = [ "Get", ] } }
-
- azurerm_key_vault_secret
-
resource "azurerm_key_vault_secret" "example" { name = "secret-sauce" value = "szechuan" key_vault_id = azurerm_key_vault.example.id }
-
- LAB:
- provider.tf
-
terraform {required_providers {azurerm = {source = "hashicorp/azurerm"version = "4.8.0"}}}
provider "azurerm" {subscription_id = "bd2ade99-0834-4cfe-bb19-ddf0e89ed9f4"tenant_id = "4b9f3326-b87a-468f-89d4-4c34403eae39"client_id = "289f6253-b6eb-4930-bc19-3557cad4b72d"client_secret = "LlM8Q~UauskuRH84yA1QDDxc3K0w8sGl1y4ZsbTi"features {}} - variable.tf
-
variable "client_secret" {type = stringsensitive = true}
variable "no_of_subnet" {type = number}
variable "no_of_nic" {type = number}variable "no_of_vm" {type = number}
-
- vnet.tf
-
locals {resource_group_name="star-RG"location="UK South"virtual_network={name="Vnet1"address_space="10.0.0.0/16"}security_group = "star-SG"}
resource "azurerm_resource_group" "RG" {name = local.resource_group_namelocation = local.location}
resource "azurerm_network_interface" "NIC" {count = var.no_of_nicname = "NIC${count.index}"location = local.locationresource_group_name = local.resource_group_name
ip_configuration {name = "Internal"subnet_id = azurerm_subnet.subnets[count.index].idprivate_ip_address_allocation = "Dynamic"public_ip_address_id = azurerm_public_ip.publicip[count.index].id}depends_on = [ azurerm_subnet.subnets,azurerm_public_ip.publicip ]}
resource "azurerm_public_ip" "publicip" {count = var.no_of_nicname = "publicip${count.index}"resource_group_name = local.resource_group_namelocation = local.locationallocation_method = "Static"sku = "Standard"zones = ["${count.index+1}"]
tags = {Dept = "IT"}depends_on = [ azurerm_resource_group.RG ]}
resource "azurerm_virtual_network" "VNET" {name = local.virtual_network.namelocation = local.locationresource_group_name = local.resource_group_nameaddress_space = [local.virtual_network.address_space]
depends_on = [ azurerm_resource_group.RG ]}
-
- key_vault.tf
-
data "azurerm_client_config" "tenantID" {}resource "azurerm_key_vault" "keyvault5" {name = "star-keyvault5"location = local.locationresource_group_name = local.resource_group_name# enabled_for_disk_encryption = truetenant_id = data.azurerm_client_config.tenantID.tenant_idsoft_delete_retention_days = 7purge_protection_enabled = false
sku_name = "standard"# in the following we define Get permissionaccess_policy {tenant_id = data.azurerm_client_config.tenantID.tenant_id# object ID can be get from app registration which is created in Entra ID with the name terraformobject_id = data.azurerm_client_config.tenantID.object_id
secret_permissions = ["Get", "Set"]}depends_on = [ azurerm_resource_group.RG ]}
# creating secret in key vault in the below section.resource "azurerm_key_vault_secret" "secret" {name = "vmpassword5"value = "India123456789"key_vault_id = azurerm_key_vault.keyvault5.id
depends_on = [ azurerm_key_vault.keyvault5 ]}
-
- vm_count.tf
-
resource "azurerm_windows_virtual_machine" "VM1" {count = var.no_of_vmname = "VM${count.index}"resource_group_name = local.resource_group_namelocation = local.locationsize = "Standard_DS1_v2"admin_username = "abdul"admin_password = azurerm_key_vault_secret.secret.valuezone = (count.index+1)network_interface_ids = [azurerm_network_interface.NIC[count.index].id]
os_disk {caching = "ReadWrite"storage_account_type = "Standard_LRS"}
source_image_reference {publisher = "MicrosoftWindowsServer"offer = "WindowsServer"sku = "2016-Datacenter"version = "latest"}depends_on = [ azurerm_network_interface.NIC, azurerm_resource_group.RG,azurerm_key_vault_secret.secret ]}
-
- #terraform init
- #terraform plan -out vm_count.tf
- #terraform apply "vm_count.tf"
- Configure Azure Key Vault as Data Source (VM Password) use it in VM.
- Step1: Register a app (terraform) in azure intra ID. (go to Entra ID/Registration/new)
- Assign contributor role to terraform app. (go to subscription , access control, assign rol, search terraform and assign).
- Step 2: Azure key vault is created(star-keyvault), secrete created (vmpassword).
- Go to portal/ security / Infrastructure and Network Security / Key Vault: create
- Basic:
- Subscription: select subscription
- Resource Group - star-RG1
- key vault name: starkeyvault1 (name should be unique)
- Region: UK South
- Pricing Teir: Standard or Premium (can get enhanced security feature)
- Soft Delete : 90 days, (accidentally delete can be recovered in number of days)
- Purge protection: Enable / Disable (If enabled than any key vault deleted by mistake and soft delete is defined than during that period no one can delete vault permanently)
- Acces Configuration:
- To access a key vault in data plane, all callers (users or applications) must have proper authentication and authorization. Authentication establishes the identity of the caller. Authorization determines which operations the caller can execute
- permission Model: following 2 permission models available
- Azure Role based Control: management group/subscription/RG or keyvault level can be assigned
- vault access policy: we can set the permission for access key or certificate within key vault. (select user and edit permissions)
- Resource Access: Azure Virtual Machines for deployment, Azure Resource Manager for template deployment, Azure Disk Encryption for volume encryption.
- Networking:
- Enable public access: select check box
- Public Access: Allow access from : all networks, selected networks,
- Private Endpoint:
- Review & Create:
- Select the resource created, go to objects/secrets and create secrete in which we define vmpassword.
- Secrets: Generates / Imports:
- Upload options: Manual
- Name: vmpassword1
- secret value: India123456789
- Content Type: optional
- Set Activation date: can set for future date
- Set Expiration date: enter expiry date for this secret
- Enabled: Yes/No
- Tags:
- Secrets: Generates / Imports:
- Step 3: Give Get permission to terraform for key vault secret
- Go to star-keyvault/acces policies/create, select get in permissions, in principal tab select terraform, create.
- Step 4: create terraform code:
- provider.tf
-
terraform {required_providers {azurerm = {source = "hashicorp/azurerm"version = "4.8.0"}}}
provider "azurerm" {subscription_id = "bd2ade99-0834-4cfe-bb19-ddf0e89ed9f4"tenant_id = "4b9f3326-b87a-468f-89d4-4c34403eae39"client_id = "363c6475-89bc-4948-9396-6dc6849eeb14"client_secret = "yUR8Q~2w~xi~~i6hUJkw4XCZRPCNVwIpIkTrcaPW"features {}}
-
- variables.tf
-
variable "client_secret" {type = stringsensitive = true}
variable "no_of_subnet" {type = number}
variable "no_of_nic" {type = number}variable "no_of_vm" {type = number}
-
- vnet.tf
-
locals {resource_group_name="star-RG"location="UK South"virtual_network={name="Vnet1"address_space="10.0.0.0/16"}security_group = "star-SG"}
resource "azurerm_resource_group" "RG" {name = local.resource_group_namelocation = local.location}
resource "azurerm_network_interface" "NIC" {count = var.no_of_nicname = "NIC${count.index}"location = local.locationresource_group_name = local.resource_group_name
ip_configuration {name = "Internal"subnet_id = azurerm_subnet.subnets[count.index].idprivate_ip_address_allocation = "Dynamic"public_ip_address_id = azurerm_public_ip.publicip[count.index].id}depends_on = [ azurerm_subnet.subnets,azurerm_public_ip.publicip ]}
resource "azurerm_public_ip" "publicip" {count = var.no_of_nicname = "publicip${count.index}"resource_group_name = local.resource_group_namelocation = local.locationallocation_method = "Static"sku = "Standard"zones = ["${count.index+1}"]
tags = {Dept = "IT"}depends_on = [ azurerm_resource_group.RG ]}
resource "azurerm_virtual_network" "VNET" {name = local.virtual_network.namelocation = local.locationresource_group_name = local.resource_group_nameaddress_space = [local.virtual_network.address_space]
depends_on = [ azurerm_resource_group.RG ]}
resource "azurerm_subnet" "subnets" {count = var.no_of_subnetname = "Subnet${count.index}"resource_group_name = local.resource_group_namevirtual_network_name = local.virtual_network.nameaddress_prefixes = ["10.0.${count.index}.0/24"]depends_on = [ azurerm_virtual_network.VNET ]}
resource "azurerm_network_security_group" "SG" {name = local.security_grouplocation = local.locationresource_group_name = local.resource_group_namedepends_on = [ azurerm_resource_group.RG ]
security_rule {name = "test123"priority = 100direction = "Inbound"access = "Allow"protocol = "Tcp"source_port_range = "*"destination_port_range = "3389"source_address_prefix = "*"destination_address_prefix = "*"}}
resource "azurerm_subnet_network_security_group_association" "assoc_subnet" {count = var.no_of_subnetsubnet_id = azurerm_subnet.subnets[count.index].idnetwork_security_group_id = azurerm_network_security_group.SG.id}
-
- vm_count.tf:
- we define data block of key vault as it has been created earlier.
- go to terraform.io/azure/documentation/search key vault and copy data block code.
-
data "azurerm_key_vault" "keyvault1" {name = "starkeyvault1"resource_group_name = "star-RG1"}
data "azurerm_key_vault_secret" "secret" {name = "vmpassword1"key_vault_id = data.azurerm_key_vault.keyvault1.id}
resource "azurerm_windows_virtual_machine" "VM1" {count = var.no_of_vmname = "VM${count.index}"resource_group_name = local.resource_group_namelocation = local.locationsize = "Standard_DS1_v2"admin_username = "abdul"admin_password = data.azurerm_key_vault_secret.secret.valuezone = (count.index+1)network_interface_ids = [azurerm_network_interface.NIC[count.index].id]
os_disk {caching = "ReadWrite"storage_account_type = "Standard_LRS"}
source_image_reference {publisher = "MicrosoftWindowsServer"offer = "WindowsServer"sku = "2016-Datacenter"version = "latest"}depends_on = [ azurerm_network_interface.NIC, azurerm_resource_group.RG ]} - data block for key vault has been defined.
- data block for secret where vmpassword as secret has been created to fetch password.
- #terraform init
- #terraform plan -out vm_count.tfplan
- #terraform apply "vm_count.tfplan"
- Code
- Code
- Creating a key vault:
Bastion Host
- Azure Bastion is a fully platform-managed PaaS service, It works as jump server. You will connect to Bastion server/host with its public IP through SSL https 443 port.
- It is provisioned inside your virtual network, It provides secure and seamless RDP/SSH connectivity to your virtual machines directly in the Azure portal over SSL.
- If you have multiple Vnets that you want to RDP or SSH into from the Azure management portal, then you should deploy Azure Bation for each of those Vnets
- Subnet name must be AzureBastionSubnet.
- All the resources will be created on different subnet with private IP. Bastion host will connect you to these resources using browser.
- bastion.tf
- enter code bastion subnet.
- enter code for public IP.
- Enter code for deployment of bastion.
-
resource "azurerm_resource_group" "example" { name = "example-resources" location = "West Europe" } resource "azurerm_virtual_network" "example" { name = "examplevnet" address_space = ["192.168.1.0/24"] location = azurerm_resource_group.example.location resource_group_name = azurerm_resource_group.example.name } resource "azurerm_subnet" "example" { name = "AzureBastionSubnet" resource_group_name = azurerm_resource_group.example.name virtual_network_name = azurerm_virtual_network.example.name address_prefixes = ["192.168.1.224/27"] } resource "azurerm_public_ip" "example" { name = "examplepip" location = azurerm_resource_group.example.location resource_group_name = azurerm_resource_group.example.name allocation_method = "Static" sku = "Standard" } resource "azurerm_bastion_host" "example" { name = "examplebastion" location = azurerm_resource_group.example.location resource_group_name = azurerm_resource_group.example.name ip_configuration { name = "configuration" subnet_id = azurerm_subnet.example.id public_ip_address_id = azurerm_public_ip.example.id } }
-
- LAB:
- provider.tf
-
terraform {required_providers {azurerm = {source = "hashicorp/azurerm"version = "4.8.0"}}}
provider "azurerm" {subscription_id = "bd2ade99-0834-4cfe-bb19-ddf0e89ed9f4"tenant_id = "4b9f3326-b87a-468f-89d4-4c34403eae39"client_id = "289f6253-b6eb-4930-bc19-3557cad4b72d"client_secret = "LlM8Q~UauskuRH84yA1QDDxc3K0w8sGl1y4ZsbTi"features {}}
-
- vnet.tf
-
locals {resource_group_name="star-RG"location="UK South"virtual_network={name="Vnet1"address_space="10.0.0.0/16"}security_group = "star-SG"}
resource "azurerm_resource_group" "RG" {name = local.resource_group_namelocation = local.location}
resource "azurerm_virtual_network" "VNET" {name = local.virtual_network.namelocation = local.locationresource_group_name = local.resource_group_nameaddress_space = [local.virtual_network.address_space]
depends_on = [ azurerm_resource_group.RG ]}
resource "azurerm_subnet" "subnets" {name = "vmsubnet"resource_group_name = local.resource_group_namevirtual_network_name = local.virtual_network.nameaddress_prefixes = ["10.0.1.0/24"]depends_on = [ azurerm_virtual_network.VNET ]}
resource "azurerm_network_security_group" "SG" {name = local.security_grouplocation = local.locationresource_group_name = local.resource_group_namedepends_on = [ azurerm_resource_group.RG ]
security_rule {name = "test123"priority = 100direction = "Inbound"access = "Allow"protocol = "Tcp"source_port_range = "*"destination_port_range = "3389"source_address_prefix = "*"destination_address_prefix = "*"}}
resource "azurerm_subnet_network_security_group_association" "assoc_subnet" {subnet_id = azurerm_subnet.subnets.idnetwork_security_group_id = azurerm_network_security_group.SG.id}
resource "azurerm_network_interface" "NIC" {name = "NIC1"location = local.locationresource_group_name = local.resource_group_name
ip_configuration {name = "Internal"subnet_id = azurerm_subnet.subnets.idprivate_ip_address_allocation = "Dynamic"}depends_on = [ azurerm_subnet.subnets]}
-
- vm_count.tf
-
resource "azurerm_windows_virtual_machine" "VM1" {
name = "VM1"resource_group_name = local.resource_group_namelocation = local.locationsize = "Standard_DS1_v2"admin_username = "abdul"admin_password = "India123456789"network_interface_ids = [azurerm_network_interface.NIC.id]
os_disk {caching = "ReadWrite"storage_account_type = "Standard_LRS"}
source_image_reference {publisher = "MicrosoftWindowsServer"offer = "WindowsServer"sku = "2016-Datacenter"version = "latest"}depends_on = [ azurerm_network_interface.NIC, azurerm_resource_group.RG]}
-
- bastion.tf
-
resource "azurerm_subnet" "bastionsubnet" {name = "AzureBastionSubnet"resource_group_name = local.resource_group_namevirtual_network_name = local.virtual_network.nameaddress_prefixes = ["10.0.2.0/24"]depends_on = [ azurerm_virtual_network.VNET ]}
resource "azurerm_public_ip" "bastionip" {name = "bastionip"resource_group_name = local.resource_group_namelocation = local.locationallocation_method = "Static"sku = "Standard"
tags = {IP = "Bastion"}depends_on = [ azurerm_resource_group.RG ]}
resource "azurerm_bastion_host" "star-bastion" {name = "star-bastion"location = local.locationresource_group_name = local.resource_group_name
ip_configuration {name = "configuration"subnet_id = azurerm_subnet.bastionsubnet.idpublic_ip_address_id = azurerm_public_ip.bastionip.id}}
-
- #terraform init
- #terraform plan -out bastion.tfplan
- #terraform apply "bastion.tfplan"
- To check:
- Go to vm1/connect and select bastion. it will open VM in browser.
- Code
- Code
Service Endpoints
- End Point make connection between two azure services privately.
- Some azure services required internet in order to access them, like storage, database etc..
- You do not provide Public IP to your applicaiton VMs but need access to storage or databse.
- Azure provides service endpoints which makes communication using private IP address of you VM to connect to these services.
- Code
- Code
App Services & Deployment Slot, GitHub Integration, Application Insights
Creating App Service, App Service Plan, Windows based.
- Create RG (star-RG), app service plan B1, windows (starplan1), web app (starapp1), runtime stack .NET 7.0
- Go to terraform.io/azure/documentation and search azurerm service plan, copy code for service plan, search for app service and copy for windows web app.
- webapp.tf
-
locals {resource_group_name="star-RG"location="UK South"}
resource "azurerm_resource_group" "RG" {name = local.resource_group_namelocation = local.location}
#creating app service planresource "azurerm_service_plan" "starplan1" {name = "starplan1"resource_group_name = local.resource_group_namelocation = local.locationos_type = "Windows"sku_name = "B1"
depends_on = [ azurerm_resource_group.RG ]}
resource "azurerm_windows_web_app" "starapp1" {name = "starapp1"resource_group_name = local.resource_group_namelocation = local.locationservice_plan_id = azurerm_service_plan.starplan1.id
site_config {application_stack {current_stack = "dotnet"dotnet_version = "v7.0"}}depends_on = [ azurerm_service_plan.starplan1 ]}
-
- provider.tf
-
terraform {required_providers {azurerm = {source = "hashicorp/azurerm"version = "4.8.0"}}}
provider "azurerm" {subscription_id = "bd2ade99-0834-4cfe-bb19-ddf0e89ed9f4"tenant_id = "4b9f3326-b87a-468f-89d4-4c34403eae39"client_id = "289f6253-b6eb-4930-bc19-3557cad4b72d"client_secret = "LlM8Q~UauskuRH84yA1QDDxc3K0w8sGl1y4ZsbTi"features {}} - #terraform init
- #terraform plan -out webapp.tfplan
- #terraform apply "webapp.tfplan"
-
Creating Deployment Slots with portal:
- Go to App Services Blade:
- Quickstart:
- Deployment slots:
- Apps are deployed on production deployment slot for users to access. changes on live apps will result in downtime and impact the users.
- Azure provide other deployment slots where you can make changes and test it than move it to production slot for users.
- create a deployment slot:
- Go to App Services blade/Deployment/Deployment slots/create
- Name = dev
- Clone settings from = define web app name (it will clone into dev slot)
- Check there will be two slots and traffic on one slot is 100% on production slot.
- Make changes in apps in your local folder.
- Go to Deployment center and deploy the site, use manual deployment using FTP. (check below Deployment Center)
- note down, username, password.
- Open filezilla and paste username, password and Quickconnect. copy files to Remote site.
- Go to deployment slot and click swap so dev slot will be swap to production.
- Deployment Center:
- Deployment of App Manually using FTPS credentials:
- Go to App service created /Deployment Center/ FTPS Credentials
- Download ftp/ftps tool (FileZilla) in your PC and install it in order to connect to Azure webapp service to upload files.
- Download a website template: In google search download sample website and select any template and download it. Extract it.
- click on FTPS credentials: URL, username and password and paste it in filezilla and quickconnect.
- Transfer files to remote site: /site/wwwroot
- Go to web apps/overview copy url and paste it in browser.
- Deployment of App Continuously: CI/CD with Github, Bitbucket, Local Git, Azure Repos
- Use these details while creating webapp(publish=code, Runtime stack=.NET 8.0, O/S=Windows)
- Install visual studio 2022 in local PC:
- create new project
- select ASP.NET Core Web App
- Enter solution name = starwebapp3 and define location
- Enter Target framework = .NET 8.0
- Create.
Creating Deployment slot with Terraform:
- provider.tf
- webapp.tf
- Go to terraform.io/azure/documentation/azurerm_windows_web_app_slot.
-
locals {resource_group_name="star-RG"location="UK South"}
resource "azurerm_resource_group" "RG" {name = local.resource_group_namelocation = local.location}
#creating app service planresource "azurerm_service_plan" "starplan1" {name = "starplan1"resource_group_name = local.resource_group_namelocation = local.locationos_type = "Windows"sku_name = "P1v2"
depends_on = [ azurerm_resource_group.RG ]}#creating app service
resource "azurerm_windows_web_app" "starapp1" {name = "starapp1"resource_group_name = local.resource_group_namelocation = local.locationservice_plan_id = azurerm_service_plan.starplan1.id
site_config {application_stack {current_stack = "dotnet"dotnet_version = "v8.0"}}depends_on = [ azurerm_service_plan.starplan1 ]}
#Integrate GitHub repository with web appresource "azurerm_app_service_source_control" "github_integration" {app_id = azurerm_windows_web_app.starapp1.idrepo_url = "https://github.com/stardistributors/starapp5"branch = "master"use_manual_integration = truedepends_on = [ azurerm_windows_web_app.starapp1 ]}#creating dev slotresource "azurerm_windows_web_app_slot" "devslot" {name = "devslot"app_service_id = azurerm_windows_web_app.starapp1.id
site_config {application_stack {current_stack = "dotnet"dotnet_version = "v8.0"}}depends_on = [ azurerm_windows_web_app.starapp1 ]}
-
- #terraform init
- #terraform plan -out webapp.tfplan
- #terraform apply "webapp.tfplan"
- Go to terraform.io/azure/documentation/azurerm_windows_web_app_slot.
Deploy App on Dev slot and perform swap with Terraform:
- provider.tf
- webapp.tf (RG is creating, app service plan, app service, integration with Github, creating dev slot)
-
locals {resource_group_name="star-RG"location="UK South"}
resource "azurerm_resource_group" "RG" {name = local.resource_group_namelocation = local.location}
#creating app service planresource "azurerm_service_plan" "starplan1" {name = "starplan1"resource_group_name = local.resource_group_namelocation = local.locationos_type = "Windows"sku_name = "P1v2"
depends_on = [ azurerm_resource_group.RG ]}#creating app service
resource "azurerm_windows_web_app" "starapp1" {name = "starapp1"resource_group_name = local.resource_group_namelocation = local.locationservice_plan_id = azurerm_service_plan.starplan1.id
site_config {application_stack {current_stack = "dotnet"dotnet_version = "v8.0"}}depends_on = [ azurerm_service_plan.starplan1 ]}
#creating dev slotresource "azurerm_windows_web_app_slot" "devslot" {name = "devslot"app_service_id = azurerm_windows_web_app.starapp1.id
site_config {application_stack {current_stack = "dotnet"dotnet_version = "v8.0"}}depends_on = [ azurerm_windows_web_app.starapp1 ]}#deploying on devslot using github repositoryresource "azurerm_app_service_source_control_slot" "deploy_on_devslot" {slot_id = azurerm_windows_web_app_slot.devslot.idrepo_url = "https://github.com/aziz27uk1/test123"branch = "master"use_manual_integration = truedepends_on = [azurerm_windows_web_app_slot.devslot]} - Web app has been deployed on devslot.
-
- Creating a block to depoy on dev slot.
- Go to terraform.io/azure/documentation/azurerm_app_service_source_control_slot
-
resource "azurerm_app_service_source_control_slot" "example" { slot_id = azurerm_linux_web_app_slot.example.id repo_url = "https://github.com/Azure-Samples/python-docs-hello-world" branch = "master" } - #terraform init
- #terraform plan -out webapp.tfplan
- #terraform apply "webapp.tfplan"
- Testing:
- If you go to deployment slots, there will be two slots (PRODUCTION, devslot), if you click production slot link there will be no deployment, if you click devslot than a deployment has been made)
- In the following we will perform swap so when you click production link site will be displayed and swap has been done. if you click devslot there will not be any deployment.
- Creating a block to swap from devslot to production slot.
- Go to terraform.io/azure/documentation/azurerm_web_app_active_slot.
-
resource "azurerm_web_app_active_slot" "swap" { slot_id = azurerm_windows_web_app_slot.devslot.id } - Insert the above block in the webapp.tf
- #terraform plan -out webapp.tfplan
- #terraform apply "webapp.tfplan"
- swap has been done from dev slot to production slot.
App Service & Github Integration, Build & deploy with credentials in portal:
- Create a project for source code: Install visual studio 2022 in local PC:
- create new project
- select ASP.NET Core Web App
- Enter solution name = starwebapp3 and define location
- Enter Target framework = .NET 8.0
- Create.
- A local repository is created with source code in c:
- Push code to Github:
- Go to Github to upload code to remote repository: Enter credentials of Github
- Create repository startest1.(https://github.com/stardistributors/startest1.git)
- Push project files/code to Github repository:
- In visual studio, Go to Git/Create Git Repository/existing remote/paste URL in remote URL.
- Push and create, It will push code from local repository to remote repository in github, check in github
- Build & Deploy code from Github to web app:
- Go to App service/deployment/deployment center/Settings/source: select CI/CD=Github
- Enter github credentials. and select org, repository, branch
- Authentication settings: user-assigned identity, Basic authentication
- Basic authentication: select & Save it. It will build and deploy, go back to overview, copy url and check in browser.
- user-assigned identity:
- Subscription:
- Identity:
- Save it.
- Make some changes in source code, push in the remote repository, in deployment click redeploy.
- Create a project for source code: Install visual studio 2022 in local PC:
App Service & Github Integration, Build & deploy Manual Deployment using Terraform:
- provider.tf
-
terraform {required_providers {azurerm = {source = "hashicorp/azurerm"version = "4.8.0"}}}
provider "azurerm" {subscription_id = "bd2ade99-0834-4cfe-bb19-ddf0e89ed9f4"tenant_id = "4b9f3326-b87a-468f-89d4-4c34403eae39"client_id = "289f6253-b6eb-4930-bc19-3557cad4b72d"client_secret = "LlM8Q~UauskuRH84yA1QDDxc3K0w8sGl1y4ZsbTi"features {}}
-
- webapp.tf
- for Github integration with web app service, go to terraform.io/azure/documentation and search app service and select azurerm_app_service_source_control
-
locals {resource_group_name="star-RG"location="UK South"}
resource "azurerm_resource_group" "RG" {name = local.resource_group_namelocation = local.location}
#creating app service planresource "azurerm_service_plan" "starplan1" {name = "starplan1"resource_group_name = local.resource_group_namelocation = local.locationos_type = "Windows"sku_name = "B1"
depends_on = [ azurerm_resource_group.RG ]}
resource "azurerm_windows_web_app" "starapp1" {name = "starapp1"resource_group_name = local.resource_group_namelocation = local.locationservice_plan_id = azurerm_service_plan.starplan1.id
site_config {application_stack {current_stack = "dotnet"dotnet_version = "v7.0"}}depends_on = [ azurerm_service_plan.starplan1 ]}
#Integrate GitHub repository with web appresource "azurerm_app_service_source_control" "github_integration" {app_id = azurerm_windows_web_app.starapp1.idrepo_url = "https://github.com/stardistributors/startest1"branch = "master"use_manual_integration = truedepends_on = [ azurerm_windows_web_app.starapp1 ]}
- #terraform init
- #terraform plan -out webapp.tfplan
- #terraform apply "webapp.tfplan"
- provider.tf
Application Insights:
- It is application performance management service through which web app health can be monitored. Can be used to find out any errors or issues in the web app.
Enable Application Insights through portal:
- Step1: Create RG, web app, web app plan.
- When Applicaiton Insights is enabled, instance for application insight and instance for workspace will be created. It will be integrated with app service instance.
- Monitoring data received from app instance will be stored in workspace, and workspace is integrated with application insight instance. You need to create another instance for workspace.
- Once the app service is created, go to Monitoring/Application Insights.
- When you create web app in Monitoring tab Application Insights is Enabled by default. An instance is created.
- click Turn on Application Insights.
- Link to an Application Insights resource.
- Your app will be connected to an auto-created Application Insights resource: starapp1
Instrumentation key will be added to App Settings. This will overwrite any instrumentation key value in web app configuration files. - New resource (starapp1) & Log Analytics Workspace will be created. click apply.
- Go to Resource Group and check an application insight instance is created, another DefaultWorkspace instance is also created in DefaultResourceGroup-SUK.
- Overview:
- Activity Log:
- Tags:
- Diagnose and solve problems:
- Investigate:
- Application map:
- Smart Detection:
- Live Metrics:
- Transaction search:
- Availability:
- Failures:
- Performance:
- Monitoring:
- Alerts:
- Metrics:
- Diagnostic settings:
- Logs:
- Workbooks
- Usage:
- Users:
- Sessions:
- Events:
- User Flows:
- Cohorts:
- more
- Configure:
- Properties:
- Smart detection settings:
- Network Isolation:
- Usage and estimated costs:
- API Access:
- Work Items
- Settings:
- Locks:
- Automation:
- CLI/PS
- Tasks
- Export Teplate
- Help
Enable Application Insights through Terraform:
- Step 1: Create web app & web app plan and deploy application.
- provider.tf
- webapp.tf
-
locals {resource_group_name="star-RG"location="UK South"}
resource "azurerm_resource_group" "RG" {name = local.resource_group_namelocation = local.location}
#creating app service planresource "azurerm_service_plan" "starplan1" {name = "starplan1"resource_group_name = local.resource_group_namelocation = local.locationos_type = "Windows"sku_name = "S1"
depends_on = [ azurerm_resource_group.RG ]}
#creating app serviceresource "azurerm_windows_web_app" "starapp1" {name = "starapp1"resource_group_name = local.resource_group_namelocation = local.locationservice_plan_id = azurerm_service_plan.starplan1.id
site_config {application_stack {current_stack = "dotnet"dotnet_version = "v7.0"}}depends_on = [ azurerm_service_plan.starplan1 ]}
#creating dev slotresource "azurerm_windows_web_app_slot" "devslot" {name = "devslot"app_service_id = azurerm_windows_web_app.starapp1.id
site_config {application_stack {current_stack = "dotnet"dotnet_version = "v7.0"}}app_settings = {"APPINSIGHTS_INTRUMENTATIONKEY" = azurerm_application_insights.app_insights.instrumentation_key"APPLICATIONINSIGHTS_CONNECTION_STRING" = azurerm_application_insights.app_insights.connection_string}depends_on = [ azurerm_windows_web_app.starapp1 ]}
#Deploy in dev slotresource "azurerm_app_service_source_control_slot" "deploy_devslot" {slot_id = azurerm_windows_web_app_slot.devslot.idrepo_url = "https://github.com/aziz27uk1/test123"branch = "master"use_manual_integration = truedepends_on = [ azurerm_windows_web_app_slot.devslot ]}
#create Log Analytics Workspaceresource "azurerm_log_analytics_workspace" "log_analytics" {name = "log_analytics_workspace"location = local.locationresource_group_name = local.resource_group_namesku = "PerGB2018"retention_in_days = 30depends_on = [ azurerm_resource_group.RG ]}
#Create Application Insightsresource "azurerm_application_insights" "app_insights" {name = "starapp1-AppInsights"location = local.locationresource_group_name = local.resource_group_nameapplication_type = "web"workspace_id = azurerm_log_analytics_workspace.log_analytics.iddepends_on = [ azurerm_log_analytics_workspace.log_analytics ]} - #terraform init
- #terraform plan -out webapp.tfplan
- #terraform apply "webapp.tfplan"
- Step 2: Go to terraform.io/azure/documentation/search log analytics workspace
- copy and paste log analytics code.
-
resource "azurerm_log_analytics_workspace" "example" { name = "acctest-01" location = azurerm_resource_group.example.location resource_group_name = azurerm_resource_group.example.name sku = "PerGB2018" retention_in_days = 30 } - Application Insights: search for application insights
-
resource "azurerm_application_insights" "example" { name = "tf-test-appinsights" location = azurerm_resource_group.example.location resource_group_name = azurerm_resource_group.example.name application_type = "web" } - #terraform init
- #terraform plan -out webapp.tfplan
- #terraform apply "webapp.tfplan"
- Step 1: Create web app & web app plan and deploy application.
Database
Create MSSQL Server & Database with Portal.
- Azure SQL Database is fully managed platform as a service (PaaS) database engine.
- It handles most of the database managemet functions such as upgrading, patching, backups, and monitoring without user involvement.
- Creating Azure SQL Server and Database:
- SQL server & database can be created separately or during creation of database can create SQL server.
- Search for SQL Database / All Services/Databases/Modernize existing applications/SQL databases and click create.
- Basics:
- Subscription & RG: pay as you go, star-RG
- Database Name: stardb1
- Server: Create new
- name=stardbserver1
- Region: UK South
- Authentication method: Select your preferred authentication methods for accessing this server. Create a server admin login and password to access your server with SQL authentication, select only Microsoft Entra authentication Learn more using an existing Microsoft Entra user, group, or application as Microsoft Entra admin Learn more , or select both SQL and Microsoft Entra authentication.
- Use Microsoft Entra-only authentication: Set Microsoft Entra Admin
- Use both SQL and Microsoft Entra authentication: Set Microsoft Entra Admin & Server admin login = abdul, password = xxxxxx
- Use SQL authentication: Server admin login = abdul, password = xxxxxx
- Want to use SQL elastic pool: Elastic pools provide a simple and cost effective solution for managing the performance of multiple databases within a fixed budget. An elastic pool provides compute (eDTUs) and storage resources that are shared between all the databases it contains. Databases within a pool only use the resources they need, when they need them, within configurable limits. The price of a pool is based only on the amount of resources configured and is independent of the number of databases it contains.
- Workload Environment: Development or Production
- Compute + Storage: click configure database
- Service Tier = vCore-based purchasing model, DTU-based purchasing model (choose model).
- computer tier: Provisioned (Compute resources are pre-allocated. Billed per hour based on vCores configured. ) or Serverless(Compute resources are auto-scaled. Billed per second based on vCores used)
- Compute Hardware: choose hardware configuration
- vCore: select
- Data max sizeL depend on vCore selection.
- Backup storage redundancy:
- locally-redundant backup storage
- zone-redundant backup storage
- Geo-redundant backup storage
- Geo-Zone-redundant backup storage.
- Networking:
- Network connectivity: Choose an option for configuring connectivity to your server via public endpoint or private endpoint. Choosing no access creates with defaults and you can configure connection method after server creation.
- No access, Public endpoint, Private endpoint.
- connection policy: Configure how clients communicate with your SQL database server.
- Default:Uses Redirect policy for all client connections originating inside of Azure (except Private Endpoint connections) and Proxy for all client connections originating outside Azure
- Proxy: All connections are proxied via the Azure SQL Database gateway
- Redirect: Clients establish connections directly to the node hosting the database
- Encrypted connections: This server supports encrypted connections using Transport Layer Security (TLS). For information on TLS version and certificates, refer to connecting with TLS/SSL.
- TLS 1.0, TLS 1.1, TLS 1.2, TLS 1.3
- Network connectivity: Choose an option for configuring connectivity to your server via public endpoint or private endpoint. Choosing no access creates with defaults and you can configure connection method after server creation.
- Security: Protect your data using Microsoft Defender for SQL, a unified security package including vulnerability assessment and advanced threat protection for your server
- Enable Microsoft Defender for SQL: Protect your data using Microsoft Defender for SQL, a unified security package including vulnerability assessment and advanced threat protection for your server.
- Ledger: Ledger cryptographically verifies the integrity of your data and detects any tampering that might have occurred.
- Server identity: Use system assigned and user assigned managed identities to enable central access management between this database and other Azure resources.
- Transparent data encryption key management: Transparent data encryption encrypts your databases, backups, and logs at rest without any changes to your application. To enable encryption, go to each database. Database level settings if enabled, will override the server level setting.
- Additional settings:
- Data Source: Start with a blank database, restore from a backup or select sample data to populate your new database.
- None:
- Backup
- Sample
- Database collation: Database collation defines the rules that sort and compare data, and cannot be changed after database creation. The default database collation is SQL_Latin1_General_CP1_CI_AS
- Maintenance window: Select a preferred maintenance window from the drop-down. During maintenance, databases remain available, but some updates may require a failover. The system default maintenance window (5pm to 8am) limits most activities to this time, but urgent updates may occur outside of it. To ensure all updates occur only during the maintenance window, select a non-default option
- Data Source: Start with a blank database, restore from a backup or select sample data to populate your new database.
- Tags
- Review + Create:
- Database Blade: After creation of server and database, firewall will restrict user to access. Need to enter user IP address to allow access to database.
- Overview:
- Activity Log:
- Tags:
- Diagnose and solve problems:
- Query editor:
- SQL server authentication: enter login details:
- Error:
- Solution: Public Network is denied. Go to Server blade/Networking/selected networks: Firewall Rules (check more details in server blade, enter client ip address).
- create a database:
-
CREATE TABLE Persons (FirstName varchar(255) CHECK (len(FirstName)>3 AND len(FirstName)<50),LastName varchar(255),Age int CHECK (Age<=130));
- run query, a table is created.
- Insert values in table:.
-
INSERT INTO Persons (FirstName, LastName, Age)VALUES ('Abdul','Aziz', 35);
- highlight these lines and run
- View the data:
- SELECT * FROM Persons;
-
- Mirror database in Fabric
- Settings:
- Data management:
- Integrations:
- Power Platform:
- Security
- Intelligent performance:
- Monitoring:
- Automation:
- Help
- SQL Server Blade:
- Overview:
- Activity Log:
- Access control (IAM)
- Quick start
- Diagnose and solve problems:
- Settings:
- Data management:
- Security:
- Netowrking:
- Public Access: Disable or Selected networks (Connections from the IP addresses configured in the Firewall rules section below will have access to this database. By default, no public IP addresses are allowed.)
- Virtual networks:
- Add a virtual network rule:
- Firewall rules:Add your client IPv4 address (x.x.x.x), Add a firewall rule.
- Add your client IPv4: enter rule name, start IPv4, End IPv4 and save it. now user can able to access database.
- Virtual networks:
- Private Access : Private endpoint connections
- Connectivity: Outbound networking, Connection policy, Encryption in transit.
- Public Access: Disable or Selected networks (Connections from the IP addresses configured in the Firewall rules section below will have access to this database. By default, no public IP addresses are allowed.)
- Microsoft Defender for Cloud:
- Transparent data encryption:
- Identity:
- Auditing:
- Netowrking:
- Intelligent performance:
- Monitoring:
- Automation:
- Help:
Create Azure MSSQL Server & Database with Terraform.
- provider.tf
- db.tf
- Go to terraform.io/azure/documentation/search sql server. search mssql database. copy and paste both codes.
-
locals {resource_group_name="star-RG"location="UK South"}
resource "azurerm_resource_group" "RG" {name = local.resource_group_namelocation = local.location}
#Creating ms SQL serverresource "azurerm_mssql_server" "sqlserver1" {name = "starsqlserver1"resource_group_name = local.resource_group_namelocation = local.locationversion = "12.0"administrator_login = "abdul"administrator_login_password = "India123456789"minimum_tls_version = "1.2"depends_on = [ azurerm_resource_group.RG ]}
#Creating a database using the above SQL serverresource "azurerm_mssql_database" "database1" {name = "stardb1"server_id = azurerm_mssql_server.sqlserver1.idcollation = "SQL_Latin1_General_CP1_CI_AS"license_type = "LicenseIncluded"max_size_gb = 2sku_name = "Basic"enclave_type = "VBS"
tags = {Database = "stardb1"}depends_on = [ azurerm_mssql_server.sqlserver1 ]}resource "azurerm_mssql_firewall_rule" "firewallRule1" {name = "starFirewallRule1"server_id = azurerm_mssql_server.sqlserver1.idstart_ip_address = "83.244.203.40"end_ip_address = "83.244.203.40"}
- #terraform init
- #terraform plan -out db.tfplan
- #terraform apply "db.tfplan"
- SQL server and database has been created. Go to database/query editor and enter credentials and it gives error as firewall block access.
- Error:
- Solution: Need to enter client IP address in firewall
- Create Azure SQL Server Firewall Rule
- Go to terraform.io/azure/documentation and search mssql firewall
-
resource "azurerm_mssql_firewall_rule" "firewallRule1" {name = "starFirewallRule1"server_id = azurerm_mssql_server.sqlserver1.idstart_ip_address = "83.244.203.40"end_ip_address = "83.244.203.40"}
- Enter the above code in db.tf and run script again.
- Enter records in the database.
-
CREATE TABLE Persons (FirstName varchar(255) CHECK (len(FirstName)>3 AND len(FirstName)<50),LastName varchar(255),Age int CHECK (Age<=130));
-
- run query, a table is created.
- Insert values in table:
-
INSERT INTO Persons (FirstName, LastName, Age)VALUES ('Abdul','Aziz', 35);
-
- highlight these lines and run
- View the data:
- SELECT * FROM Persons;
- Create Diagnostic settings
- Create Service Endpoint in Vnet to access SQL Database.
- Code
- Code
- Code
- Code
Storage:
Storage Overview
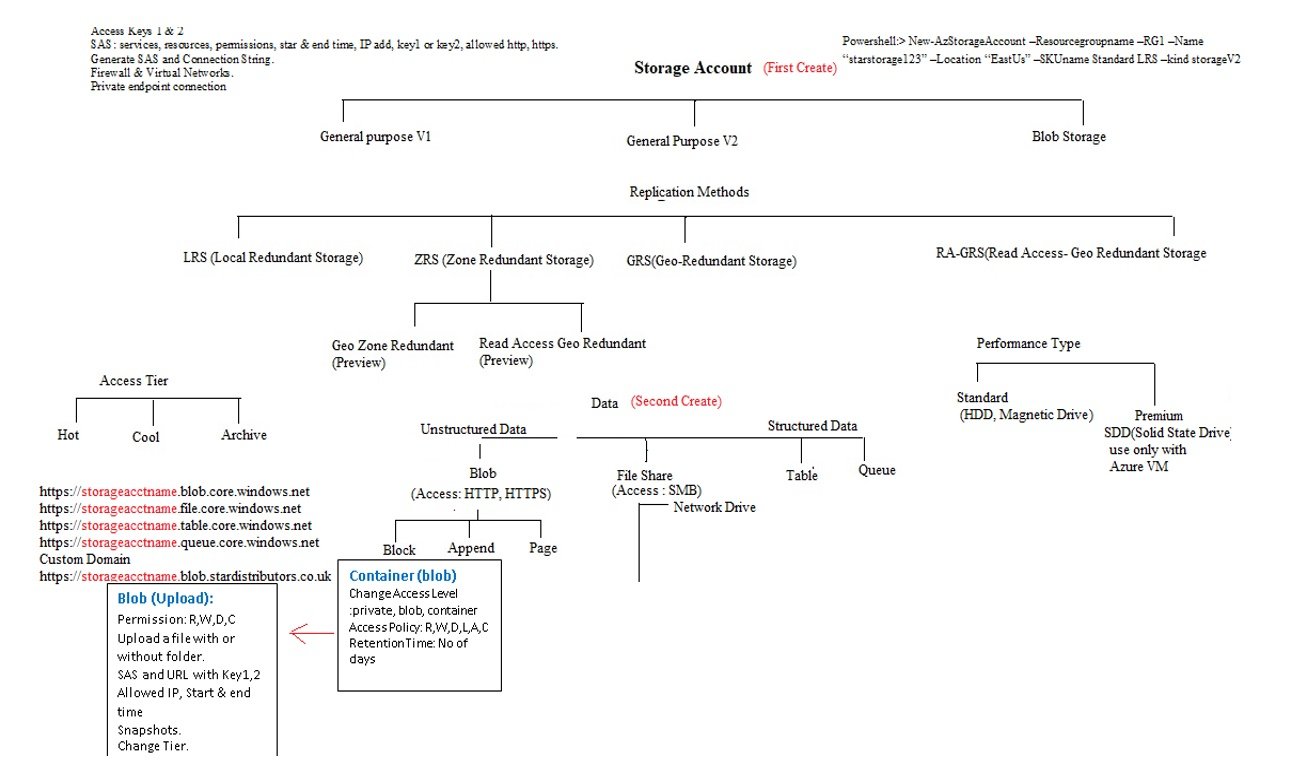
- Azure provides storage services in which different type of data can be stored. The hierarch of storage as follows:
- On top level storage account comes in which you define performance type (standard or Premium) on which different type of data can be store.
- Once storage account is created and choose the performance type container (folder) will be created and different level of permission can be defined.
- Performance type = Standard. It provides following type of services: It uses HHD drive.
- Container (Blob): unstructured data can be store
- FileShare: File share (SMB)
- Queue: structured data can be store
- Table: structured data can be store
- Performance type: Premium. It provides following types of services: It uses SSD drive.
- Block Blob + Append Blob:
- FileShare:
- Page Blob:
- Within a container(Folder), blobs(files) can be uploaded which can be access from any where with its URL.
- Storage account name should be unique because it convert into URL and every URL should be unique.
- Blob storage and general purpose V1 type can be upgraded to general purpose V2 without downtime.
- Storage accounts can be access with url http://storageaccountname.blob.core.windows.net. (file, table, que.core.windows.net) you can change to custom domain http://storageaccountname.blob.stardistributors.co.uk/rgname/filename (to define custom domain go to storage account and click custom domain and save) verify custom domain name by entering cname record in DNS.
- Access Tier (hot, cool, archive) is supported in V2 and Blob, V1 does not support.
- Account types:
- General Purpose V1: storage account is the oldest type of storage account. It offers storage for page blobs, block blobs, files, queues, and tables, but it is not the most cost-effective storage account type. It is the only storage account type that can be used for the classic deployment model. It doesn't support the latest features, such as access tiers.
- General Purpose V2: (V1 +Blob) It the newest type of storage account, and it combines the V1 storage with blob storage. It offers all the latest features, such as access tiers for blob storage, with a reduction in costs. Microsoft recommends using this account type over the V1 and blob storage account types.
- Blob: It support all V2 features except “page blob”.
- Types of data you can store: Blob, File, Queue, Table:
- Blob (Binary Large Object): It has three types, Block, Append and Page blob storage. It offers to store unstructured data.
- Block Blob: files and documents, Size 200GB
- Append Blob: Used by Azure for internal purpose.
- Page Blob: store disk VHD and attach to VM. Size 1TB
- File Share: It is like network file share (network drive) which is accessible with SMB (server message block) 3.0 protocol. It can be map as a drive in your local system where as blob cannot.
- Queue: used by developers, like credit card transaction where thousands of transaction takes place and which are in the que and done one by one.
- Table: stored structured data
- Blob (Binary Large Object): It has three types, Block, Append and Page blob storage. It offers to store unstructured data.
- Access Tiers: Hot, Cool and Archive
- Hot: The hot access tier is most suitable for storing data that's accessed frequently and data that is in active use.
- Cool: The cool access tier is the most suitable for storing data that is not accessed frequently (less than once in 30 days).
- Archive: The archive storage tier is set on the blob level and not on the storage level. It has the lowest costs for storing data and the highest cost for accessing data compared to the hot and cool access tiers. This tier is for data that will remain in the archive for at least 180 days, and it will take a couple of hours of latency before it can be accessed. This tier is most suitable for long-term backups or compliance and archive data.
- Data Copy: There are many ways you can copy data to blob storage: through portal, azure storage explorer. .NET PowerShell, CLI or REST API.
- Storage Account Redundancy: Data that is stored in Azure is always replicated to ensure durability and high availability. This way, it is protected from unplanned and planned events, such as network or power outages, natural disasters, and terrorism. It also ensures that, during these types of events, your storage account still meets the SLA. Data can be replicated within the same data center, across zonal data centers within the same region and across different regions. These replication types are named:
LRS-Locally Redundant Storage
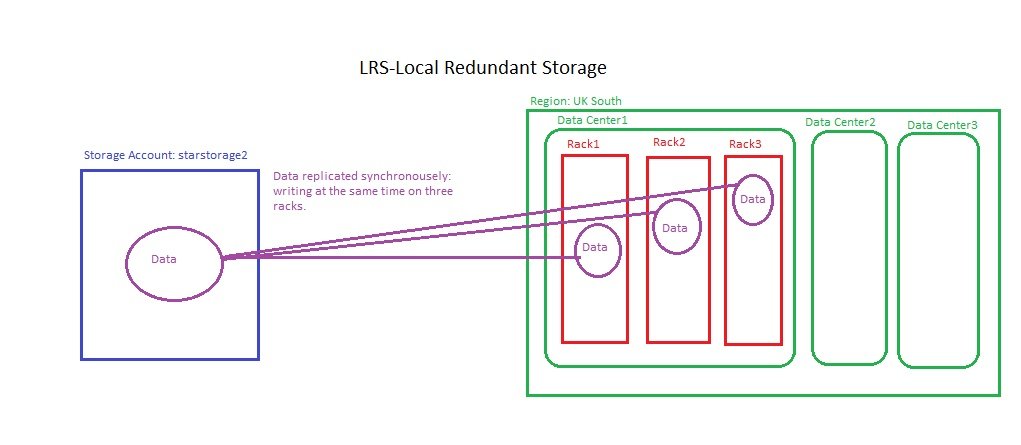
- Replicates your storage account synchronously across the three azure Racks in the primary data center. The data will be replicated across multiple update domains and fault domains within one storage scale unit.
- LRS provides at least 99.99999999999(11 nines) durability of objects over a given year.
- LRS protects your data against server rack and drive failures within a data center. However, if a disaster such as fire, flooding occurs within a data center, all replicas of a storage account using LRS may be lost.
ZRS-Zone Redundant Storage
GRS-Geo Redundant Storage

- GRS replicates the data three times within the same region, like ZRS, and also replicates three copies to other regions asynchronously.
- GRS offers durability for storage resources of atleas 99.9999999999999999 (16 9's) over a given year.
- When you create a storage account, you select the primary region for the account. The paired secondary region is determined based on the primary region and can't be changed.
GZRS- Geo Zone Rredundant Storage:
- Azure File Storage: You can create file shares in the cloud. You can access your files using the Server Message Block (SMB) protocol and it used port 445.
- Azure VM disk storage: The disks that are used for virtual machines are stored in Azure blob storage as page blobs. Azure stores two disks for each virtual machine: the actual operating system (VHD) of the VM, and a temporary disk that is used for short term storage. This data is erased when the VM is turned off or rebooted.
- Managed and Unmanaged Disk: During creation of VM storage account is created automatically in managed disk while in unmanaged disk you need to create manually.
- code
Create storage account
- Go to terraform.io\azure\documentation\search storage account. scroll down to check arguments (Required fields)
- provider.tf
-
terraform {required_providers {azurerm = {source = "hashicorp/azurerm"version = "4.8.0"}}}
provider "azurerm" {subscription_id = "bd2ade99-0834-4cfe-bb19-ddf0e89ed9f4"tenant_id = "4b9f3326-b87a-468f-89d4-4c34403eae39"client_id = "289f6253-b6eb-4930-bc19-3557cad4b72d"client_secret = "LlM8Q~UauskuRH84yA1QDDxc3K0w8sGl1y4ZsbTi"features {}}
-
- storage.tf
-
#In the following two resources are creating, RG and storage account#creating resource groupresource "azurerm_resource_group" "RG" {name = "star-RG"location = "UK South"}
#Creating storage account, first create storage account, container like folder than blob like filesresource "azurerm_storage_account" "storage" {name = "starstorage1"resource_group_name = "star-RG"location = "UK South"account_tier = "Standard"account_replication_type = "LRS"
tags = {storage = "starstorage1"}}
-
- #terraform init
- #terraform plan -out storage.tfplan
- #terraform apply "storage.tfplan"
- #terraform destroy
Create storage account, container (folder) in the storage account.
- Go to terraform.io\azure\documentation\search storage container. scroll down to check arguments (Required fields)
- provider.tf
-
terraform {required_providers {azurerm = {source = "hashicorp/azurerm"version = "4.8.0"}}}
provider "azurerm" {subscription_id = "bd2ade99-0834-4cfe-bb19-ddf0e89ed9f4"tenant_id = "4b9f3326-b87a-468f-89d4-4c34403eae39"client_id = "289f6253-b6eb-4930-bc19-3557cad4b72d"client_secret = "LlM8Q~UauskuRH84yA1QDDxc3K0w8sGl1y4ZsbTi"features {}}
-
- storage.tf
-
#In the following two resources are creating, RG and storage account#creating resource groupresource "azurerm_resource_group" "RG" {name = "star-RG"location = "UK South"}
#Creating storage account, first create storage account, container like folder than blob like filesresource "azurerm_storage_account" "storage" {name = "starstorage1"resource_group_name = "star-RG"location = "UK South"account_tier = "Standard"account_replication_type = "LRS"
tags = {storage = "starstorage1"}}
-
- container.tf
- Go to terraform.io\azure\documentation\search storage container, you can add the code in a new file or paste it in storage.tf
- container.tf
-
resource "azurerm_storage_container" "container" {name = "starcontainer1"storage_account_name = "starstorage1"container_access_type = "private"}
- Go to terraform.io\azure\documentation\search storage container, you can add the code in a new file or paste it in storage.tf
- #terraform plan -out storage.tfplan
- #terraform apply "storage.tfplan"
Create storage account, container (folder), upload file (blob) in the container.
- provider.tf
-
terraform {required_providers {azurerm = {source = "hashicorp/azurerm"version = "4.8.0"}}}
provider "azurerm" {subscription_id = "bd2ade99-0834-4cfe-bb19-ddf0e89ed9f4"tenant_id = "4b9f3326-b87a-468f-89d4-4c34403eae39"client_id = "289f6253-b6eb-4930-bc19-3557cad4b72d"client_secret = "LlM8Q~UauskuRH84yA1QDDxc3K0w8sGl1y4ZsbTi"features {}}
-
- storage.tf
-
#In the following two resources are creating, RG and storage account#creating resource groupresource "azurerm_resource_group" "RG" {name = "star-RG"location = "UK South"}
#Creating storage account, first create storage account, container like folder than blob like filesresource "azurerm_storage_account" "storage" {name = "starstorage1"resource_group_name = "star-RG"location = "UK South"account_tier = "Standard"account_replication_type = "LRS"
tags = {storage = "starstorage1"}}
-
- container.tf
- Go to terraform.io\azure\documentation\search storage container, you can add the code in a new file or paste it in storage.tf
- container.tf
-
resource "azurerm_storage_container" "container" {name = "starcontainer1"storage_account_name = "starstorage1"container_access_type = "container"}
- Go to terraform.io\azure\documentation\search storage container, you can add the code in a new file or paste it in storage.tf
- Blob upload
- Go to terraform.io\azure\documentation\search storage blob
- blob.tf
-
#uploading a blob (install_iis.ps1), powershell script file to install iis, it is located in the same folder of all tf files otherwise define path, name and source are sameresource "azurerm_storage_blob" "blob" {name = "install_iis.ps1"storage_account_name = "starstorage1"storage_container_name = "starcontainer1"type = "Block"source = "install_iis.ps1"}
-
- #terraform plan -out storage.tfplan
- #terraform apply "storage.tfplan"
- #terraform destroy
- provider.tf
Code
- code
Code
- code
Code
- code
code
- Code
- Code
- Code
code
- Code
- Code
- Code
code
- Code
- Code
- Code
code
- Code
- Code
- Code
code
- Code
- Code
- Code
code
- Code
- Code
- Code
code
- Code
- Code
- Code
code
- Code
- Code
- Code
code
- Code
- Code
- Code
Syntax in AWS:
Structure of terraform.tf file
- codes are define in different .tf files.
- File Structure:
- file_structure.jpg
- Environment-Specific Structure
- file_structure2.jpg
- Serviced-based Structure
- file_structure3.jpg
Provider:
- Provider is a plugin that transform your code into code that cloud provider understands.
- We careate the code (.tf) using HCL (Hashicorp Language) which needs to be translated to the code which cloud providers can understand, it can be done with prvider plugin.
- When you run $terraform init , it initialize the provider and download the provider's plugin.
- provider1.jpg
- AWS Provider Block
- Visit https://registry.terraform.io/providers/hashicorp/aws/latest
- for more details visit: https://registry.terraform.io/providers/hashicorp/aws/latest/docs
- Create a file with extension .tf and write code
- #vim test.tf
- Enter Provider and version details:
- Go to terraform.io and select aws provider and click on provider and copy code.
- If you want to define specific version than define with the below block or it will take lastest version.
- provider2.jpg
- There are different versions, AWS version (maintain by AWS), other providers and terraform version(maintian by Hashicorp). check version compatability, if you do not mention version number than it will take latst.
-
terraform { required_providers { aws = { source = "hashicorp/aws" version = "5.74.0" } } } provider "aws" {region = "eu-west-2"access_key = "AKIAX2XVEK27GJNREDX4"secret_key = "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"} - provider "AWS": The code enter in this file is written for AWS cloud.
- Region in which service should be created.
- Acces key and secret key is the authentication to get access into aws account. Create IAM user and use access key and secret key. It is not recommended to hardcode keys, use vault or AWS CLI.
- How to get access_key/secret_key: Get for root user or IAM user, Go to IAM and create a user and get access key. click on user top right corner and click my security credentials and create access key.
- $terraform init (Terraform has been initiated successfully. Plugin has been downloaded and installed. terraform.lock.hcl is created which contain provider details.
- $terraform plan -out provider.tfplan (it will check the resources on AWS and compare with the file and gives output what will be plan of action), it will not create resources.
- It shows plan which will be executed, check output.
- $terraform apply "provider.tfplan" (it will execute and create resource)
- Azure Provider Block
- Go to terraform.io and click providers and select azure, click on user provider and copy code and paste it.
- create a file provide.tf
-
terraform {required_providers {azurerm = {source = "hashicorp/azurerm"version = "4.8.0"}}}
provider "azurerm" {subscription_id = ""tenant_id = ""client_id = ""client_secret = ""features {}} - Subscription Id: login to portal.azure.com and click subscription and copy ID.
- Tenant Id: Go to entra ID and in overview coy tenant ID
- Client Id: Go to Entra ID/manage/App Registration/New Registration/Enter name (terraform) and click ok.
- Client_Secret: In terrafom blade/manage/Certificates & secrets/new client secret/enter name(star-ClientSecret), copy value and save it in notepad. If it is not copied than generate new one.
- Assign Required Permission to terraform application: To create resources required permission needed, Go to subscription/Access control (IAM)/add role assignment/select privileged administrator roles and select contributor role /search for member terraform and select terraform and review and assign.
- Now resrouces can be created. add code to create resource
Dependency: Azure
- Resources are dependant to other resources, for example VM, storage account, Vnet are depend on Resource Group, without RG these resources can be created.
- If all resources are created through one configuration file then we refer/call the dependency in the configuration file.
- Terraform used declarative method, it means it should not be in sequence.
- code
remove yellow boxes in VS code when copy and paste
- copy the yellow box and go to view/search or Ctrl+Shift+F and paste the box and in Replace = click space bar and click replace all
- Code
Map of Values:
-
terraform {required_providers {azurerm = {source = "hashicorp/azurerm"version = "4.8.0"}}}
provider "azurerm" {subscription_id = "bd2ade99-0834-4cfe-bb19-ddf0e89ed9f4"tenant_id = "4b9f3326-b87a-468f-89d4-4c34403eae39"client_id = "363c6475-89bc-4948-9396-6dc6849eeb14"client_secret = "YFU8Q~gf2nHQyuv50lQjGkCZ0-M8YdZbGVoklcvs"features {}}locals {resource_group_name = "star-RG"location = "UK South"virtual_network={name="star-Vnet1"address_space="10.0.0.0/16"
}}resource "azurerm_resource_group" "RG" {name = local.resource_group_namelocation = local.location}
resource "azurerm_virtual_network" "vnet1" {name = local.virtual_network.namelocation = local.locationresource_group_name = local.resource_group_nameaddress_space = [local.virtual_network.address_space]
subnet {name = "subnet1"address_prefixes = ["10.0.1.0/24"]}
subnet {name = "subnet2"address_prefixes = ["10.0.2.0/24"]}
tags = {environment = "vnet-production"}
depends_on = [ azurerm_resource_group.RG ]} - code
- code
-
Terraform command:
- You should run the execution commands from the folder in which terraform .tf template files exist.
- $terraform validate
- Validate the reorganized structure
- $terraform fmt -recursive
- Format all files consistently
- $terraform init: it will download providers plugin in.
- .terraform folder will be created which container providers details.
- $terraform validate:
- It will check the configuration.
- $terraform plan -out filename.tfplan :
- It will output the action will be performed.
- $terraform apply "filename.tfplan"
- It will create resources in the given provider's location. Before apply you will have xyz.tf and .terraform in the folder.
- terraform.tfstate: it stores the details what it has created. If you run #terraform apply again then it will check terraform.tfstate file and plan and perform task if there is any change.
- terraform.tfstate.backup: It contain last known good configuration.
- Code
Count Parameter/ Count Meta Argument:
- Creating multiple instances:
- we dont need to define resources multiple times in configuration file but use count parameter.
- It works like loop, if you define count =3 then it will create 3 resources, suppose if you want to create 3 instances/VM then in instance resource use parameter count =3.
- names for all three instances must be unique, tags name will be different for easy identification, we use count.index parameter where it adds number before name.
-
provider "aws" {
region = "eu-west-2"
access_key = "AKIAX2XVEK27GJNREDX4"
secret_key = "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"
}resource "aws_instance" "server"{
ami = "ami-0dbec48abfe298cab"
instance_type = "t2.micro"
count = 3tags = {
Name = "WebServer.${count.index}"
}
} - 3 servers will be created. but all three instance tag name will be webserver.
- You can use ${count.index} , index value start from 0, so tag name will be (webserver0, webserver1. webserver2). Index numbers can be use before or after the name. If you want to start index with 1 then user ${count.index+1}
- If you want to give particular names then should use variable list and call in tags.
-
provider "aws" {
region = "eu-west-2"
access_key = "AKIAX2XVEK27GJNREDX4"
secret_key = "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"
}
variable "instance_name" {
type = list
default = ["dev_server","test_server","prod_server"]
}resource "aws_instance" "server"{
ami = "ami-0dbec48abfe298cab"
instance_type = "t2.micro"
count = 3tags = {
Name = var.instance_name[count.index]
}
} - Instance tag names will be (dev_server, test_server, prod_server) but instane type for all is "t2.micro".
- To assign different instance type (t2.small,t2.medium, t2.large etc).
-
provider "aws" {
region = "eu-west-2"
access_key = "AKIAX2XVEK27GJNREDX4"
secret_key = "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"
}
variable "instance_name" {
type = list
default = ["dev_server","test_server","prod_server"]
}
variable "instance_type" {
type = list
default = ["t2.small","t2.medium","t2.large"]
}
resource "aws_instance" "server"{
ami = "ami-0dbec48abfe298cab"
instance_type = var.instance_type[count.index]
count = 3tags = {
Name = var.instance_name${count.index}
}
} - code
- Creating multiple storage accounts using count Meta Argument:
- Go to terraform.io, click documentation and search storage account, copy code.
-
resource "azurerm_resource_group" "RG" {name = "star-RG"location = "UK South"}
resource "azurerm_storage_account" "starstorage" {count = 3name = "starstorage${count.index}"resource_group_name = "star-RG"location = "UK South"account_tier = "Standard"account_replication_type = "GRS"
tags = {Dept = "testing"}depends_on = [ azurerm_resource_group.RG ]} - storage account is created in resource group so we can define depends_on.
- Go to portal and check in storage account.
- Creating multiple containers in the storage account using for_each Meta Argument:
- Go to terraform.io, click documentation and search container, copy code.
-
resource "azurerm_storage_container" "example" { name = "vhds" storage_account_id = azurerm_storage_account.example.id container_access_type = "private" }
- for_each Meta Argument with "tomap" function, upload blob in containers
- in C drive create 3 folders dir1, dir2, dir3 and 3 text files in each folder namely file1, file2, file3
- Go to terraform.io and click documentation and search blob, copy code
-
resource "azurerm_storage_blob" "example" { name = "my-awesome-content.zip" storage_account_name = azurerm_storage_account.example.name storage_container_name = azurerm_storage_container.example.name type = "Block" source = "some-local-file.zip" } - cc
- LAB: Creating multiple containers in the storage account using for_each Meta Argument:
-
resource "azurerm_resource_group" "RG" {name = "star-RG"location = "UK South"}
resource "azurerm_storage_account" "starstorage" {name = "starstorage1"resource_group_name = "star-RG"location = "UK South"account_tier = "Standard"account_replication_type = "GRS"
tags = {Dept = "testing"}depends_on = [ azurerm_resource_group.RG ]}
resource "azurerm_storage_container" "container" {for_each = toset(["container1","container2","container3"])name = each.keystorage_account_name = "starstorage1"container_access_type = "private"depends_on = [ azurerm_storage_account.starstorage ]}
- Creating multiple containers in the storage account without using for_each Meta Argument:
- code
-
- LAB: for_each Meta Argument with "tomap" function, upload blob in container using the above storage and containers:
- in C drive created 3 folders dir1, dir2, dir3 and 3 text files in each folder namely file1, file2, file3
- Go to terraform.io and click documentation and search blob, copy code
-
resource "azurerm_resource_group" "RG" {name = "star-RG"location = "UK South"}
resource "azurerm_storage_account" "starstorage" {name = "starstorage1"resource_group_name = "star-RG"location = "UK South"account_tier = "Standard"account_replication_type = "GRS"
tags = {Dept = "testing"}depends_on = [ azurerm_resource_group.RG ]}
resource "azurerm_storage_container" "container" {for_each = toset(["container1","container2","container3"])name = each.keystorage_account_name = "starstorage1"container_access_type = "private"depends_on = [ azurerm_storage_account.starstorage ]}
resource "azurerm_storage_blob" "blob" {for_each = tomap({file1 = "C:\\dir1\\file1.txt"file2 = "C:\\dir2\\file2.txt"file3 = "C:\\dir3\\file3.txt"})name = "${each.key}.txt"storage_account_name = "starstorage1"storage_container_name = "container1"type = "Block"source = each.valuedepends_on = [ azurerm_storage_container.container ]} - three files are uploaded in container1.
- Code
- Code
- Code
- Creating multiple instances:
Input Value:
- provider
- Code
Variables (Input, Output, Locals, precedence):

- Variables allows you to define piece of data in one location instead of repeating the hardcoded value of it in multiple different locations in the code. Then when you need to modify the variable's value, you do it in one location instead of changing each one of the hardcoded values in the entire code.
- When you need to use certain values repeatedly in a program or script than you define the variable & value and call anywhere to avoid repetative typing.
- Input Variable:
- visit https://developer.hashicorp.com/terraform/language/values/variables
- User will define variable and provide value.
- Types of constraints supported in terraform variables: String, number, bool, list, set, map, object, tuple, data source,
-
-
variable "variablename" {type = stringdefault = "value"}
- Interpolation: calling the values of variable is called interpolation. For Example var.variablename. or in previous version "${var.variablename}"
- Lab: Manually defining the values.
- Create two files:
- $vim variable.tf copy and paste the following:
-
variable "accesskey" {type = stringdefault = "AKIAYHJANJLZX2BBGS5K"}variable "secretkey" {type = stringdefault = "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"}variable "region" {type = stringdefault = "eu-west-2"}
-
- $provider.tf copy and paste the follwing code:
-
provider "aws" {access_key = var.accesskeysecret_key = var.secretkeyregion = var.region}
-
- You can hardcode variable values using default, if you do not hardcode then system will prompt to enter values.String: values could be in character, numbers etc..
- $terraform init
- $terraform validate (it will check the configuration is correct or not)
- $terraform plan -out provider.tfplan (system will ask to enter accesskey, secretkey and region as we have not defined in variable file.
- $terrraform apply "provider.tfplan"
- You can enter values during apply:
- $terraform apply "provider.tfplan" -var 'accesskey=AKIAX2XVEK27GJNREDX4' -var 'secretkey=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' -var 'region=eu-west-2' (variable values are defined in command)
- If you do not want to enter value each time, remove variable and enter value in configuration file. once you entered and variable file is still exist then system will ask to enter value then you only enter as value has been hardcoded.
- If you do not want system to ask the value, delete variable file or remove related variable block or comment the block.
- Lab: Variables defined for CIDR block and call it in creating vpc and subnet (string):
- Create a file vpcvariable.tf, define the variable, type and its value as default and call it in resource where it is creating.
-
variable "vpccidr" {type = stringdefault = "10.0.0.0/16"}
variable "publicsubnetcidr" {type = stringdefault = "10.0.1.0/24"}variable "privatesubnetcidr" {type = stringdefault = "10.0.2.0/24"} - Create a file vpc.tf and copy the following code in which it call values from vpcvariable.tf file.
-
resource "aws_vpc" "star_vpc" {cidr_block = var.vpccidrinstance_tenancy = "default"
tags = {Name = "star_vpc"}}
resource "aws_subnet" "public_subnet" {vpc_id = aws_vpc.star_vpc.idcidr_block = var.publicsubnetcidr
tags = {Name = "public_subnet"}}
resource "aws_subnet" "private_subnet" {vpc_id = aws_vpc.star_vpc.idcidr_block = var.privatesubnetcidr
tags = {Name = "private_subnet"}}
- #terraform validate (it will check the configuration is correct or not)
- #terraform plan -out vpc.tfplan (system will ask to enter accesskey, secretkey and region as we have not defined in variable file.
- #terrraform apply "vpc.tfplan"
-
- number: 123
- Create 10 AWS instances
-
resource "aws_instance" "star-web1" {ami = "ami-005e54dee72cc1d00" # us-west-2instance_type = "t2.micro"region = "us-west-2"count = 10subnet = "VPC1"tags = {Name = "star web server"}}
- Terraform initialization
- #terraform init
- Terraform Plan
- #terraform plan -out star_instance.tfplan
- Terraform apply
- #terrafrom apply "star_instance.tfplan"
- Delete resource
- #terraform destroy
- bool: true/false
- list: The syntax is var.list .For example, var.subnets would get the value of the list, as a list.
- map: The syntax is var.<map>["KEY"]. For example, var.az["eu-west-2"] would get the value of the eu-west-2 key within the az map variable.
- self: The syntax is
self.<ATTRIBUTE>. For example${self.private_ip}will interpolate that resource's private IP address. - data source:
- Data source used to get data from providers or in general from external resources to terraform, (ex. public clouds like AWS, Azure, GCP). It is read only.
- output from a module:
- path information:
- condition:
-
- Built-in-functions: Terraform ships with built-in functions. Functions are called with the syntax
name(arg, arg2, ...). For example, to read a file:${file("path.txt")}.
- Output Values:
- It gives value on screen which is assigned by providers after creating the resource. Every resource will have a unique ID which can be call or refer in other application/code.
- Create files: variable.tf, vpc.tf
- $vim variable.tf copy and paste the following:
-
variable "accesskey" {type = stringdefault = "AKIAYHJANJLZX2BBGS5K"}variable "secretkey" {type = stringdefault = "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"}variable "region" {type = stringdefault = "eu-west-2"}variable "vpccidr" {type = stringdefault = "10.0.0.0/16"}
variable "publicsubnetcidr" {type = stringdefault = "10.0.1.0/24"}variable "privatesubnetcidr" {type = stringdefault = "10.0.2.0/24"}
-
- $vim vpc.tf copy and paste the following code.
-
provider "aws" {access_key = var.accesskeysecret_key = var.secretkeyregion = var.region}resource "aws_vpc" "star_vpc" {cidr_block = var.vpccidrinstance_tenancy = "default"
tags = {Name = "star_vpc"}}
resource "aws_subnet" "public_subnet" {vpc_id = aws_vpc.star_vpc.idcidr_block = var.publicsubnetcidr
tags = {Name = "public_subnet"}}
resource "aws_subnet" "private_subnet" {vpc_id = aws_vpc.star_vpc.idcidr_block = var.privatesubnetcidr
tags = {Name = "private_subnet"}} - output "star_vpc_id" {
value = aws_vpc.star_vpc.id
}
- $vim variable.tf copy and paste the following:
- $terraform init
- $terraform plan -out vpc.tfplan
- $terraform apply "vpc.tfplan"
-
Outputs:
star_vpc_id = "vpc-0e450a7a8fab169ef"
- You can also run $terraform output
- $terraform destroy
- Locals:
- Some values are used repetatively in configuration file, it can be defined and use in code by giving reference.
- locals {
resource_group_name="star-RG"
location="UK South"
} - Call the locals in code.
- name = local.resource_group_name
location = local.location - System will search and assingn resource_group_name "star-RG" and location "UK South"
- Variable Precedence:
- The value which you define in variable precedence will take predence than value in code. There are 3 ways you can define variable precedence value.
-
Default Values (temporarily hide terraform.tfvars)
mv terraform.tfvars terraform.tfvars.backup
terraform plan
# Uses: environment = "staging" (from variables.tf default)
mv terraform.tfvars.backup terraform.tfvars # restore
2. Using terraform.tfvars (automatically loaded)
terraform plan
# Uses: environment = "demo" (from terraform.tfvars)
3. Command Line Override (highest precedence)
terraform plan -var="environment=production"
# Overrides tfvars: environment = "production"
4. Environment Variables
export TF_VAR_environment="staging-from-env"
terraform plan
# Uses environment variable (but command line still wins)
5. Using Different tfvars Files
terraform plan -var-file="dev.tfvars" # environment = "development"
terraform plan -var-file="production.tfvars" # environment = "production"## 📁 Simple File Structure
├── main.tf # S3 bucket resource ├── variables.tf # Input variables (2 simple variables) ├── locals.tf # Local variables (tags and computed name) ├── output.tf # Output variables (bucket details) ├── provider.tf # AWS provider ├── terraform.tfvars # Default variable values └── README.md # This file
## 🧪 Practical Examples### Example 1: Testing Different Input Values
```bash
# Test with defaults (temporarily hide terraform.tfvars)
mv terraform.tfvars terraform.tfvars.backup
terraform plan
# Shows: Environment = "staging", bucket will be "staging-my-terraform-bucket-xxxxx"# Test with terraform.tfvars
mv terraform.tfvars.backup terraform.tfvars
terraform plan
# Shows: Environment = "demo", bucket will be "demo-terraform-demo-bucket-xxxxx"# Test with command line override
terraform plan -var="environment=test" -var="bucket_name=my-test-bucket"
# Shows: Environment = "test", bucket will be "test-my-test-bucket-xxxxx"
Example 2: Viewing All Variable Types in Action
# Apply the configuration
terraform apply -auto-approve# See all outputs (shows output variables)
terraform output
# bucket_arn = "arn:aws:s3:::demo-terraform-demo-bucket-abc123"
# bucket_name = "demo-terraform-demo-bucket-abc123"
# environment = "demo" # (input variable)
# tags = { # (local variable)
# "Environment" = "demo"
# "Owner" = "DevOps-Team"
# "Project" = "Terraform-Demo"
# }# See how local variables computed the bucket name
echo "Input: environment = $(terraform output -raw environment)"
echo "Input: bucket_name = terraform-demo-bucket (from tfvars)"
echo "Local: full_bucket_name = $(terraform output -raw bucket_name)"
echo "Random suffix was added by local variable!"
Example 3: Variable Precedence in Action
# Start with terraform.tfvars (environment = "demo")
terraform plan | grep Environment
# Shows: "Environment" = "demo"# Override with environment variable
export TF_VAR_environment="from-env-var"
terraform plan | grep Environment
# Shows: "Environment" = "from-env-var"# Override with command line (highest precedence)
terraform plan -var="environment=from-command-line" | grep Environment
# Shows: "Environment" = "from-command-line"# Clean up
unset TF_VAR_environment
🔧 Try These Commands
# Initialize
terraform init# Plan with defaults
terraform plan# Plan with command line override
terraform plan -var="environment=test"# Plan with different tfvars file
terraform plan -var-file="dev.tfvars"# Apply and see outputs
terraform apply
terraform output# Clean up
terraform destroy
Split Configuration File:
- creating multiple resources result increasing the size of a file and will be difficult to manage. It can be split into files to manage easily.
- We have a complete code in a file vpc.tf, split into two, create a file provider.tf and copy provider portion in provider.tf and save both files. both files are in same folder.
- #terraform plan -out vpc.tfplan. Run terraform plan and both files will be considered and a plan will be generated.
- #terraform apply "vpc.tfplan" : it will create resources by reading provider.tf and vpc.tf
- Code
- Code
Loop:
- provider
- Code
Comments:
- comments are used in the configuration file to provider information about the code,
- Single line comment: use # or // and type
-
terraform {required_providers {azurerm = {source = "hashicorp/azurerm"version = "4.8.0"}}}
provider "azurerm" {subscription_id = ""tenant_id = ""client_id = ""client_secret = ""features {}} - # This block is used to provide azure provider details. or
- // This block is used to provide azure provider details.
-
- Multiple line comment:
-
terraform {required_providers {azurerm = {source = "hashicorp/azurerm"version = "4.8.0"}}}
provider "azurerm" {subscription_id = "bd2ade99-0834-4cfe-bb19-ddf0e89ed9f4"tenant_id = "4b9f3326-b87a-468f-89d4-4c34403eae39"client_id = "0df6190d-31bc-4d6a-ba38-3115d352e7ca"client_secret = "xkH8Q~OQ-Rg7XXu7Zz-I6IkVHijsxsZeOwGs5cKz"features {}} - /*
In this block azure providers details has been provided.
Values has been hard coded
*/
-
- Code
Condition statement:
- You can define condition in the code where if condition met then perform such action and if not perform different action.
- Creating X number of VMs if condition met.
- Define variables for instance type & image, and call variable where we enter condition.
- Creating x number of VMs in certain department if condition met.
- Code
syntax
- provider
- Code
syntax
- provider
- Code
syntax
- provider
- Code
syntax
- provider
- Code
syntax
- provider
- Code
syntax
- provider
- Code
syntax
- provider
- Code
syntax
- provider
- Code
syntax
- provider
- Code
AWS Resources
AWS Authentication Method
- Before creating resources, you need to configure AWS user credentials for Terraform to authenticate with AWS APIs.
- It can be done with using AWS CLI or write user's Access key and secret key in the code.
- AWS CLI:
- Install AWS CLI in your computer.(check in installation section)
- $aws configure (enter credentials)
Networking: VPC, subnets, Security Group with Ingress & Egress Rules, Elastic IP, Endpoints, NAT gateways
Default VPC:
a default VPC is exist in AWS, to use default VPC:-
resource "aws_default_vpc" "default" { tags = { Name = "Default VPC" } } - you can use default VPC if you do not want to create a custom VPC.
-
Creating a custom VPC:
-
resource "aws_vpc" "VPC1" { cidr_block = "10.0.0.0/16" } - "aws_vpc" = AWS VPC identification
- "VPC1" = name of VPC
- cidr-block ="10.0.0.0/16" = will create a cidr block for VPC1.
- LAB:
- $vim main.tf (copy and paste the following code)
-
terraform {required_providers {aws = {source = "hashicorp/aws"version = "5.74.0"}}}provider "aws" {region = "eu-west-2"access_key = "AKIAYHJANJLZX2BBGS5K"secret_key = "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"}resource "aws_vpc" "VPC1" {cidr_block = "10.0.0.0/16"}
- $terraform init
- $terraform plan -out main.tfplan
- $terraform apply "main.tfplan"
-
Creating VPC with Tag:
-
resource "aws_vpc" "VPC1" { cidr_block = "10.0.0.0/16" instance_tenancy = "default" tags = { Name = "VPC1" } } - VPC1 will be created with tag VPC1
- LAB:
- $vim main.tf (copy and paste the following code)
- $terraform init
- $terraform plan -out main.tfplan
- $terraform apply "main.tfplan"
-
terraform {required_providers {aws = {source = "hashicorp/aws"version = "5.74.0"}}}provider "aws" {region = "eu-west-2"access_key = "AKIAYHJANJLZX2BBGS5K"secret_key = "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"}resource "aws_vpc" "VPC1" {cidr_block = "10.0.0.0/16"instance_tenancy = "default"
tags = {Name = "VPC1"}}
-
Creating VPC with Subnets:
-
resource "aws_subnet" "subnet1" { vpc_id = aws_vpc.VPC1.id cidr_block = "10.0.1.0/24" tags = { Name = "Subnet1" } } - LAB:
- $vim main.tf (copy and paste the following code)
- $terraform init
- $terraform plan -out main.tfplan
- $terraform apply "main.tfplan"
-
terraform {required_providers {aws = {source = "hashicorp/aws"version = "5.74.0"}}}provider "aws" {region = "eu-west-2"access_key = "AKIAYHJANJLZX2BBGS5K"secret_key = "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"}resource "aws_vpc" "VPC1" {cidr_block = "10.0.0.0/16"instance_tenancy = "default"
tags = {Name = "VPC1"}}resource "aws_subnet" "subnet1" {vpc_id = aws_vpc.VPC1.idcidr_block = "10.0.1.0/24"
tags = {Name = "Subnet1"}}resource "aws_subnet" "subnet2" {vpc_id = aws_vpc.VPC1.idcidr_block = "10.0.2.0/24"
tags = {Name = "Subnet2"}}
-
Creating Security Group:
-
resource "aws_security_group" "star-SG" { name = "star-SG" description = "Allow TLS inbound traffic and all outbound traffic" vpc_id = aws_vpc.VPC1.id tags = { Name = "Allow Traffic" } } - Security group is created within a VPC, so we have define vpc_id = aws_vpc.VPC1.id where VPC1 is the name of VPC.
- VPC should be define before security group.
- LAB:
- Ingress Rule (Inbound Traffic) define in Security Group IPv4 & IPv6:
-
resource "aws_vpc_security_group_ingress_rule" "Allow_443_Inbound_ipv4" { security_group_id = aws_security_group.star-SG.id cidr_ipv4 = aws_vpc.VPC1.cidr_block from_port = 443 ip_protocol = "tcp" to_port = 443 } -
resource "aws_vpc_security_group_ingress_rule" "allow_443_Inbound_ipv6" { security_group_id = aws_security_group.star-SG.id cidr_ipv6 = aws_vpc.VPC1.ipv6_cidr_block from_port = 443 ip_protocol = "tcp" to_port = 443 } -
- Egress Rule (Outbound Traffic) define in security group:
- By default, AWS creates an ALLOW ALL egress rule when creating a new Security Group inside of a VPC. When creating a new Security Group inside a VPC, Terraform will remove this default rule, and require you specifically re-create it if you desire that rule. We feel this leads to fewer surprises in terms of controlling your egress rules. If you desire this rule to be in place, you can use this egress block:
-
resource "aws_vpc_security_group_egress_rule" "allow_all_traffic_ipv4" { security_group_id = aws_security_group.allow_tls.id cidr_ipv4 = "0.0.0.0/0" ip_protocol = "-1" # semantically equivalent to all ports } -
resource "aws_vpc_security_group_egress_rule" "allow_all_traffic_ipv6" { security_group_id = aws_security_group.allow_tls.id cidr_ipv6 = "::/0" ip_protocol = "-1" # semantically equivalent to all ports } - LAB:
- $vim main.tf (copy and paste the following code)
- $terraform init
- $terraform plan -out main.tfplan
- $terraform apply "main.tfplan"
-
terraform {required_providers {aws = {source = "hashicorp/aws"version = "5.74.0"}}}provider "aws" {region = "eu-west-2"access_key = "AKIAYHJANJLZX2BBGS5K"secret_key = "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"}resource "aws_vpc" "VPC1" {cidr_block = "10.0.0.0/16"instance_tenancy = "default"
tags = {Name = "VPC1"}}resource "aws_security_group" "star-SG" {name = "star-SG"description = "Allow TLS inbound traffic and all outbound traffic"vpc_id = aws_vpc.VPC1.id
tags = {Name = "star-SG"}
}
resource "aws_vpc_security_group_ingress_rule" "allow_Inbound_ipv4" {security_group_id = aws_security_group.star-SG.idcidr_ipv4 = aws_vpc.VPC1.cidr_blockfrom_port = 443ip_protocol = "tcp"to_port = 443}
resource "aws_vpc_security_group_egress_rule" "allow_all_traffic_ipv4" {security_group_id = aws_security_group.star-SG.idcidr_ipv4 = "0.0.0.0/0"ip_protocol = "-1" # semantically equivalent to all ports}resource "aws_subnet" "subnet1" {vpc_id = aws_vpc.VPC1.idcidr_block = "10.0.1.0/24"
tags = {Name = "Subnet1"}}resource "aws_subnet" "subnet2" {vpc_id = aws_vpc.VPC1.idcidr_block = "10.0.2.0/24"
tags = {Name = "Subnet2"}}
-
Removing all Ingress and Egress rules:
-
resource "aws_security_group" "example" { name = "sg" vpc_id = aws_vpc.example.id ingress = [] egress = [] } - LAB: creating VPC, subnets, Security Group, Rule for inbound/outbound
- $vim main.tf (copy and paste the following code)
- $terraform init
- $terraform plan -out main.tfplan
- $terraform apply "main.tfplan"
-
terraform {required_providers {aws = {source = "hashicorp/aws"version = "5.74.0"}}}provider "aws" {region = "eu-west-2"access_key = "AKIAYHJANJLZX2BBGS5K"secret_key = "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"}resource "aws_vpc" "VPC1" {cidr_block = "10.0.0.0/16"tags = {Name = "star-VPC1"}}
resource "aws_subnet" "Private-Subnet" {vpc_id = aws_vpc.VPC1.idcidr_block = "10.0.1.0/24"
tags = {Name = "Private-Subnet"}}
resource "aws_security_group" "star-SG" {name = "star-SG"description = "Security Group to allow/deny traffic"vpc_id = aws_vpc.VPC1.id
tags = {Name = "star-SG"}}
resource "aws_vpc_security_group_ingress_rule" "Allow_443_Inbound_ipv4" {security_group_id = aws_security_group.star-SG.idcidr_ipv4 = aws_vpc.VPC1.cidr_blockfrom_port = 443ip_protocol = "tcp"to_port = 443}
resource "aws_vpc_security_group_egress_rule" "allow_all_Outbound_ipv4" {security_group_id = aws_security_group.star-SG.idcidr_ipv4 = "0.0.0.0/0"ip_protocol = "-1" # semantically equivalent to all ports}
-
Creating Internet Gateway:
-
resource "aws_internet_gateway" "gw" { vpc_id = aws_vpc.main.id tags = { Name = "main" } } - ss
-
Creating Route Table:
-
resource "aws_route_table" "example" { vpc_id = aws_vpc.example.id route { cidr_block = "10.0.1.0/24" gateway_id = aws_internet_gateway.example.id } route { ipv6_cidr_block = "::/0" egress_only_gateway_id = aws_egress_only_internet_gateway.example.id } tags = { Name = "example" } } - ss
-
Creating NAT Gateway:
-
resource "aws_nat_gateway" "example" { allocation_id = aws_eip.example.id subnet_id = aws_subnet.example.id tags = { Name = "NAT-Gateway" } - NAT gateway required a public IP which will translate private IP into Public IP. create an enter in allocation_id = aws_eip.natIP.id
- Create public IP (EIP) and Associate with NAT.
-
resource "aws_eip" "star-nat-eip" {}
- Need to create Route Table and associate with subnet (public subnet) to which traffic goes to internet. NAT & IGW does not associate directly with subnet so we create route table and associate one side with subnet and other side with NAT.
- Create route table and route:
-
resource "aws_route_table" "example" { vpc_id = aws_vpc.example.id route { cidr_block = "10.0.1.0/24" gateway_id = aws_internet_gateway.example.id } tags = { Name = "example" } }
-
- Associate Route Table:
-
resource "aws_route_table_association" "a" { subnet_id = aws_subnet.foo.id route_table_id = aws_route_table.bar.id }
-
- LAB:
- $vim main.tf (copy and paste the following code)
- $terraform init
- $terraform plan -out main.tfplan
- $terraform apply "main.tfplan"
-
terraform {required_providers {aws = {source = "hashicorp/aws"version = "5.74.0"}}}provider "aws" {region = "eu-west-2"access_key = "AKIAYHJANJLZX2BBGS5K"secret_key = "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"}resource "aws_vpc" "VPC1" {cidr_block = "10.0.0.0/16"tags = {Name = "star-VPC1"}}
resource "aws_subnet" "Public-Subnet" {vpc_id = aws_vpc.VPC1.idcidr_block = "10.0.1.0/24"
tags = {Name = "Public-Subnet"}}
resource "aws_subnet" "Private-Subnet" {vpc_id = aws_vpc.VPC1.idcidr_block = "10.0.2.0/24"
tags = {Name = "Private-Subnet"}}
resource "aws_security_group" "star-SG" {name = "star-SG"description = "Security Group to allow/deny traffic"vpc_id = aws_vpc.VPC1.id
tags = {Name = "star-SG"}}
resource "aws_vpc_security_group_ingress_rule" "Allow_443_Inbound_ipv4" {security_group_id = aws_security_group.star-SG.idcidr_ipv4 = aws_vpc.VPC1.cidr_blockfrom_port = 443ip_protocol = "tcp"to_port = 443}
resource "aws_vpc_security_group_egress_rule" "allow_all_Outbound_ipv4" {security_group_id = aws_security_group.star-SG.idcidr_ipv4 = "0.0.0.0/0"ip_protocol = "-1" # semantically equivalent to all ports}
resource "aws_internet_gateway" "star-GW" {vpc_id = aws_vpc.VPC1.id
tags = {Name = "Star-Gateway"}}
resource "aws_route_table" "star-RT" {vpc_id = aws_vpc.VPC1.id
route {cidr_block = "0.0.0.0/0"gateway_id = aws_internet_gateway.star-GW.id}
tags = {Name = "estar-RoutTable"}}
resource "aws_instance" "star-web" {ami = "ami-0e8d228ad90af673b"instance_type = "t2.micro"subnet_id = aws_subnet.Public-Subnet.idvpc_security_group_ids = [aws_security_group.star-SG.id]tags = {Name = "Web Server1"}}
resource "aws_instance" "star-db" {ami = "ami-0e8d228ad90af673b"instance_type = "t2.micro"subnet_id = aws_subnet.Private-Subnet.idvpc_security_group_ids = [aws_security_group.star-SG.id]tags = {Name = "db Server1"}}
resource "aws_eip" "star-nat-eip" {}
resource "aws_nat_gateway" "star-NAT" {allocation_id = aws_eip.star-nat-eip.idsubnet_id = aws_subnet.Public-Subnet.id
tags = {Name = "NAT-Gateway"}}
resource "aws_route_table" "NAT-rt" {vpc_id = aws_vpc.VPC1.id
route {cidr_block = "0.0.0.0/0"gateway_id = aws_nat_gateway.star-NAT.id}
tags = {Name = "NAT-RT"}}resource "aws_route_table_association" "NAT-RT-Assoc" {subnet_id = aws_subnet.Private-Subnet.idroute_table_id = aws_route_table.NAT-rt.id}
-
Code
- Code
- Code
Code
- Code
- Code
Code
- Code
- Code
Code
- Code
- Code
Code
- Code
- Code
Code
- Code
- Code
Code
- Code
- Code
Code
- Code
- Code
Compute: EC2 Instance, Key_pair, EIP (Elastic IP), AMI,
EC2 Instance creation with default values:
- AWS:
-
resource "aws_instance" "star-web1" {ami = "ami-005e54dee72cc1d00" # us-west-2instance_type = "t2.micro"region = "us-west-2"subnet = "VPC1"tags = {Name = "star web server"}}
- Terraform initialization
- #terraform init
- Terraform Plan
- #terraform plan -out star_instance.tfplan
- Terraform apply
- #terrafrom apply "star_instance.tfplan"
- Delete resource
- #terraform destroy
- create 10 instances write in code count= 10 below instance_type.
- resource "aws_instance" "star-web1" {
ami = data.aws_ami.ubuntu.id
instance_type = "t3.micro"
count = 10
tags = {
Name = "star web server"
}
}
- resource "aws_instance" "star-web1" {
-
- Search aws_instance in registry.terraform.io site and copy instance part from the code. https://registry.terraform.io/providers/hashicorp/aws/latest/docs/resources/instance
- Azure:
- Search
- terraform {required_providers {azurerm = {source = "hashicorp/azurerm"version = "4.8.0"}}}
provider "azurerm" {subscription_id = "bd2ade99-0834-4cfe-bb19-ddf0e89ed9f4"tenant_id = "4b9f3326-b87a-468f-89d4-4c34403eae39"client_id = "0df6190d-31bc-4d6a-ba38-3115d352e7ca"client_secret = "xkH8Q~OQ-Rg7XXu7Zz-I6IkVHijsxsZeOwGs5cKz"features {}}resource "aws_instance" "star-web1" {ami = data.aws_ami.ubuntu.idinstance_type = "t3.micro"tags = {Name = "star web server"}} - Terraform initialization
- #terraform init
- Terraform Plan
- #terraform plan
- Terraform apply
- #terrafrom apply
- Delete resource
- #terraform destroy
- create 10 instances write in code count= 10 below instance_type.
- resource "aws_instance" "star-web1" {
ami = data.aws_ami.ubuntu.id
instance_type = "t3.micro"
count = 10
tags = {
Name = "star web server"
}
}
- resource "aws_instance" "star-web1" {
- AWS:
Create key_pair and Assign to Instance:
- Login to console.aws.amazon.com and select region and go to EC2/Network & Security click on keypair, enter name (keypair1), select keypair type = RSA, select .pem (use with openssh) or .ppk (use with putty) and download.
- Define key pair in Instance:
- key_name = "star-key"
- use existing keypair:
-
provider "aws" {
region = "eu-west-2"
access_key = "xxxxxxxx"
secret_key = "xxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxx"
}resource "aws_instance" "Webserver" {
ami = "ami-0dbec48abfe298cab"
instance_type = "t2.micro"
key_name = "keypair1"tags = {
Name = "WebServer"
}
} - Public Key stored in a file locally:
-
provider "aws" {
region = "eu-west-2"
access_key = "xxxxxx"
secret_key = "xxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxx"
}
resource "aws_key_pair" "keypair1" {
key_name = "keypair1"
public_key = file("/root/test/tf1.pub")resource "aws_instance" "server"{
ami = "ami-0dbec48abfe298cab"
instance_type = "t2.micro"
key_name = "aws_key_pair.keypair1"tags = {
Name = "WebServer"
}
}
Choosing and filtering ami
-
provider "aws" {region = "UK South"access_key = "AKIAX2XVEK27GJNREDX4"secret_key = "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"}
data "aws_ami" "ubuntu" {most_recent = true
filter {name = "name"values = ["ubuntu/images/hvm-ssd/ubuntu-focal-20.04-amd64-server-*"]}
filter {name = "virtualization-type"values = ["hvm"]}
owners = ["099720109477"] # Canonical}
resource "aws_instance" "web" {ami = data.aws_ami.ubuntu.idinstance_type = "t3.micro"
tags = {Name = "HelloWorld"}} - data "aws_ami" "ubuntu": It will look AMI (Amazon Machine Image) for ubuntu.
- most_recent=true: look latest version.
- When it gets data then filter applies the filter to choose desired image. two filters have been mentioned.
- first filter: it will search for ubuntu/images/hvm-ssd/ubuntu-focal-20.04-amd64-server-*"
- second filter: virtualization-type=hvm : it will further filter with virtualization-type hvm.
- it will further look into owner of image, every owner of image has got an Id number. You can search particular AMI with owner ID during instance launch.
- resource: instance is creating with the name web.
- ami=data.aws_ami.ubuntu.id (it passes parameter to select AMI with above mentioned data reference )
- Code
- Code
-
Define Subnet in Instance:
- Enter the following line in instance block.
- subnet_id = aws_subnet.subnet_reference.id (taken from subnet resource where it was defined as resource "aws_subnet" "public_subnet", take both keyword insert . and add id )
Define Security Group in Instance:
- Enter the following line in instance block.
- vpc_security_group_ids = [aws_security_group.star-SG.id] (taken from security group resource where it was defined as "aws_security_group" "star-SG", take both keyword insert . and add .id in string=square bracket).
Creating Elastic IP (Public IP) in Instance:
- Single Elastic IP Associated with Instance:
-
resource "aws_eip" "eip" { instance = aws_instance.star-web.id }
-
- Multiple Elastic IP Associated with single Network Interface:
-
resource "aws_network_interface" "multi-ip" { subnet_id = aws_subnet.main.id private_ips = ["10.0.0.10", "10.0.0.11"] } resource "aws_eip" "one" { domain = "vpc" network_interface = aws_network_interface.multi-ip.id associate_with_private_ip = "10.0.0.10" } resource "aws_eip" "two" { domain = "vpc" network_interface = aws_network_interface.multi-ip.id associate_with_private_ip = "10.0.0.11" }
-
- code
- code
- Single Elastic IP Associated with Instance:
Associate EIP to an Instance or Network Interface:
-
resource "aws_eip_association" "eip_assoc" {instance_id = aws_instance.star-web.idallocation_id = aws_eip.eip.id} - ss
-
Creating Internet Gateway:
Creating Route Table for IG:
Creatng NAT Gateway, RT, association:
- Instance without public IP will not have internet but a private IP is assigned. we define NAT (network address translation from private IP to Public IP and ge internet).
- check in VPC/natgateway.
-
resource "aws_nat_gateway" "example" { allocation_id = aws_eip.example.id subnet_id = aws_subnet.example.id tags = { Name = "NAT-Gateway" } - NAT gateway required a public IP which will translate private IP into Public IP. create an enter in allocation_id = aws_eip.natIP.id
- Create public IP (EIP) and Associate with NAT.
-
resource "aws_eip" "star-nat-eip" {}
- Need to create Route Table and associate with subnet (public subnet) to which traffic goes to internet. NAT & IGW does not associate directly with subnet so we create route table and associate one side with subnet and other side with NAT.
- Create route table and route:
-
resource "aws_route_table" "example" { vpc_id = aws_vpc.example.id route { cidr_block = "10.0.1.0/24" gateway_id = aws_internet_gateway.example.id } tags = { Name = "example" } }
-
- Associate Route Table:
-
resource "aws_route_table_association" "a" { subnet_id = aws_subnet.foo.id route_table_id = aws_route_table.bar.id }
-
-
LAB: Creating VPC, Subnets, IG, RT, SG, NAT, EC2 (AWS Linix) webserver & DB server.
-
terraform {required_providers {aws = {source = "hashicorp/aws"version = "5.74.0"}}}provider "aws" {region = "eu-west-2"access_key = "AKIAYHJANJLZX2BBGS5K"secret_key = "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"}resource "aws_vpc" "VPC1" {cidr_block = "10.0.0.0/16"tags = {Name = "star-VPC1"}}
resource "aws_subnet" "Public-Subnet" {vpc_id = aws_vpc.VPC1.idcidr_block = "10.0.1.0/24"
tags = {Name = "Public-Subnet"}}
resource "aws_subnet" "Private-Subnet" {vpc_id = aws_vpc.VPC1.idcidr_block = "10.0.2.0/24"
tags = {Name = "Private-Subnet"}}
resource "aws_security_group" "star-SG" {name = "star-SG"description = "Security Group to allow/deny traffic"vpc_id = aws_vpc.VPC1.id
tags = {Name = "star-SG"}}
resource "aws_vpc_security_group_ingress_rule" "Allow_22_Inbound_ipv4" {security_group_id = aws_security_group.star-SG.idcidr_ipv4 = aws_vpc.VPC1.cidr_blockfrom_port = 22ip_protocol = "tcp"to_port = 22}
resource "aws_vpc_security_group_egress_rule" "allow_all_Outbound_ipv4" {security_group_id = aws_security_group.star-SG.idcidr_ipv4 = "0.0.0.0/0"ip_protocol = "-1" # semantically equivalent to all ports}
resource "aws_internet_gateway" "star-GW" {vpc_id = aws_vpc.VPC1.id
tags = {Name = "Star-Gateway"}}
resource "aws_route_table" "star-RT" {vpc_id = aws_vpc.VPC1.id
route {cidr_block = "0.0.0.0/0"gateway_id = aws_internet_gateway.star-GW.id}
tags = {Name = "estar-RoutTable"}}resource "aws_route_table_association" "IGW-RT-Assoc" {subnet_id = aws_subnet.Public-Subnet.idroute_table_id = aws_route_table.star-RT.id}
resource "aws_instance" "star-web" {ami = "ami-0e8d228ad90af673b"instance_type = "t2.micro"key_name = "keypair2"subnet_id = aws_subnet.Public-Subnet.idvpc_security_group_ids = [aws_security_group.star-SG.id]tags = {Name = "Web Server1"}}
resource "aws_eip" "web-IP" {instance = aws_instance.star-web.id}resource "aws_instance" "star-db" {ami = "ami-0e8d228ad90af673b"instance_type = "t2.micro"key_name = "keypair2"subnet_id = aws_subnet.Private-Subnet.idvpc_security_group_ids = [aws_security_group.star-SG.id]tags = {Name = "db Server1"}}
resource "aws_eip" "star-nat-eip" {}
resource "aws_nat_gateway" "star-NAT" {allocation_id = aws_eip.star-nat-eip.idsubnet_id = aws_subnet.Public-Subnet.id
tags = {Name = "NAT-Gateway"}}
resource "aws_route_table" "NAT-rt" {vpc_id = aws_vpc.VPC1.id
route {cidr_block = "0.0.0.0/0"gateway_id = aws_nat_gateway.star-NAT.id}
tags = {Name = "NAT-RT"}}resource "aws_route_table_association" "NAT-RT-Assoc" {subnet_id = aws_subnet.Private-Subnet.idroute_table_id = aws_route_table.NAT-rt.id}
-
Creating AMI of an Instance, copy to other region, Launch Permission:
- There are two ways to creating AMI of an Instance, create a snapshot of instance root volume and then create AMI with snapshot or directly create AMI with instance.
- Creating AMI with root volume of an instance:
- Create snapshot of a root volume:
- Go to instance / storage and copy root device name (/dev/sda1, volume ID =vol-0d6c4d0fdbab492ff), click on volume ID, click on Action and click create snapshot.
- Go to terraform.io click documentation and search aws_ami and copy code
-
resource "aws_ami" "example" { name = "terraform-example" virtualization_type = "hvm" root_device_name = "/dev/xvda" imds_support = "v2.0" # Enforce usage of IMDSv2. You can safely remove this line if your application explicitly doesn't support it. ebs_block_device { device_name = "/dev/xvda" snapshot_id = "snap-xxxxxxxx" volume_size = 8 } } - LAB:
-
terraform {required_providers {aws = {source = "hashicorp/aws"version = "5.74.0"}}}
provider "aws" {region = "eu-west-2"access_key = "AKIAYHJANJLZX2BBGS5K"secret_key = "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"}
resource "aws_ami" "web-ami" {name = "star-web-ami"virtualization_type = "hvm"root_device_name = "/dev/sda1"ebs_block_device {device_name = "/dev/sda1"snapshot_id = "snap-0d2caab732ea89f6f"volume_size = 8}}
-
- root_device_name: it can be get from instance/storage,
- device_name= similar as root _device_name
- snapshot_id: go to storage and get snapshot ID
- Volume_size = 8 it will be size of volume.
- #terraform init
- #terraform plan -out ami.tfplan
- #terraform apply "ami.tfplan"
- Confirm: Go to instance/images/ami
- Create a AMI with instance:
- search aws_ami_from_instance.
-
resource "aws_ami_from_instance" "example" { name = "terraform-example" source_instance_id = "i-xxxxxxxx" } - Enter reference name, name and instance id
- LAB:
-
terraform {required_providers {aws = {source = "hashicorp/aws"version = "5.74.0"}}}
provider "aws" {region = "eu-west-2"access_key = "AKIAYHJANJLZX2BBGS5K"secret_key = "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"}
resource "aws_ami_from_instance" "web-ami-instance" {name = "web-ami-instance"source_instance_id = "i-0525a0afbd8405b27"}
-
- #terraform init
- #terraform plan -out ami.tfplan
- #terraform apply "ami.tfplan"
- Creating AMI with root volume of an instance:
- Copy AMI to different region:
- Go to terraform.io/documentation and search aws_ami_copy
-
resource "aws_ami_copy" "example" { name = "terraform-example" source_ami_id = "ami-xxxxxxxx" source_ami_region = "us-west-1" tags = { Name = "HelloWorld" } } - name = enter the name for destination region ami.
- source_ami_id = copy existing ami id
- source_ami_region = enter region of existing ami
- Destination region should be enter in provider where access key and secret key is defined.
- LAB:
-
terraform {required_providers {aws = {source = "hashicorp/aws"version = "5.74.0"}}}
provider "aws" {region = "us-west-1"access_key = "AKIAYHJANJLZX2BBGS5K"secret_key = "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"}
resource "aws_ami_copy" "aws_ami_copy" {name = "aws_ami_copy"source_ami_id = "ami-0ffd94daf9342fc20"source_ami_region = "eu-west-2"
tags = {Name = "web ami copy"}}
-
- #terraform init
- #terraform plan -out ami.tfplan
- #terraform apply "ami.tfplan"
- To check select region (us-west-1/instance/images/ami
- AMI Launch Permission:
- Grant permission to create instance using AMI.
- search for aws_ami_launch_permission
- AWS Account ID permission:
-
resource "aws_ami_launch_permission" "example" { image_id = "ami-12345678" account_id = "123456789012" } - Public Access:
-
resource "aws_ami_launch_permission" "example" { image_id = "ami-12345678" group = "all" } - Organization Access:
-
data "aws_organizations_organization" "current" {} resource "aws_ami_launch_permission" "example" { image_id = "ami-12345678" organization_arn = data.aws_organizations_organization.current.arn }
- There are two ways to creating AMI of an Instance, create a snapshot of instance root volume and then create AMI with snapshot or directly create AMI with instance.
- Code
- Code
- Code
- Code
Storage:
code
- Code
- Code
- Code
code
- Code
- Code
- Code
code
- Code
- Code
- Code
code
- Code
- Code
- Code
code
- Code
- Code
- Code
code
- Code
- Code
- Code
code
- Code
- Code
- Code
code
- Code
- Code
- Code
code
- Code
- Code
- Code
code
- Code
- Code
- Code
Security Identity & Compliance (IAM)
- code
- code
- code
Database
- code
- code
- code
Route 53:
- code
- code
- code
Containers:
- code
- code
- code
S3 Bucket:
- Create an S3 bucket
- visit https://registry.terraform.io/providers/hashicorp/aws/latest/docs/resources/s3_bucket
-
resource "aws_s3_bucket" "example" {bucket = "my-tf-test-bucket"
tags = {Name = "My bucket"Environment = "Dev"}} - $vim s3.tf
-
terraform {required_providers {aws = {source = "hashicorp/aws"version = "~> 6.0"}}}
provider "aws" {# Configuration optionsregion = "eu-west-2"#Enter user access key & secret key
#access_key = "AKIAYHJANJLZX2BBGS5K"#secret_key = "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"}
# Create a S3 bucketresource "aws_s3_bucket" "star-s3" {bucket = "star-s3-bucket"
tags = {Name = "star-s3-bucket"Environment = "Dev"}} - (Optional, Forces new resource) Name of the bucket. If omitted, Terraform will assign a random, unique name. Must be lowercase and less than or equal to 63 characters in length. A full list of bucket naming rules may be found here. The name must not be in the format
[bucket_name]--[azid]--x-s3. Use theaws_s3_directory_bucketresource to manage S3 Express buckets. - version has been defined
- AWS Provider defined, here you can hardcode user access key and secret key as well.
- $terraform init
- $terraform validate
- $terraform plan -out s3.tfplan
- $terraform apply "s3.tfplan" -auto-approve
- $terraform destroy -auto-approve
-
- Create S3 bucket with Versioning and encryption enable to store terraform state file remotely.
- Terraform update the infrastructure with the help of .tfstate file, when you execute terraform file it creates .tfstate and .tfstate.backup file which contains information of resources.
- .tfstate file is very important which is use to create infra, modify the infra and destroy the infra. It compares desired state with actual state, desired state which you want to create and actual state is some/none resources is available.
- When you run the terraform file it will not check directly resources on provider but it uses .tfstate file to check and compare.
- Remote Backend:
- .tfstate file should be kept remotely and as a best practice we will keep it in S3 bucket and access will be restricted.
- Perform state locking which means multiple users should not execute same infra at the same time . Do not update or delete manually.
- DynamoDB:
- It has been use to store tfstate file remotely which is deprecated now and using S3 bucket.
- Create S3 bucket and store tfstate file remotely.
- visit https://developer.hashicorp.com/terraform/language/backend/s3
-
It should be define in terraform block -
backend "s3" { bucket = "star-s3-bucket" key = "dev/terraform.tfstate" region = "eu-west-2" }
-
- $vim s3_tfstate.tf
- copy and paste the following code.
- Note: S3 bucket is already created in above step, so it will be used (star-s3-bucket)
-
terraform {backend "s3" {bucket = "star-s3-bucket"key = "dev/terraform.tfstate"region = "eu-west-2"encrypt = trueuse_lockfile = true}}resource "aws_s3_bucket" "star-s3-bucket1" {bucket = "star-s3-bucket1"
tags = {Name = "star-s3-Bucket1"Environment = "Dev"}}
-
- encrypt = true (file will be stored in encrypt format)
- use_lockfile = true (it will lock the file so multiple user cannot execute)
- $terraform init
- $terraform validate
- $terraform plan
- $terraform apply -auto-approve
- terraform.tfstate file will be stored in star-s3-bucket/dev folder & star-s3-bucket1 will be created.
- $terraform destroy -auto-approve
- visit https://developer.hashicorp.com/terraform/language/backend/s3
- Create S3 Bucket using variable.
- Create an S3 bucket
Code:
- code
- code
- code
Code:
- code
- code
- code
Code:
- code
- code
- code
Code:
- code
- code
- code
Code:
- code
- code
- code
Code
- Code
- code
- code
Projects:
- EKS(Elastic Kubernetes Service) setup with Terraform.
- Code
- Code
Code:
- code
- code
- code
Code:
- code
- code
- code
Code:
- code
- code
- code
Code:
- code
- code
- code
Code:
- code
- code
- code
Code:
- code
- code
- code
Code:
- code
- code
- code
Terraform Commands:
- You should run the execution commands from the folder in which terraform .tf template files exist.
- $terraform validate
- Validate the reorganized structure
- $terraform fmt -recursive
- Format all files consistently
- $terraform init: it will download providers plugin in.
- .terraform folder will be created which container providers details.
- $terraform validate:
- It will check the configuration.
- $terraform plan -out filename.tfplan :
- It will output the action will be performed.
- $terraform apply "filename.tfplan"
- It will create resources in the given provider's location. Before apply you will have xyz.tf and .terraform in the folder.
- terraform.tfstate: it stores the details what it has created. If you run #terraform apply again then it will check terraform.tfstate file and plan and perform task if there is any change.
- terraform.tfstate.backup: It contain last known good configuration.
- code
- code
Mock Interview:
- Github Link
- https://github.com/AbdulAziz-uk/terraform-AWS-piyush.git click for youtube/videos
- Stacksimplify-hashicorp-certified-terraform-associate
Code:
- code
- code
- code
Code:
- code
- code
- code
Code:
- code
- code
- code
Code:
- code
- code
- code
Code:
- code
- code
- code
Code:
- code
- code
- code
Code:
- code
- code
- code
Code:
- code
- code
- code
Realtime Interview:
Code:
- code
- code
- code
Code:
- code
- code
- code
Code:
- code
- code
- code
Code:
- code
- code
- code
Code:
- code
- code
- code
Code:
- code
- code
- code
Code:
- code
- code
- code
Code:
- code
- code
- code
- code
Videos
Sanjay Terraform with AWS
- Introduction
- API_Installation_createInstance
- Create_VPC_Subnet_NIC_Instance
- Create_SG_Keypair_EIP_Instance
- AMI
- EBS_Volume
- Project1
- Variable_Part1
- Variable_Part2
- Count_Parameter
- Conditions
- Local_value
- Output_Value
- TFState_Management1
- TFState_Management2
- TFState_Management3
- Provisioners1
- Provisioners2 - LAB
- Provisioners3
- code
techlearning by Sanjay Karakoti Terraform with Azure
- techlearning.spayee.com
- username: aziz27uk@gmail.com, p: Yez.....!
code
- code
- code
- code
code
- code
- code
- code
code
- code
- code
- code
code
- code
- code
- code
last
- code
- code
- code
Multiple .tf files to create infrastrcture.
- To create instance can create multiple .tf files as follows
Project1: creation of VPC, Subnets, IGW, SG, RT, Instance, Key pair, EIP.
- input.tf (access key and secret key as variable value is stored)
- provider.tf (provider variable is defined)
- network.tf (all network resource is defined)
- instance (instance resource is defined)
| variable "accesskey" { type = string default = "AKIAX2XVEK27GJNREDX4" } variable "secretkey" { type = string default = "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" } variable "region" { type = string default = "eu-west-2" } |
provider "aws" { access_key = var.accesskey secret_key = var.secretkey region = var.region } |
resource "aws_vpc" "star_vpc" { tags = { tags = { tags = { ingress { tags = { tags = { resource "aws_route_table" "star_rt" { route { route { |
resource "aws_key_pair" "tf1" { tags = { tags = { resource "aws_eip" "star_eip" { tags = { |
Loop: Create 3 subnets in different availability zones using terraform loop, count, element and length:
- https://www.terraform.io/docs/configuration-0-11/interpolation.html
- video of below exercise: http://stardistributors.co.uk/deveops/tools/terraform/other%20videos/Session-2%20_%20%20AWS%20-%20Terraform%20variables%20_%20Data%20Sources%20_%20Terraform%20Loops.mp4
|
variable "vpccidr" {
type = string
default = "10.0.0.0/16"
}
variable "publicsubnet" {
type = string
default = "10.0.1.0/24"
}
variable "privatesubnet"{
type = list
default = ["10.0.2.0/24","10.0.3.0/2","10.0.4.0/24"]
}
|
resource "aws_vpc" "star_vpc" {
cidr_block = var.vpccidr
instance_tenancy = "default"
tags = {
Name = "star_vpc"
}
}
resource "aws_subnet" "publicsubnet" {
vpc_id = aws_vpc.star_vpc.id
tags = {
Name = "public_subnet"
}
}
resource "aws_subnet" "privatesubnet" {
vpc_id = aws_vpc.star_vpc.id
cidr_block = element(var.privatesubnet,count.index)
count = 3 #to define tag name to every subnet
tags = {
Name = "private_subnet-count.index+1"
}
}
|
- loop is used to define mutiple values, where variable list is used to define values. create a varialble and call its value, you can use count function =3 but to make it dynamic use length funciton. you have hardcode the 3 subnets list variable and call it in code.
- element is built-in-function used to take a one value at a time with list and index
- suppose one subnet is increased and add cidr value in variable then change count =4.
- You can use dynamic function so you do not need to change count when it increase or decrease, to make it dynamic use length function.
Defining Availability Zones for multiple subnets: 3 subnets and 3 availability zone:
- defining subnets CIDR dynamically
- defining availability zone to subnets
-
variable "vpccidr" {type = stringdefault = "10.0.0.0/16"}
variable "publicsubnet" {type = stringdefault = "10.0.1.0/24"}variable "privatesubnet"{type = listdefault = ["10.0.2.0/24","10.0.3.0/2","10.0.4.0/24"]}variable "az" {type = listdefault = ["eu-west2a", "eu-west-2b","eu-west-2c"]resource "aws_vpc" "star_vpc" {cidr_block = var.vpccidrinstance_tenancy = "default"
tags = {Name = "star_vpc"}}
resource "aws_subnet" "publicsubnet" {vpc_id = aws_vpc.star_vpc.id
tags = {Name = "public_subnet"}}
resource "aws_subnet" "privatesubnet" {count = length(var.az)vpc_id = aws_vpc.star_vpc.idcidr_block = element(var.privatesubnet,count.index)
#to define tag name to every subnettags = {Name = "private_subnet-${count.index+1}"}} - when creating multiple subnets need to define multiple cidr block for subnet and call function to it can use one element at a time . define element in function (list, index) which picks one value at a time.
- It creates 3 subnets, In the first iteration count is 0 which picks az = eu-west-2a and second iteration count is 1 and will eu-west-2b and go on
- subnet tag name should be different, used count.index.+1, it start with 0.
- Availability zone is still hardcoded, use data source to get availability zone from aws.
Data Sources: Based on region the availability zone should be picked using source data.
|
variable "vpccidr" {
type = string
default = "10.0.0.0/16"
}
variable "publicsubnet" {
type = string
default = "10.0.1.0/24"
}
variable "privatesubnet"{
type = string
default = ["10.0.2.0/24","10.0.3.0/2","10.0.4.0/24"]
}
#variable "az" {
# type = list
# default = ["eu-west-2a","eu-west-2b","eu-west-2c"]
#}
#Declare the data source
data "aws_availability_zones" "az" {
}
|
resource "aws_vpc" "star_vpc" {
cidr_block = var.vpccidr
instance_tenancy = "default"
tags = {
Name = "star_vpc"
}
}
resource "aws_subnet" "publicsubnet" {
vpc_id = aws_vpc.star_vpc.id
tags = {
Name = "public_subnet"
}
}
resource "aws_subnet" "privatesubnet" {
vpc_id = aws_vpc.star_vpc.id
cidr_block = element(var.privatesubnet,count.index)
availability_zone = element(data.aws_availability_zones.az.names,count.index)
count = length(data.aws_availability_zones.az.names)
tags = {
Name = "private_subnet-count.index+1"
}
}
|
- availability_zone = element(data.aws_availability_zones.az.names,count.index)= This will make all subnets be creaed in three different AZ.
- you can define code in a separate file
- if you change region in the code then it will automatically choose availability zones.
- change region and execute again.
Defining Load Balancer: click for AWS_LoadBalancer,
Elastic Load Balancer in AWS supports the following load balancers:
- Classic LB (ELB):
- Application LB:
- Network LB:
- Gateway LB:
Application LB: Link for tutorial,
Lab Setup: variable, provider, VPC, IGW, Securitygroup, instances, install_httpd.sh, alb
ALB key words:
- Target groups:
- Target types:
- Instances (2webserver with webpage to check)
- IP
- Lambda Functions
- Subnets and Availability Zones of Instances.
- Instances port for LB and Application Instances
- Health Check for healthy instances
- Target types:
- Load Balancer
- Listener Port for user requests
- Security Group
- IP Version
- Stickiness
- Connection Draining
- Add SSL Certificate
- ELB Logs
ELB: Elastic Load Balancer: link for turorial,
Lab setup: created the following files: https://registry.terraform.io/providers/hashicorp/aws/latest/docs/resources/lb
Files: provider, variable, instances, vpc, igw, securitygroup, httpd_insall.sh, classicELB
Things to define in ELB (classic Load Balancer, VPC ELB)
- Subnets (required for VPC ELB)
- Availability Zones (requied for EC2 classic ELB)
- security group
- Listener
- Health Checks
- Instances
Output Value: When infra is created and you want to see values assigned by provider, example: resource IDs, Public IP, Private IP etc..
https://www.terraform.io/docs/language/values/outputs.html
Syntax of output: During resource creation the required output value will be displayed.
|
#Syntax: #Add the below code in the source file. #If you have multiple servers or resources. output "publicIP" |
Once the resource is created and want to display the output value:
Get console: run command at the terraform folder prompt # terraform console
> aws_instance.webserver.*.public_ip
You can display any attribute (attribute is output value generated by resouce provider)
> aws_instance.webserver.id
Variable defined in a file: To set lots of variables, it is more convenient to specify their values in a variable definitions file (with a filename ending in either .tfvars or .tfvars.json) and then specify that file on the command line with -var-file:
variable.tfvars
- #terraform apply -var-file="variable.tfvars"
- It is used to update *.tfstate with resources created.
- it is used for recreating resources. it will delete the resource and recreate it.
- #terraform taint resource_type.resource_name
- example: suppose a subnet3 in vpc want to be deleted and recreate it.
- #terraform taint aws_subnet.star_privatesubnet3 (privatesubnet3 is marked as taint)
- #terraform apply (when you run terraform apply again all taint marked resource will delete and recreate it. It will prompt to confirm for taint action, you can avoid this manual confirmation to automatic by using option #terraform apply -auto-approve
- It generate a graph from terraform.tf (template file)
- Need to install dot tool (search in google: dot by graphviz), download and install
- #terraform graph | dot -Tsvg > graph.svg
- you will see graph.svg file in terraform working folder, open with chrome.
- Display the result.
- #terraform apply
- Create AMI of an instance. can achieved with two methods
- create snapshot of root volume of an instance and create an AMI.
- create directly with instance.
- copy AMI to other regions
- Give access to AMI to other account ID.
Method1`: Create AMI with snapshot of an instance. (To create an snapshot> got to volume and create snapshot)
Volume => snapshot => AMI
Instance => AMI
|
provider "aws" { ebs_block_device { |
- #terraform init
- #terraform plan
- #terraform apply
- Check AMI is created in EC2/Images/AMI (terraform_AMI)
- You can create an instance using the above AMI (terraform_AMI)
Copy AMI to different Region: https://registry.terraform.io/providers/hashicorp/aws/latest/docs/resources/ami_copy
|
provider "aws" { tags = { |
- destination region is defined in provider.
- destination nae is defined in resource.
- source AMI id, description and region is defined in resource.
- #terraform plan
- #terraform apply
- to verify: Go to us-east-1 region (N.Virginia) EC2/Images/AMI
Method2: Create AMI from Instance: https://registry.terraform.io/providers/hashicorp/aws/latest/docs/resources/ami_from_instance
| provider "aws" { access_key = "AKIAX2XVEK27GJNREDX4" secret_key = "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" region = "eu-west-2" } resource "aws_ami_from_instance" "terraform_ami2" { name = "terraform_ami2" source_instance_id = "i-0b31e653a4e810c4a" } |
- Image will be created directly from instance.
- image name = terraform_ami2
AMI Launch Permission: Give AMI access to other account ID: https://registry.terraform.io/providers/hashicorp/aws/latest/docs/resources/ami_launch_permission
| provider "aws" { access_key = "AKIAX2XVEK27GJNREDX4" secret_key = "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" region = "eu-west-2" } resource "aws_ami_launch_permission" "terraform_eu-west-2" { image_id = "ami-0371f85fc88e9007c" account_id = "723581589149" } |
- To verify: Go to account_Id AWS console page, go to images/AMI/ choose private images.
- Create EBS Volume (disk)
- Increase size of EBS volume
- Snapshot of EBS volume
- copy snapshot taken from EBS volume to other region.
1. Create EBS Volume: https://registry.terraform.io/providers/hashicorp/aws/latest/docs/resources/ebs_volume
|
provider "aws" { tags = { |
- #terraform apply
- To verify go to volumes.
2. Increase size of volume to 20 GB.
|
provider "aws" { tags = { |
- #terraform apply (it will modify the volume created earlier)
- First it will refresh state and perform modification as there is change in state(terraform.tfstate) file and terraform.tf file.
3. Create snapshot from volume: https://registry.terraform.io/providers/hashicorp/aws/latest/docs/resources/ebs_snapshot
|
provider "aws" { resource "aws_ebs_volume" "terraform-server_volume" { tags = { tags = { |
- It creates a volume of 20 GB and snapshot of that volume.
4. Copy snapshot to different region: https://registry.terraform.io/providers/hashicorp/aws/latest/docs/resources/ebs_snapshot_copy
|
provider "aws" {
tags = { |
- change region to destination region
- define source snapshot id, source region.
- to verify check in us-east-1/snapshot
- Condition defined in the code where if condition met then perform certain action. Ex code contains instances creation for dev, test and prod and define condition if input is dev then create dev instance.
- To achieve this need to define variable.
|
provider "aws" { variable "instance_type" { variable input {} resource "aws_instance" "dev" { |
- variable input is defined where input value will be used to perform task.
- condition parameter == (equal) is used with count to define condition where if input value = "dev" then ? = what to do where 1 = create 1 dev instance.
- if input value is not dev then ? = what to do then where 0 = perform no action.
- #terraform apply
- will prompt to enter value = dev (it will create dev instance)
- count = var.input > "2" ? 1 : 0 (condition parameter greater is used) if the value is > 2 then create 1 instance and if value is less then do not create.
- operators ( greater > , less than <, equal ==, not equal !=, greater and equal >=,
- repeat resource code for "test" and "prod".
|
provider "aws" { variable "instance_type" { variable input {} resource "aws_instance" "dev" { tags = { resource "aws_instance" "test" { tags = { tags = { |
Local Value: used for tag names for all resources.
- If you need to make replicas of resources in different department or different branches of company then you create a complete infra coding. you can use variable and store name which will reflect in every resource and by changing variable name you can use the code in any department or branches.
- You can enter tag names for each resource and change all tag names for different department resource.
- Locals parameter can be used and call in tags.
|
locals
provider "aws" { locals { tags = local.common_tag } tags = local.common_tag resource "aws_ebs_volume" "ebs_volume" { tags = local.common_tag |
with tags provider "aws" { resource "aws_vpc" "star_vpc" { tags = { tags = { tags = { |
For multiple departments or branches: if you need to change the name then change it in variable which will reflect in all resources.
|
provider "aws" { locals { resource "aws_vpc" "star_vpc" { tags = local.common_tag } tags = local.common_tag resource "aws_ebs_volume" "ebs_volume" { tags = local.common_tag
tags = local.hr_tag } tags = local.hr_tag resource "aws_ebs_volume" "ebs_volume1" { tags = local.hr_tag |
Terraform State Management: shared storage of sate file locally, shared storage of state file remotely, staging and production environment.
Shared storage of terraform.tfstate file Locally:
- when multiple users working on the same project and they perform their task after copying file.tf and terraform.tfstate file in their local folders.

Shared storage of state file remotely:
- In the shared storage of state file locally where files where copied and stored in each users local folder. it creates a big problem for every users to get latest state file from the last user execution.
- state file can be shared remotely where all users will get access and work on one terraform.tfstate file.
- Define in the code to store terraform.tfstate file remotely in the specified location, ex. S3, terraform cloud storage, azure storage etc..
- https://www.terraform.io/docs/language/settings/backends/s3.html
- create s3 bucket (starsharedstatefile): (enable versioning, server side encryption - enabled),
code:
|
provider "aws" { tags = { tags = { |
- When you execute the above file, terraform will store state file in s3 bucket in project folder at location key="starsharedstatefile/project"
- #terraform init
- #terraform plan
- #terraform apply
- resource will be created, check local folder there will be no terraform.tfstate file. which is stored in s3 bucket.
- Go to s3/starsharedstatefile/project/version, download the file and open in notepad, it will be json file (terraform.tfstate).
- make changes in the code and execute terraform apply and check versioning, new file should be created.
- The advantage of version enabling here is you will get all versions for every change has been done, while in terraform.tfstate.backup file you only get last changed configuration.
- when other users work on the same project then they will only get instance.tf file and make necessary changes and execute, latest state file will be modified in s3 bucket.
- Drawback: In AWS s3 bucket there is no locking features so that only one user can execute at a time, otherwise it will accept any command from all users. To achieve this install DynamoDB and apply locking feature.
- Go to DynamoDB/create table/lockfeature/primary key = LockID(case sensitive)/create.
- go to resource file and add locking feature
- dynamodb_table = "lockfeature"
- #terraform init
- amend resource file in all users.
- Now only one user will be allowed to execute command.
- try to execute command from both users, only one user will be allowed and another will be locked.
- locking feature is available in other cloud provider like azure, terraform cloud (
Staging and Production Environment:
- Executing changes directly on production is highly risky, it is recommended to have pre production staging environment before applying to production system.
- It can be achieved by manual or terraform provided workspace method, although manual is lenghtly process where you maintain two folders staging and produciton and first try execution on staging and after successful completion copy the terraform.tfsatate file to production system and execute.
Manual Method 1 and Method 2:
Method 3 = Terraform workspace:
- You create a folder Project in which you have one workspace.tf file, create two folders using terraform workspace command and workspace.tf will be copied in both folders automatically. it is linked with stage and prod environment in AWS automatically.
- you maintain only one folder and one source.tf file.
- #terraform init
- #terraform workspace list (it will show list of workspace in the folder, * default)
- #terraform workspace show (it will show your location in workspace folder)
- #terraform workspace --help (help for workspace)
- Create two workspace stage and proud
- #terraform workspace new stage
- #terraform workspace new prod
- #terraform workspace show (default, stage, prod *), * = current location
- #terraform workspace select stage (move to other workspace)
- #ls (you will see workspace.tf )
- #terraform workspace select prod
- #ls (you will see workspace.tf)
- When you make changes in workspace.tf file in stage or prod, it will reflect in both.
- In stage run #terraform init #terraform apply
- go to prod #terraform workspace select prod
- #terraform init
- #terraform apply
- Check in S3 bucket env:/ folder will have two folders stage and prod.
- When you make changes in stage or prod workspace.tf file it will reflect in both workspace.tf files, once it is successful in stage you can run command in prod.
- #terraform workspace -force delete stage (forcefully can be deleted as it says stage is not empty), it you delete forcefully then workspace will be deleted but resources will not be deleted, once workspace is deleted then you cannot make changes.
- It is recommended to delete resources (#terraform destroy) then delete workspace.
- Configuration of software or application in the resource can be done with terraform provisioner, this can also be achieved by shell scripting, python scripting, ANT, SALT or Ansible, Terraform does not support Ansible.
- provisioner code has to be define within instance resource.
- use following provisioner
- file : Create a file index.html
- local-exec
- remote-exec
Project2: provision of instance and Apache configuration in AWS through terraform using file:
- When you define file option source is the location of file in your system, destination location alway be /tmp (destination = it is the location in the instance created in the AWS)
|
provider "aws" { resource "aws_key_pair" "tf1" {
tags = { |
IAM: user creation
Example1: Creating IAM user only and user ARN output..
Files: variable, provider, users, output
|
variable "accesskey" { variable "secretkey" { variable "region" { variable "username" { |
provider "aws" { access_key = var.accesskey secret_key = var.secretkey region = var.region } |
#1. syntax to create a user tags = { #2. syntax to create multiple users using count index resource "aws_iam_user" "newuser" { tags = {
resource "aws_iam_user" "newuser" { tags = { }
|
output "user_arn" { |
Example2: Creating IAM policy only with ec2 describe permissio:
Files: policy1
|
resource "aws_iam_policy" "policy1" { policy = <<EOF |
Example3: Lets attach the above policy1(ec2-describe) policy to both users created in example1.
Files: variable, provider, users, output, policy1, policy_attach
| resource "aws_iam_policy_attachment" "policy1-attachment" { name = "policy1-attachment" users = aws_iam_user.newuser.*.name policy_arn = aws_iam_policy.policy1.arn } |
Login with the above created users, users can describe or display instances.
- To create a resource you store all required files in a afolder and execute. For simple management you can keep files of different resources in different folders and use modules for reference. Folders are considered as modules.
- You create a new folder and call files from existing folders using module to create resource so that you do not need to create script from scratch. Ex: provider, vpc etc
- Modules are provided or shared by terraform community and your own terraform templates can be used as module.